Obstetric malpractice claims dip when hospitals stress patient safety
2014-06-10
A Connecticut hospital saw a 50% drop in malpractice liability claims and payments when it made patient safety initiatives a priority by training doctors and nurses to improve teamwork and communication, hiring a patient safety nurse, and standardizing practices, according to a study by Yale School of Medicine researchers.
The results, published in the June 9 online issue of the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, come at a time when mounting concerns about liability are thinning the ranks of obstetricians in the United States, according first author Christian ...
LSTM researchers identify the complex mechanisms controlling changes in snake venom
2014-06-10
Specialist researchers from LSTM have identified the diverse mechanisms by which variations in venom occur in related snake species and the significant differences in venom pathology that occur as a consequence.
Working with colleagues from Bangor University and Instituto de Biomedicina de Valencia in Spain, the team assessed the venom composition of six related viperid snakes, examining the differences in gene and protein expression that influence venom content. The research, published in PNAS, also assessed how these changes in venom composition impacted upon venom-induced ...
Grain legume crops sustainable, nutritious
2014-06-10
Popular diets across the world typically focus on the right balance of essential components like protein, fat, and carbohydrates. These items are called macronutrients, and we consume them in relatively large quantities. However, micronutrients often receive less attention. Micronutrients are chemicals, including vitamins and minerals, that our bodies require in very small quantities. Common mineral micronutrients include zinc, iron, manganese, magnesium, potassium, copper, and selenium.
A recent study published in Crop Science examined the mineral micronutrient content ...
Seafarers brought Neolithic culture to Europe, gene study indicates
2014-06-10
How the Neolithic people found their way to Europe has long been a subject of debate. A study published June 6 of genetic markers in modern populations may offer some new clues.
Their paper, "Maritime route of colonization of Europe," appears in the online edition of the Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences.
Between 8,800 to 10,000 B.C., in the Levant, the region in the eastern Mediterranean that today encompasses Israel and the West Bank, Jordan, Syria and part of southern Turkey, people learned how to domesticate wild grains. This accomplishment eventually ...
In fighting obesity, targeting popular teens not all that effective
2014-06-10
MAYWOOD, Ill. – In the fight against teenage obesity, some researchers have proposed targeting popular teens, in the belief that such kids would have an outsize influence on their peers.
But in a Loyola University Chicago study, researchers were surprised to find that this strategy would be only marginally more effective than targeting overweight kids at random.
Results are published in the journal Social Science & Medicine.
"I don't think targeting popular kids would be worth the extra effort it would take to identify them," said David Shoham, PhD, MSPH, senior ...
Study: Little evidence that No Child Left Behind has hurt teacher job satisfaction
2014-06-10
WASHINGTON, D.C., June 10, 2014 ─ The conventional wisdom that No Child Left Behind (NCLB) has eroded teacher job satisfaction and commitment is off the mark, according to new research published online today in Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association.
"Estimating the Effects of No Child Left Behind on Teachers and Their Work Environment," by Jason A. Grissom of Vanderbilt University, Sean Nicholson-Crotty of Indiana University, and James R. Harrington of the University of Texas at Dallas, ...
Scientific breakthrough: International collaboration has sequenced salmon genome
2014-06-10
Vancouver, BC - Today the International Cooperation to Sequence the Atlantic Salmon Genome (ICSASG) announced completion of a fully mapped and openly accessible salmon genome. This reference genome will provide crucial information to fish managers to improve the production and sustainability of aquaculture operations, and address challenges around conservation of wild stocks, preservation of at-risk fish populations and environmental sustainability. This breakthrough was announced at the International Conference on Integrative Salmonid Biology (ICISB) being held in Vancouver ...
Summertime cholesterol consumption key for wintertime survival for Siberian hamsters
2014-06-10
Increasingly, scientific findings indicate that an organism's diet affects more than just general health and body condition. In an article published in a forthcoming issue of the journal Physiological and Biochemical Zoology, researchers from Nicolaus Copernicus University have found evidence that the diet of some animals must include cholesterol in order for them to enter necessary periods of energy conservation known as torpor.
Torpor is a temporary, strategic decrease of body temperature and metabolic, heart, and respiration rates that can enable an organism to survive ...
RHM announces publication latest issue: Population, environment & sustainable development
2014-06-10
London, June 10, 2014 – Papers published in the latest themed issue of Reproductive Health Matters demonstrate the extent of evidence and progressive thinking around population dynamics and sustainability that is informing development policies and programs. The theme of this issue is timely given that meetings and negotiations are currently taking place around the world to decide what will be included in the post-2015 development goals.
The discussions about the post-2015 agenda have focused on calling out to sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR) advocates ...
Male dwarf spiders make sure offspring is their own
2014-06-10
Chastity belts were not first thought out in mediaeval times – members of many animal groups have evolved similar mechanical safeguards to ensure their paternity. Male dwarf spiders, for instance, use mating plugs to block off the genital tract of the female they have just mated with. The larger and older the plug, the better the chances are that other males will not make deposits in a female's sperm storage organ, too. So says Katrin Kunz and co-authors of the Zoological Institute and Museum in Greifswald, Germany, in an article published in Springer's journal Behavioral ...
Signpost for health services: Teenagers go from school psychologist to family doctor
2014-06-10
After initially visiting a school psychologist, adolescents in the United States with a mental disorder often go to seek care from their pediatricians or family doctors. Fewer of them continue their treatment directly with a psychotherapist or doctor specialized in mental disorders. This shows an analysis conducted by scientists at the University of Basel that has just been published in the academic journal PLOS ONE. The results are based on a nationally representative cohort of 6,500 U.S. teenagers.
A considerable number of children and adolescents suffer from a mental ...
ESMO survey sheds light on common clinical practice for incompletely resected lung cancer
2014-06-10
VIDEO:
R.Califano explains why ESMO Young Oncologists launched a survey on common clinical practice for incompletely resected lung cancer and analyses interesting results claiming for more adherence to guidelines and more...
Click here for more information.
Lugano, Switzerland, 10 June 2014 -- A landmark survey of more than 700 specialists provides crucial real-world insight into the treatments most oncologists choose for lung cancer patients whose tumour has been incompletely ...
Game changer for leukemia therapy
2014-06-10
Australian researchers are zeroing in on a promising new approach to killing off cancer cells in patients with leukemia.
In a study led by the South Australian Health and Medical Research Institute (SAHMRI) and the University of Adelaide's Centre for Personalised Cancer Medicine, researchers have found that cancer cells decide whether to live or die after a short period of intense exposure to targeted therapy, opposing the current requirement for continuous treatment.
The researchers say this study presents a new treatment strategy which will translate to a significant ...
Women appear in only 5 percent of sports newsprint
2014-06-10
This news release is available in Spanish.
Women are the subject of news in sports papers in only 5.11% of the cases, sometimes alone (2.18%) and others accompanied by men (2.93%). On the other hand, men are the focus of this kind of information in 92.2% of the cases, according to a study presented recently by UC3M professor Clara Sainz de Baranda at the II International Conference on Gender and Communication. "The remaining 5% is neutral information, which is why, in these kinds of topics, like soccer balls, fields, field houses and goals, men appear more often ...
New teaching approach touted for engineering education
2014-06-10
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Purdue University researchers who developed a new approach to more effectively teach large numbers of engineering students are recommending that the approach be considered for adoption by universities globally.
The system, called the Purdue Mechanics Freeform Classroom, allows students to interact with each other and faculty online while accessing hundreds of instructional videos and animations. It was pioneered by Charles Krousgrill, a professor of mechanical engineering, and has been used for more than two years in two mechanical engineering core ...
Virginia Tech architect reveals 'green roofs' need not go to great depths to work
2014-06-10
Hot town, summer in the city — it's nothing new, but ways to handle the heat, humidity, and stormwater haven't changed much since the invention of the sewer system.
One solution offered by architectural researchers is known as a "green roof" — a roof covered in living, growing plants to soften the effects of heat, flooding, noise, and stormwater runoff.
Elizabeth J. Grant, an assistant professor of architecture and design at Virginia Tech, will present ways for architects to determine the most effective depths of green roofing for stormwater control on Thursday at the ...
Scientific breakthrough: International collaboration has sequence salmon genome
2014-06-10
Vancouver, BC - Today the International Cooperation to Sequence the Atlantic Salmon Genome (ICSASG) announced completion of a fully mapped and openly accessible salmon genome. This reference genome will provide crucial information to fish managers to improve the production and sustainability of aquaculture operations, and address challenges around conservation of wild stocks, preservation of at-risk fish populations and environmental sustainability. This breakthrough was announced at the International Conference on Integrative Salmonid Biology (ICISB) being held in Vancouver ...
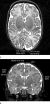
MRI shows brain abnormalities in late preterm infants
2014-06-10
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Babies born 32 to 36 weeks into gestation may have smaller brains and other brain abnormalities that could lead to long-term developmental problems, according to a new study published online in the journal Radiology.
Much of the existing knowledge on preterm birth and brain development has been drawn from studies of individuals born very preterm, or less than 32 weeks into gestation at birth.
For the new study, researchers in Australia focused on moderate and late preterm (MLPT) babies —those born between 32 weeks, zero days, and 36 weeks, six days, ...
Bacteria help explain why stress, fear trigger heart attacks
2014-06-10
WASHINGTON, DC – June 10, 2014 - Scientists believe they have an explanation for the axiom that stress, emotional shock, or overexertion may trigger heart attacks in vulnerable people. Hormones released during these events appear to cause bacterial biofilms on arterial walls to disperse, allowing plaque deposits to rupture into the bloodstream, according to research published in published today in mBio®, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
"Our hypothesis fitted with the observation that heart attack and stroke often occur following ...
Fox Chase doctors urge caution over new analysis of Medicare payments
2014-06-10
PHILADELPHIA, PA (June 9, 2014)—There's much to learn from the recent release of unprecedented amounts of data from the nation's second largest health insurer, Medicare, but only if interpreted cautiously, write two doctors at Fox Chase Cancer Center in the June 9 online edition of the Annals of Internal Medicine.
In April, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) released the most detailed data in its history, related to $77 billion worth of physician billings to Medicare. In its analysis of the data, The New York Times showed that only a small percentage ...
Lifetime cancer risk from heart imaging low for most children; rises with complex tests
2014-06-09
DURHAM, N.C. -- Children with heart disease are exposed to low levels of radiation during X-rays, which do not significantly raise their lifetime cancer risk. However, children who undergo repeated complex imaging tests that deliver higher doses of radiation may have a slightly increased lifetime risk of cancer, according to researchers at Duke Medicine.
The findings, published June 9, 2014, in the American Heart Association journal Circulation, represent the largest study of cumulative radiation doses in children with heart disease and associated predictions of lifetime ...
'Jekyll and Hyde' protein linked to type 1 diabetes
2014-06-09
Researchers are a step closer to establishing the link between a protein with a split personality and type 1 diabetes.
New research, published today in the journal PNAS, shows how a protein, called GAD65, changes its shape when it turns itself on and off. Curiously, this characteristic may also link it to type 1 diabetes.
In the human brain, GAD65 performs an essential role: it makes 'neurotransmitters' - chemicals that pass messages between brain cells.
GAD65 is also found in the pancreas. Previous studies linked it to type 1 diabetes because the body makes antibodies ...
Mount Sinai researchers identify protein that keeps blood stem cells healthy as they age
2014-06-09
(New York – June 9, 2014) -- A protein may be the key to maintaining the health of aging blood stem cells, according to work by researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai recently published online in Stem Cell Reports. Human adults keep stem cell pools on hand in key tissues, including the blood. These stem cells can become replacement cells for those lost to wear and tear. But as the blood stem cells age, their ability to regenerate blood declines, potentially contributing to anemia and the risk of cancers like acute myeloid leukemia and immune deficiency. ...
Viewing plant cells in 3-D (no glasses required)
2014-06-09
VIDEO:
This shows 3-D ortho-rotation of leaf mesophyll cells. Micrographs were collected by milling fixed tissue accompanied by SEM imaging using FIB-SEM. The complete videos published with the article are available...
Click here for more information.
Plant cells are beginning to look a lot different to Dr. A. Bruce Cahoon and his colleagues at Middle Tennessee State University (MTSU). They've adopted a new approach that combines the precision of an ion beam with the imaging ...
Needle biopsy underused in breast cancer diagnosis, negatively impacting diagnosis and care
2014-06-09
Needle biopsy, the standard of care radiological procedure for diagnosing breast cancer, is underused with too many patients undergoing the more invasive, excisional biopsy to detect their disease, according to research from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
The study, published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, also finds that patients are often influenced by surgeons to undergo the unnecessary surgery -- a decision that's costly and can negatively impact their diagnosis and treatment.
A needle biopsy is a non-surgical procedure typically performed ...
[1] ... [3562]
[3563]
[3564]
[3565]
[3566]
[3567]
[3568]
[3569]
3570
[3571]
[3572]
[3573]
[3574]
[3575]
[3576]
[3577]
[3578]
... [8833]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.