Meteorite that doomed dinosaurs remade forests
2014-09-16
The meteorite impact that spelled doom for the dinosaurs 66 million years ago decimated the evergreens among the flowering plants to a much greater extent than their deciduous peers, according to a study led by UA researchers. The results are published in the journal PLOS Biology.
Applying biomechanical formulas to a treasure trove of thousands of fossilized leaves of angiosperms — flowering plants excluding conifers — the team was able to reconstruct the ecology of a diverse plant community thriving during a 2.2 million-year period spanning the cataclysmic impact event, ...
A novel therapy for sepsis?
2014-09-16
This release is available in Japanese.
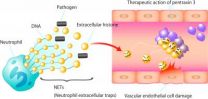
A University of Tokyo research group has discovered that pentatraxin 3 (PTX3), a protein that helps the innate immune system target invaders such as bacteria and viruses, can reduce mortality of mice suffering from sepsis. This discovery may lead to a therapy for sepsis, a major cause of death in developed countries that is fatal in one in four cases.
Professor Takao Hamakubo's group at the Department of Quantitative Biology and Medicine, Research Center for Advanced Science and Technology (RCAST), have shown that PTX3 forms ...
Meteorite that doomed the dinosaurs helped the forests bloom
2014-09-16
66 million years ago, a 10-km diameter chunk of rock hit the Yukatan peninsula near the site of the small town of Chicxulub with the force of 100 teratons of TNT. It left a crater more than 150 km across, and the resulting megatsunami, wildfires, global earthquakes and volcanism are widely accepted to have wiped out the dinosaurs and made way for the rise of the mammals. But what happened to the plants on which the dinosaurs fed?
A new study led by researchers from the University of Arizona reveals that the meteorite impact that spelled doom for the dinosaurs also decimated ...
The genetics of coping with HIV
2014-09-16
We respond to infections in two fundamental ways. One, which has been the subject of intensive research over the years, is "resistance," where the body attacks the invading pathogen and reduces its numbers. Another, which is much less well understood, is "tolerance," where the body tries to minimise the damage done by the pathogen. Now an elegant study using data from a large Swiss cohort of HIV-infected individuals gives us a tantalising glimpse into why some people cope with HIV better than others.
The authors find that tolerance varies substantially between individuals, ...
Point-of-care CD4 testing is economically feasible for HIV care in resource-limited areas
2014-09-16
A new point-of-care test to measure CD4 T-cells, the prime indicator of HIV disease progression, can expedite the process leading from HIV diagnosis to antiretroviral therapy (ART) and improve clinical outcomes. Now a study by Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) investigators, working in collaboration with colleagues in Mozambique and South Africa, indicates that routine use of point-of-care CD4 testing at the time of HIV diagnosis could be cost effective in countries where health care and other resources are severely limited. Their analysis is being published in the ...
Nanoribbon film keeps glass ice-free
2014-09-16
Rice University scientists who created a deicing film for radar domes have now refined the technology to work as a transparent coating for glass.
The new work by Rice chemist James Tour and his colleagues could keep glass surfaces from windshields to skyscrapers free of ice and fog while retaining their transparency to radio frequencies (RF).
The technology was introduced this month in the American Chemical Society journal Applied Materials and Interfaces.
The material is made of graphene nanoribbons, atom-thick strips of carbon created by splitting nanotubes, ...
Journal of Clinical Psychiatry: Long-term benefit of NeuroStar TMS Therapy in depression
2014-09-16
Malvern, Pennsylvania, September 16, 2014 – Neuronetics, Inc., today announced that results of a study designed to assess the long-term effectiveness of NeuroStar TMS Therapy in adult patients with Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) who have failed to benefit from prior treatment with antidepressant medications, were published online in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. The study found that TMS treatment with the NeuroStar TMS Therapy System induced statistically and clinically meaningful response and remission in patients with treatment resistant MDD during the acute phase ...
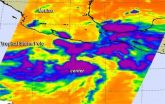
NASA spots center of Typhoon Kalmaegi over Hainan Island, headed for Vietnam
2014-09-16
NASA's Aqua satellite saw Typhoon Kalmaegi's center near northern Hainan Island, China when it passed overhead on September 16 at 06:00 UTC (2 a.m. EDT). Hours later, the storm crossed the Gulf of Tonkin, the body of water that separates Hainan Island from Vietnam, and was making landfall there at 11:30 a.m. EDT.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument aboard Aqua captured a picture of the typhoon that shows the center near the northern end of Hainan Island, China, while the storm stretches over the mainland of southeastern China, east into ...
Computerized emotion detector
2014-09-16
Face recognition software measures various parameters in a mug shot, such as the distance between the person's eyes, the height from lip to top of their nose and various other metrics and then compares it with photos of people in the database that have been tagged with a given name. Now, research published in the International Journal of Computational Vision and Robotics looks to take that one step further in recognizing the emotion portrayed by a face.
Dev Drume Agrawal, Shiv Ram Dubey and Anand Singh Jalal of the GLA University, in Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, India, suggest ...
Newborn Tropical Storm Polo gives a NASA satellite a 'cold reception'
2014-09-16
The AIRS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite uses infrared light to read cloud top temperatures in tropical cyclones. When Aqua passed over newborn Tropical Storm Polo off of Mexico's southwestern coast it got a "cold reception" when infrared data saw some very cold cloud top temperatures and strong storms within that hint at intensification.
Polo formed close enough to land to trigger a Tropical Storm Watch for the southwestern coast of Mexico. The watch was issued by the government of Mexico on September 16 and extends from Zihuatanejo to Cabo Corrientes, Mexico. ...
EARTH Magazine: The Bay Area's next 'big one could strike as a series of quakes
2014-09-16
Alexandria, Va. — Most people are familiar with the Great 1906 San Francisco Earthquake and are aware of the earthquake risk posed to the Bay Area — and much of California — by the San Andreas Fault. Most people are not aware, however, that a cluster of large earthquakes struck the San Andreas and quite a few nearby faults in the 17th and 18th centuries. That cluster, according to new research, released about the same amount of energy throughout the Bay Area as the 1906 quake. Thus, it appears that the accumulated stress on the region's faults could be released in a series ...
New research decodes virus-host interactions in ocean dead zones
2014-09-16
A complex web of interaction between viruses, bacteria, and their environment is becoming ever more untangled by a growing international collaboration between Matthew Sullivan, associate professor in the University of Arizona's Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology and Steven Hallam from the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, Canada.
"Bacteria are drivers of nutrient and energy cycles that power the earth," Sullivan said. "As the climate is changing, so are the environments these bacteria live in, and they in turn loop back to impact their environments. ...
New research shows tornadoes occurring earlier in 'Tornado Alley'
2014-09-16
BOZEMAN, Mont. -- Peak tornado activity in the central and southern Great Plains of the United States is occurring up to two weeks earlier than it did half a century ago, according to a new Montana State University study whose findings could help states in "Tornado Alley" better prepare for these violent storms.
Tornado records from Nebraska, Kansas, Oklahoma, and northern Texas – an area of high tornado activity dubbed "Tornado Alley" -- show that peak tornado activity is starting and ending earlier than it did 60 years ago.
Peak tornado activity, which occurs ...
Long-term results of RTOG 0236 confirm good primary tumor control, positive 5-year survival rates
2014-09-16
San Francisco, September 15, 2014—Patients with inoperable, early-stage lung cancer who receive stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) have a five-year survival rate of 40 percent, according to research presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology's (ASTRO's) 56th Annual Meeting. Such a positive survival rate is encouraging considering that historically conventional RT resulted in poor tumor control for patients with inoperable lung cancer. This study is an update of RTOG 0236, originally published in 2010 , and also conducted by the original researchers ...
Politics divide coastal residents' views of environment, UNH research finds
2014-09-16
DURHAM, N.H. – From the salmon-rich waters of Southeast Alaska to the white sand beaches of Florida's Gulf Coast to Downeast Maine's lobster, lumber and tourist towns, coastal residents around the U.S. share a common characteristic: their views about coastal environments divide along political lines. That's a primary finding of a new study by University of New Hampshire sociologists published this month in the journal Society & Natural Resources.
"We found a lot of environment-related differences from place to place to place. Each environment is different so that's just ...
Artworks are people!
2014-09-16
Not all things are created equally. We don't view a Picasso sculpture in the same way we look at a hammer, for example — no matter how fancy the hammer.
The reason? We see the Picasso more as a person than an object, according to new research from the University of Chicago Booth School of Business.
And in some cases, we make distinctions between artworks — say, an exact replica of a piece created by the artist, versus one created by a different artist.
Art, in other words, is an extension of the creator, write Professor Daniel M. Bartels of Chicago Booth, and Professor ...
For electronics beyond silicon, a new contender emerges
2014-09-16
Cambridge, Mass. – September 16, 2014 – Silicon has few serious competitors as the material of choice in the electronics industry. Yet transistors, the switchable valves that control the flow of electrons in a circuit, cannot simply keep shrinking to meet the needs of powerful, compact devices; physical limitations like energy consumption and heat dissipation are too significant.
Now, using a quantum material called a correlated oxide, Harvard researchers have achieved a reversible change in electrical resistance of eight orders of magnitude, a result the researchers ...
NASA's Global Hawk and satellites investigating Hurricane Edouard today
2014-09-16
The unmanned Global Hawk aircraft that's part of NASA's airborne Hurricane and Severe Storm Sentinel, or HS3 mission was winging its way to Hurricane Edouard on September 16. In addition to the Global Hawk, various NASA satellites are continually providing data on the Atlantic hurricane.
Scientific instruments aboard NASA's remotely piloted Global Hawk aircraft have been studying the hurricane over the last couple of days, and the Global Hawk returned to Edouard again today, September 16. Two of the instruments aboard the Global Hawk that will study Edouard are the S-HIS ...
Cancer patients with malignant spinal cord compression have preserved mobility
2014-09-16
San Francisco, September 15, 2014—Mobility is equally preserved in cancer patients suffering from malignant spinal cord compression (MSCC) who receive a single dose of 10 Gy of radiation therapy (RT), compared to patients who receive five daily doses of 4 Gy of RT each, according to research presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology's (ASTRO's) 56th Annual Meeting.
Malignant spinal cord compression (MSCC) is a complication of metastatic cancer mostly with bone involvement that occurs when a tumor's secondary deposit presses on the spinal cord and ...
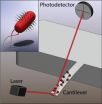
And so they beat on, flagella against the cantilever
2014-09-16
WASHINGTON D.C., September 16, 2014 – A team of researchers at Boston University and Stanford University School of Medicine has developed a new model to study the motion patterns of bacteria in real time and to determine how these motions relate to communication within a bacterial colony.
The researchers chemically attached colonies of Escherichia coli bacteria to a microcantilever – a microscopic beam anchored at one end, similar to a diving board – thus coupling its motion to that of the bacteria. As the cantilever itself isn't doesn't generate any vibrations, or 'noise,' ...
NASA sees Tropical Storm Odile knocking at US Southwest
2014-09-16
Tropical Storm Odile continues to drench western Mexico and has now entered into the U.S. Southwest. On September 15, NASA's Terra satellite saw Odile's northernmost edge crossing the Mexican border into southern California. NOAA's GOES-East satellite on September 16 showed Odile's outer bands were already bringing storms to southern Arizona.
NASA Sees Odile Knocking on U.S. Border
On Sept. 15 at 2:35 p.m. EDT, the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite saw the northern fringes of Hurricane Odile straddling the border ...
Scientists twist radio beams to send data
2014-09-16
Building on previous research that twisted light to send data at unheard-of speeds, scientists at USC have developed a similar technique with radiowaves, reaching high speeds without some of the hassles that can go with optical systems.
The researchers, led by electrical engineering professor Alan Willner of the USC Viterbi School of Engineering, reached data transmission rates of 32 gigabits per second across 2.5 meters of free space in a basement lab at USC.
For reference, 32 gigabits per second is fast enough to transmit more than 10 hour-and-a-half-long HD movies ...
Kessler Foundation scientists link slowed processing speed with executive deficits in MS
2014-09-16
West Orange, NJ. September 16, 2014. Kessler Foundation researchers have published a study supporting the role of slowed processing speed in the executive deficits found in individuals with multiple sclerosis (MS). "Does slowed processing speed account for executive deficits in multiple sclerosis? Evidence from neuropsychological performance and structural neuroimaging," was published online ahead of print on August 18 by Rehabilitation Psychology The authors are Victoria Leavitt, PhD, of the Manhattan Memory Center, formerly of Kessler Foundation. Co-authors are Foundation ...
Tornadoes occurring earlier in 'Tornado Alley'
2014-09-16
WASHINGTON, D.C. – Peak tornado activity in the central and southern Great Plains of the United States is occurring up to two weeks earlier than it did half a century ago, according to a new study whose findings could help states in "Tornado Alley" better prepare for these violent storms.
Tornado records from Nebraska, Kansas, Oklahoma, and northern Texas – an area of high tornado activity dubbed "Tornado Alley" -- show that peak tornado activity is starting and ending earlier than it did 60 years ago.
Peak tornado activity, which occurs in the region from early ...
Water-based nuclear battery developed by MU can be used to generate electrical energy
2014-09-16
COLUMBIA, Mo. – From cell phones to cars and flashlights, batteries play an important role in everyday life. Scientists and technology companies constantly are seeking ways to improve battery life and efficiency. Now, for the first time using a water-based solution, researchers at the University of Missouri have created a long-lasting and more efficient nuclear battery that could be used for many applications such as a reliable energy source in automobiles and also in complicated applications such as space flight.
"Betavoltaics, a battery technology that generates power ...
[1] ... [3337]
[3338]
[3339]
[3340]
[3341]
[3342]
[3343]
[3344]
3345
[3346]
[3347]
[3348]
[3349]
[3350]
[3351]
[3352]
[3353]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.