Early exposure to certain bacteria may protect toddlers from wheezing
2014-06-06
WHAT: Research funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) suggests that exposure to specific combinations of allergens and bacteria within the first year of life may protect children from wheezing and allergic disease. These observations come from the Urban Environment and Childhood Asthma (URECA) study, which aims to identify factors responsible for asthma development in children from inner-city settings, where the disease is more prevalent and severe. Since 2005, the URECA study has enrolled 560 children from four cities—Baltimore, Boston, New York and St. Louis. ...
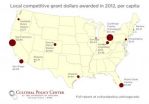
New report: Local public grants for art varies across US
2014-06-06
Local direct public funding provided through grants for the arts in Chicago is low compared to peer regions in both total dollar and per capita terms, according to a new report from the Cultural Policy Center at the University of Chicago.
The study tracks direct public funding for the arts in 13 regions from 2002-2012. It provides a nuanced look at how much money comes to the nonprofit arts from national, state and local arts agencies, with an emphasis on the important role of local arts agencies. While most studies of public funding for the arts use appropriations made ...
HIV transmission networks mapped to reduce infection rate
2014-06-06
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have mapped the transmission network of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in San Diego. The mapping of HIV infections, which used genetic sequencing, allowed researchers to predictively model the likelihood of new HIV transmissions and identify persons at greatest risk for transmitting the virus.
The findings are published online in the June 5 issue of the journal PLOS ONE.
"The more we understand the structure and dynamics of an HIV transmission network, the better we can identify 'hot spots' ...
Alcohol may protect trauma patients from later complications
2014-06-06
Injured patients who have alcohol in their blood have a reduced risk for developing cardiac and renal complications, according to a study from the University of Illinois at Chicago School of Public Health. Among patients who did develop complications, those with alcohol in their blood were less likely to die.
The study is published in the June issue of the journal Alcohol.
"After an injury, if you are intoxicated there seems to be a substantial protective effect," says UIC injury epidemiologist Lee Friedman, author of the study. "But we don't fully understand why this ...
Is glaucoma a brain disease?
2014-06-06
Rockville, Md. — Findings from a new study published in Translational Vision Science & Technology (TVST) show the brain, not the eye, controls the cellular process that leads to glaucoma. The results may help develop treatments for one of the world's leading causes of irreversible blindness, as well as contribute to the development of future therapies for preserving brain function in other age-related disorders like Alzheimer's.
In the TVST paper, Refined Data Analysis Provides Clinical Evidence for Central Nervous System Control of Chronic Glaucomatous Neurodegeneration, ...
Clinical review published in JAMA
2014-06-06
Many women experience bothersome urine loss with laughing, coughing and sneezing (stress urinary incontinence) AND on their way to the bathroom (urge urinary incontinence). When women experience both types of urine leakage, their condition is called mixed urinary incontinence. It is estimated that 20 to 36 percent of women suffer from mixed urinary incontinence, which is challenging to diagnose and treat because symptoms vary and guidelines for treatment are not clear.
A clinical review entitled "Clinical Crossroads – Female Mixed Urinary Incontinence" by Deborah L. ...
Prostate cancer biomarkers identified in seminal fluid
2014-06-06
Improved diagnosis and management of one of the most common cancers in men – prostate cancer – could result from research at the University of Adelaide, which has discovered that seminal fluid (semen) contains biomarkers for the disease.
Results of a study now published in the journal Endocrine-Related Cancer have shown that the presence of certain molecules in seminal fluid indicates not only whether a man has prostate cancer, but also the severity of the cancer.
Speaking in the lead-up to Men's Health Week (9-15 June), University of Adelaide research fellow and lead ...
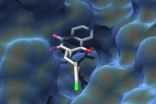
Toward a better drug against malaria
2014-06-06
This news release is available in German.
A research team led by Prof. Dr. Carola Hunte of the University of Freiburg/ Germany has succeeded in describing how the antimalarial drug atovaquone binds to its target protein. The scientists used x-ray crystallography to determine the three-dimensional structure of the protein with the active substance bound. The drug combination atovaquone-proguanil (Malarone®) is a medication used worldwide for the prevention and treatment of malaria. The data and the resulting findings concerning the mode of action of atovaquone could ...
Football for untrained 70-year-old men
2014-06-06
Research carried out by the Copenhagen Centre for Team Sport and Health in Denmark shows that untrained elderly men get markedly fitter and healthier as a result of playing football (soccer). After only 4 months of twice-weekly 1-hour training sessions, the men achieved marked improvements in maximum oxygen uptake, muscle function and bone mineralization.
Later today, three scientific articles will be published in the Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports describing the fitness and health effects of football training for 63‒75-year-old untrained men. ...
Deadly diseases overlooked for too long, scientists say
2014-06-06
Decades of neglect have allowed infectious diseases to devastate the lives of thousands of people in the developing world, a study reveals.
Researchers say three diseases in particular – anthrax, brucellosis and bovine tuberculosis – have failed to receive the official recognition and funding needed to combat them effectively.
All three impact greatly on human and animal health in developing nations, posing a major threat to safe and plentiful food supplies.
The disorders – known as zoonotic diseases – are spread between animals and humans. They are common ...
Saving trees in tropics could cut emissions by one-fifth, study shows
2014-06-06
Reducing deforestation in the tropics would significantly cut the amount of carbon dioxide emitted into the atmosphere – by as much as one-fifth – research shows.
In the first study of its kind, scientists have calculated the amount of carbon absorbed by the world's tropical forests and the amounts of greenhouse gas emissions created by loss of trees, as a result of human activity.
They found that tropical forests absorb almost two billion tonnes of carbon each year, equivalent to one-fifth of the world's carbon emissions, by storing it in their bark, leaves and soil. ...
York scientists provide new insights into biomass breakdown
2014-06-06
Scientists at the University of York are playing a key role in the quest for a better understanding of how a recently discovered family of enzymes can degrade hard-to-digest biomass into its constituent sugars.
The enzymes – lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases (LPMOs) – are secreted by both fungi and bacteria and have the ability to 'chip away' at cellulose and other intractable materials. This allows cellulosic materials such as plant stems, wood chips and cardboard waste, as well as other tricky polysaccharides such as insect/crustacean shells, to be broken down.
Finding ...
Infection in malaria-transmitting mosquito discovered
2014-06-06
Boston, MA – Researchers have found the first evidence of an intercellular bacterial infection in natural populations of two species of Anopheles mosquitoes, the major vectors of malaria in Africa. The infection, called Wolbachia, has been shown in labs to reduce the incidence of pathogen infections in mosquitoes and has the potential to be used in controlling malaria-transmitting mosquito populations.
"Wolbachia is an interesting bacterium that seems perfectly suited for mosquito control. However, there were strong doubts that it could ever be used against field Anopheles ...
Three gene networks discovered in autism, may present treatment targets
2014-06-06
A large new analysis of DNA from thousands of patients has uncovered several underlying gene networks with potentially important roles in autism. These networks may offer attractive targets for developing new autism drugs or repurposing existing drugs that act on components of the networks.
Furthermore, one of the autism-related gene pathways also affects some patients with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and schizophrenia—raising the possibility that a class of drugs may treat particular subsets of all three neurological disorders.
"Neurodevelopmental ...
Asymmetric continental margins and the slow birth of an ocean
2014-06-06
When South America split from Africa 150 to 120 million years ago, the South Atlantic formed and separated Brazil from Angola. The continental margins formed through this separation are surprisingly different. Along offshore Angola 200 km wide, very thin slivers of continental crust have been detected, whereas the Brazilian counterpart margin features an abrupt transition between continental and oceanic crust.
For decades, geoscientists have struggled to explain not only why the amount of thinning and the geometries of opposite rifted continental margin are not symmetric, ...
Text messaging program helps smokers fight the urge to light up
2014-06-06
WASHINGTON, DC (June 6, 2014) — More than 11 percent of smokers who used a text- messaging program to help them quit did so and remained smoke free at the end of a six- month study as compared to just 5 percent of controls, according to a new report by researchers at Milken Institute School of Public Health at the George Washington University (Milken Institute SPH.)
"Text messages seem to give smokers the constant reminders they need to stay focused on quitting," says Lorien C. Abroms, ScD, MA, an associate professor of prevention and community health at Milken Institute ...
Sleep apnea tied to diabetes in large study
2014-06-06
In the largest study to date of the relationship between sleep apnea and diabetes, a new study of more than 8,500 Canadian patients has demonstrated a link between obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and the development of diabetes, confirming earlier evidence of such a relationship from smaller studies with shorter follow-up periods.
"Our study, with a larger sample size and a median follow-up of 67 months was able to address some of the limitations of earlier studies on the connection between OSA and diabetes," said lead author Tetyana Kendzerska, MD, PhD, of the University ...
Newborns exposed to dirt, dander and germs may have lower allergy and asthma risk
2014-06-06
Infants exposed to rodent and pet dander, roach allergens and a wide variety of household bacteria in the first year of life appear less likely to suffer from allergies, wheezing and asthma, according to results of a study conducted by scientists at the Johns Hopkins Children's Center and other institutions.
Previous research has shown that children who grow up on farms have lower allergy and asthma rates, a phenomenon attributed to their regular exposure to microorganisms present in farm soil. Other studies, however, have found increased asthma risk among inner-city ...
Biomarkers accurately distinguish mesothelioma from non-cancerous tissue
2014-06-06
Philadelphia, PA, June 6, 2014 – Scientists have identified four biomarkers that may help resolve the difficult differential diagnosis between malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) and non-cancerous pleural tissue with reactive mesothelial proliferations (RMPs). This is a frequent differential diagnostic problem in pleural biopsy samples taken from patients with clinical suspicion of MPM. The ability to make more accurate diagnoses earlier may facilitate improved patient outcomes. This new study appears in the Journal of Molecular Diagnostics.
"Our goal was to identify ...
Our ability to identify the source of pain varies across the body
2014-06-06
"Where does it hurt?" is the first question asked to any person in pain.
A new UCL study defines for the first time how our ability to identify where it hurts, called "spatial acuity", varies across the body, being most sensitive at the forehead and fingertips.
Using lasers to cause pain to 26 healthy volunteers without any touch, the researchers produced the first systematic map of how acuity for pain is distributed across the body. The work is published in the journal Annals of Neurology and was funded by the Wellcome Trust.
With the exception of the hairless skin ...
Turbulent black holes: Fasten your seatbelts ... gravity is about to get bumpy!
2014-06-06
Fasten your seatbelts – gravity is about to get bumpy.
Of course, if you're flying in the vicinity of a black hole, a bit of extra bumpiness is the least of your worries. But it's still surprising. The accepted wisdom among gravitational researchers has been that spacetime cannot become turbulent. New research from Perimeter, though, shows that the accepted wisdom might be wrong.
The researchers followed this line of thought: Gravity, it's thought, can behave as a fluid. One of the characteristic behaviours of fluids is turbulence – that is, under certain conditions, ...
YbeY is essential for fitness and virulence of V. cholerae, keeps RNA household in order
2014-06-06
YbeY is a conserved protein that is present in most bacteria. A study published on June 5th in PLOS Pathogens examines the function of YbeY in the cholera bacterium and reveals critical roles in RNA metabolism in this and other pathogenic bacteria.
Graham Walker, from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, USA, and colleagues previously studied E. coli YbeY and found that it acts as an "RNase"—a protein that deliberately and specifically cuts RNA molecules and thereby regulates their availability and activity. Turning to Vibrio cholerae to examine the role of YbeY ...
Silent mutations speak up
2014-06-06
June 5, 2014 – So-called silent DNA mutations earned their title because, according to the fundamental rules of biology, they should be inconsequential. Reported on June 5 in PLOS Genetics online, University of Utah researchers experimentally proved there are frequent exceptions to the rule. The work was conducted in the bacteria, Salmonella enterica, used to study basic biological mechanisms that are often conserved in humans.
"In this post-genomic era, where a patient's DNA sequence can be used to diagnose predisposition to diseases, silent mutations are usually ignored," ...
Improved glucose control slows progression to end-stage renal disease in type 1 diabetes
2014-06-06
BOSTON – June 5, 2014 - People with type 1 diabetes who have developed kidney complications can slow the progression of their complications by improving control of their glycemic (blood glucose) levels over the long term.
This finding, which may change clinical practice at many institutions for this population, was drawn from a long-term observational study led by Andrzej Krolewski, M.D., Ph.D., head of Joslin Diabetes Center's Section on Genetics and Epidemiology.
Running for almost 20 years, the study showed that "you have to improve glycemic control for a long period ...
For forests, an earlier spring than ever
2014-06-06
Every spring, as the weather warms, trees in forests up and down the east coast explode in a bright green display of life as leaves fill their branches, and every fall, those same leaves provide one of nature's great color displays of vivid yellow, orange and red.
Over the last two decades, spurred by higher temperatures caused by climate change, Harvard scientists say, forests throughout the Eastern U.S. have experienced earlier springs and later autumns than ever before.
Using a combination of satellite imagery, tower-mounted instruments and on-the-ground observations, ...
[1] ... [3567]
[3568]
[3569]
[3570]
[3571]
[3572]
[3573]
[3574]
3575
[3576]
[3577]
[3578]
[3579]
[3580]
[3581]
[3582]
[3583]
... [8833]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.