Study finds public awareness of head and neck cancers low
2014-06-05
Bottom Line: Public awareness of head and neck cancer (HNC) is low, with few Americans knowing much about risk factors such as tobacco use and human papillomavirus (HPV).
Author: Alexander L. Luryi, B.S., of the Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Conn.
Background: HNC is the 10 th most common cancer in the United States. It is a potentially preventable disease with about 75 percent of cases caused by tobacco use. In recent years, HPV has been established as a risk factor for HNC. Increased public awareness of HNC and its risk factors could help improve ...
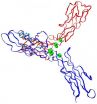
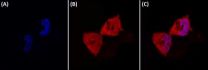
Scientists find new targets that could increase effectiveness of breast cancer treatments
2014-06-05
JUPITER, FL, June 5, 2014 – Scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have found new targets for potential intervention in breast cancer. These new targets could eventually increase effectiveness and reduce the undesirable side effects associated with current treatments.
The study was published online ahead of print on June 5, 2014 by the journal Structure.
Approximately two out of three breast cancers are driven by receptors that bind the hormones estrogen and progesterone—when the hormones bind to these receptors in cancer cells, ...
Researchers at the Gladstone Institutes find novel approach to reactivate latent HIV
2014-06-05
SAN FRANCISCO, CA–June 5, 2014–A team of scientists at the Gladstone Institutes has identified a new way to make latent HIV reveal itself, which could help overcome one of the biggest obstacles to finding a cure for HIV infection. They discovered that increasing the random activity, or noise, associated with HIV gene expression–without increasing the average level of gene expression–can reactivate latent HIV. Their findings were published today in the journal Science.
When HIV infects an immune cell, it inserts its genetic material into the DNA of the infected cell. In ...
Demographics drive fitness partner decisions online, Penn study finds
2014-06-05
Who would you rather have as a fitness partner: a paragon of athleticism and dedication who could motivate you to exceed your current level of fitness or an equal, with whom you could exchange tips and encouragement on the road to better health?
Or neither? According to a new study led by University of Pennsylvania's Damon Centola, participants in an online fitness program ignored the fitness aptitude of their potential partners.
"Instead they chose contacts based on characteristics that would largely be observable in regular, offline face-to-face networks: age, gender ...
New tuberculosis test more than skin deep
2014-06-05
A new screening process for tuberculosis (TB) infections in Canadian prisons could mean that more than 50 per cent of those screened won't undergo unnecessary treatment due to false positives.
According to research by Wendy Wobeser and medical resident Ilan Schwartz, a test for TB using interferon-gamma release assays (IGRA) will detect a pre-existing TB infection, or latent TB, that might not present itself for many years, or until the body becomes weakened by another source.
"It's fairly uncommon that latent TB will reactivate – only about a 10 per cent chance," says ...
Seemingly invincible cancers stem cells reveal a weakness
2014-06-05
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. (June 5, 2014) – Metastatic cancer cells, which can migrate from primary tumors to seed new malignancies, have thus far been resistant to the current arsenal of anticancer drugs. Now, however, researchers at Whitehead Institute have identified a critical weakness that actually exploits one of these cells' apparent strengths—their ability to move and invade tissues.
"This is the first vulnerability of invasive cancer cells that we really understand," says Whitehead Member Piyush Gupta, whose lab's latest work is described in the June issue of the journal ...
New evidence links air pollution to autism, schizophrenia
2014-06-05
A new study published in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives describes how exposure to air pollution early in life produces harmful changes in the brains of mice, including an enlargement of part of the brain that is seen in humans who have autism and schizophrenia.
As in autism and schizophrenia, the changes occurred predominately in males. The mice also performed poorly in tests of short-term memory, learning ability, and impulsivity.
The new findings are consistent with several recent studies that have shown a link between air pollution and autism ...
New findings out on brain networks in children at risk for mental disorders
2014-06-05
DETROIT – Attention deficits are central to psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder, and are thought to precede the presentation of the illnesses. A new study led by Wayne State University School of Medicine researcher Vaibhav Diwadkar, Ph.D. suggests that the brain network interactions between regions that support attention are dysfunctional in children and adolescents at genetic risk for developing schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
"The brain network mechanisms that mediate these deficits are poorly understood, and have rarely been tackled ...
Rice developing mobile DNA test for HIV
2014-06-05
Rice University bioengineers are developing a simple, highly accurate test to detect signs of HIV and its progress in patients in resource-poor settings.
The current gold standard to diagnose HIV in infants and to monitor viral load depends on lab equipment and technical expertise generally available only in clinics, said Rice bioengineer Rebecca Richards-Kortum. The new research features a nucleic acid-based test that can be performed at the site of care.
Richards-Kortum, director of the Rice 360˚: Institute for Global Health Technologies, and her colleagues reported ...
Iowa State, Ames Lab researchers find the mechanism that forms cell-to-cell catch bonds
2014-06-05
AMES, Iowa – Certain bonds connecting biological cells get stronger when they're tugged. Those bonds could help keep hearts together and pumping; breakdowns of those bonds could help cancer cells break away and spread.
Those bonds are known as catch bonds and they're formed by common adhesion proteins called cadherins. Sanjeevi Sivasankar, an Iowa State University assistant professor of physics and astronomy and an associate of the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory, has described catch bonds as "nanoscale seatbelts. They become stronger when pulled."
But how ...
Short nanotubes target pancreatic cancer
2014-06-05
Short, customized carbon nanotubes have the potential to deliver drugs to pancreatic cancer cells and destroy them from within, according to researchers at Rice University and the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Pristine nanotubes produced through a new process developed at Rice can be modified to carry drugs to tumors through gaps in blood-vessel walls that larger particles cannot fit through.
The nanotubes may then target and infiltrate the cancerous cells' nuclei, where the drugs can be released through sonication – that is, by shaking them.
The ...
LSU biologist James Caprio, Japanese colleagues identify unique way catfish locate prey
2014-06-05
BATON ROUGE – Animals incorporate a number of unique methods for detecting prey, but for the Japanese sea catfish, Plotosus japonicus, it is especially tricky given the dark murky waters where it resides.
John Caprio, George C. Kent Professor of Biological Sciences at LSU, and colleagues from Kagoshima University in Japan have identified that these fish are equipped with sensors that can locate prey by detecting slight changes in the water's pH level.
A paper, "Marine teleost locates live prey through pH sensing," detailing the work of Caprio and his research partners, ...
Termites, fungi and climate change
2014-06-05
Climate change models could have a thing or two to learn from termites and fungi, according to a new study released this week.
For a long time scientists have believed that temperature is the dominant factor in determining the rate of wood decomposition worldwide. Decomposition matters because the speed at which woody material are broken down strongly influences the retention of carbon in forest ecosystems and can help to offset the loss of carbon to the atmosphere from other sources. That makes the decomposition rate a key factor in detecting potential changes to the ...
Brazil leads the world in reducing carbon emissions
2014-06-05
As the world turns its attention to Brazil with the opening of the World Cup this month, many people around the globe know the country's soccer fame, but few realize that it is the world's leader in reducing carbon emissions. A new study published in Science magazine provides the first in-depth analysis of how Brazil reached this global-leader status and managed to increase its agriculture production at the same time.
"Brazil is known as a leading favorite to win the World Cup, but they also lead the world in mitigating climate change," says the study's lead author, ...
New isotopic evidence supporting moon formation via Earth collision with planet-sized body
2014-06-05
A new series of measurements of oxygen isotopes provides increasing evidence that the Moon formed from the collision of the Earth with another large, planet-sized astronomical body, around 4.5 billion years ago. This work will be published in Science* on 6th June, and will be presented to the Goldschmidt geochemistry conference in California on 11th June.
Most planetary scientists believe that the Moon formed from an impact between the Earth and a planet-sized body, which has been given the name Theia. Efforts to confirm that the impact had taken place had centred ...
International collaboration explains sheep genome, secrets of unique digestive and metabolic systems
2014-06-05
HOUSTON – (June 6, 2014) -- An international team of scientists including the Human Genome Sequencing Center at Baylor College of Medicine has completed the first ever sequence of the sheep genome, shedding new information on the species' unique and specialized digestive and metabolic systems.
Sheep, a major source of meat, milk, and fiber in the form of wool, are important to the agriculture industry. This exploration of sheep genetic characteristics found features that comprise their specialized digestive systems including the rumen (the first chamber of their stomach ...
Amunix presents XTEN half-life extension technology at Next Generation Protein Therapeutics Summit
2014-06-05
Mountain View, CA – June 5, 2014 – Amunix Operating Inc. said today it is presenting unpublished data from its XTEN half-life extension technology development programs during two sessions this week at IBC's 9th Annual Next Generation Protein Therapeutics Summit in San Francisco, CA. Amunix is a biotechnology company developing hydrophilic, unstructured polypeptides which can be recombinantly fused or chemically conjugated to other peptides, proteins and small molecules.
Vladimir N. Podust, PhD, Director of Analytical Chemistry, Amunix Operating Inc., will present "Extension ...
New EU reforms fail European wildlife
2014-06-05
Despite political proclamation of increased environmental focus, experts argue that the European Union's recent agricultural reforms are far too weak to have any positive impact on the continent's shrinking farmland biodiversity, and call on member states to take action.
About half of all farmland and at least 88% of EU farmers are exempt from Ecological Focus Areas, the main "greening measure" that could help wildlife on farmland.
Meeting EU's own biodiversity targets for 2020 now relies on initiatives from member states.
Experts from leading organisations offer ...
What's in the sheep genome? Wool see
2014-06-05
After eight years of work, researchers have completed the first sequencing of the entire sheep genome.
Scientists from CSIRO led an international research team to complete the sequencing, which could lead to more effective breeding strategies and new approaches to the management of sheep in Australia and around the world.
With about 70m head of sheep in Australia and 1bn globally, the sequencing of the genome could have a massive impact for the rural economy given that sheep are a major source of meat, milk and wool products.
"We investigated the completed genome to ...
Sleep after learning strengthens connections between brain cells and enhances memory
2014-06-05
June 5, 2014 -- In study published today in Science, researchers at NYU Langone Medical Center show for the first time that sleep after learning encourages the growth of dendritic spines, the tiny protrusions from brain cells that connect to other brain cells and facilitate the passage of information across synapses, the junctions at which brain cells meet. Moreover, the activity of brain cells during deep sleep, or slow-wave sleep, after learning is critical for such growth.
The findings, in mice, provide important physical evidence in support of the hypothesis that ...
Scientists crack sheep genome, shining spotlight on rumen evolution and lipid metabolism
2014-06-05
Shenzhen, June 5, 2014--- The latest study, led by scientists from Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, BGI and other institutes, presents a high-quality sheep genome and reveals genomic and transcriptomic events that may be associated with rumen evolution and lipid metabolism that have relevance to both diet and wool. The work was published online today in Science.
Sheep are ruminants with a complex, 4-compartmented "stomach", the largest compartment is the rumen, which is thought to have evolved around 35-40 million years ago, and has the ability ...
Gene study shows how sheep first separated from goats
2014-06-05
Scientists have cracked the genetic code of sheep to reveal how they became a distinct species from goats around four million years ago.
The study is the first to pinpoint the genetic differences that make sheep different from other animals.
The findings could aid the development of DNA testing to speed-up selective breeding programmes, helping farmers to improve their stocks.
The research identifies the genes that give sheep their fleece and uncovers features of their digestive system, which makes them so well-suited to a diet of low quality grass and other plants.
It ...
Brain circuit problem likely sets stage for the 'voices' that are symptom of schizophrenia
2014-06-05
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – June 5, 2014) St. Jude Children's Research Hospital scientists have identified problems in a connection between brain structures that may predispose individuals to hearing the "voices" that are a common symptom of schizophrenia. The work appears in the June 6 issue of the journal Science.
Researchers linked the problem to a gene deletion. This leads to changes in brain chemistry that reduce the flow of information between two brain structures involved in processing auditory information.
The research marks the first time that a specific circuit in the ...
Research could lead to new cancer assay, aid both dogs and humans
2014-06-05
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Veterinary researchers at Oregon State University have identified a unique group of proteins that indicate the presence of transitional cell carcinoma – the most common cause of bladder cancer – and may lead to a new assay which could better diagnose this disease in both dogs and humans.
Bladder cancer is particularly common in some dog breeds, such as collies, sheepdogs and terriers, but is rarely diagnosed in animals before it has spread significantly. Some assays exist to detect it in humans, but they often have a high-number of false-positive identifications.
An ...
New clues to why older women are more vulnerable to breast cancer
2014-06-05
Scientists from the Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have gained more insights into why older women are more susceptible to breast cancer. They found that as women age, the cells responsible for maintaining healthy breast tissue stop responding to their immediate surroundings, including mechanical cues that should prompt them to suppress nearby tumors.
Their work sheds light on how aging alters cellular and molecular functions, and how these changes contribute to the prevalence of breast cancer in older women. The disease is ...
[1] ... [3568]
[3569]
[3570]
[3571]
[3572]
[3573]
[3574]
[3575]
3576
[3577]
[3578]
[3579]
[3580]
[3581]
[3582]
[3583]
[3584]
... [8833]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.