UNC study may lead to treatments that are effective against all MRSA strains
2013-01-31
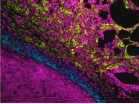
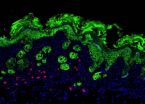
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – In the last decade, a new strain of MRSA has emerged that can spread beyond hospital walls, putting everyone at risk of contracting the dangerous bacterial infection. This particular strain of MRSA – known as USA300 – contains a chunk of genes not shared by any other strains, though it is unclear how this unique genetic material enables the bacteria to survive and persist in the community.
Now, research from the University of North Carolina School of Medicine has pinpointed a gene that causes the infection to linger on the skin longer than other strains, ...
How the tilt of a cell-surface receptor prevents cancer
2013-01-31
January 31, 2013, New York, NY and Brussels, Belgium – Clear communication between cells is essential to every aspect of the body's internal function. But since cells can't talk, or send emails, how do they communicate?
The answer, in a nutshell, is by dispatching signaling molecules that selectively bind to protein receptors on the outer surface of other cells with which they must "talk." This activates the tail end of such receptors inside the cell, initiating a cascade of enzymatic reactions, or signaling pathways that reach into the nucleus, turning genes on and off. ...
1 of the key circuits in regulating genes involved in producing blood stem cells is deciphered
2013-01-31
Researchers from the group on stem cells and cancer at IMIM (Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute) have deciphered one of the gene regulation circuits which would make it possible to generate hematopoietic blood cells, i.e. blood tissue stem cells. This finding is essential to generate these cells in a laboratory in the future, a therapy that could benefit patients with leukaemia or other diseases who need a transplant and who, in many cases, do not have a compatible donor.
In the process of generating stem cells, many molecule signals intervene which, through ...
In the planetary nursery
2013-01-31
This press release is available in German.
The disk surrounding the young star TW Hydrae is regarded as a prototypical example of planetary nurseries. Due to its comparatively close proximity of 176 light-years, the object plays a key role in cosmological birth models. Using the Herschel Space Telescope, researchers including Thomas Henning from the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy in Heidelberg have, for the first time, determined the mass of the disk very precisely. The new value is larger than previous estimates and proves that planets similar to those of our solar ...
A positive family climate in adolescence is linked to marriage quality in adulthood
2013-01-31
Experiencing a positive family climate as a teenager may be connected to your relationships later in life, according to new research published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
While research has demonstrated long-term effects of aggression and divorce across generations, the impact of a positive family climate has received less attention. Psychological scientist Robert Ackerman of the University of Texas at Dallas and colleagues wanted to examine whether positive interpersonal behaviors in families might also have long-lasting ...
Zebrafish may hold the answer to repairing damaged retinas and returning eyesight to people
2013-01-31
Zebrafish, the staple of genetic research, may hold the answer to repairing damaged retinas and returning eye-sight to people.
University of Alberta researchers discovered that a zebrafish's stem cells can selectively regenerate damaged photoreceptor cells.
Lead U of A researcher Ted Allison says that for some time geneticists have known that unlike humans, stem cells in zebrafish can replace damaged cells involved in many components of eyesight. Rods and cones are the most important photoreceptors. In humans, rods provide us with night vision while cones give us a full ...
Time spent watching television is not associated with death among breast cancer survivors
2013-01-31
Spending a lot of time watching television after breast cancer diagnosis is not linked to death in these breast cancer survivors. It appears that after accounting for self-reported physical activity levels after diagnosis, sedentary behavior was not an independent risk factor for death. These findings by Stephanie George, from the National Cancer Institute, and her colleagues, are published online in Springer's Journal of Cancer Survivorship.
On the one hand, research indicates that taking part in regular, moderate-to-vigorous intensity physical activity after a breast ...
Policy, enforcement may stop employees from wasting time online at work, researcher finds
2013-01-31
MANHATTAN, Kan. -- Businesses must deal with weary-eyed office workers who are sitting behind computer screens and watching cat videos, shopping online and updating their Facebook statuses.
A Kansas State University researcher studied cyberloafing -- wasting time at work on the Internet -- and the effects of Internet use policies and punishment on reducing cyberloafing.
Joseph Ugrin, assistant professor of accounting at Kansas State University, and John Pearson, associate professor of management at Southern Illinois University in Carbondale, found that company policies ...
A new mechanism that contributes to the evolution of cancer
2013-01-31
Cancer arises from the accumulation of mutations and structural changes in chromosomes, which in some cases give rise to combinations that favour the growth or expansion of the disease. In this context, chromosomes tend to lose or duplicate entire regions, although, the mechanisms that initiate these chromosomal abnormalities are not fully understood.
A study published this week in the journal Cell, in which researchers from the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) participated, demonstrates a new mechanism that explains how these changes originate in the chromosomes ...
New Geology study raises questions about long-held theories of human evolution
2013-01-31
What came first: the bipedal human ancestor or the grassland encroaching on the forest?
A new analysis of the past 12 million years' of vegetation change in the cradle of humanity is challenging long-held beliefs about the world in which our ancestors took shape – and, by extension, the impact it had on them.
The research combines sediment core studies of the waxy molecules from plant leaves with pollen analysis, yielding data of unprecedented scope and detail on what types of vegetation dominated the landscape surrounding the African Rift Valley (including present-day ...
Joslin scientists find first human iPSC from patients with maturity onset diabetes of the young
2013-01-31
BOSTON – January 31, 2013 – Joslin scientists report the first generation of human induced pluripotent stem cells from patients with an uncommon form of diabetes, maturity onset diabetes of the young (MODY). These cells offer a powerful resource for studying the role of genetic factors in the development of MODY and testing potential treatments. The findings appear in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
Human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) are adult cells that have been genetically reprogrammed to exhibit the characteristics of embryonic stem cells, including ...
Personalized medicine eliminates need for drug in 2 children
2013-01-31
This press release is available in French.Using genome-wide analysis, investigators at the Sainte-Justine University Hospital Research Center and the University of Montreal have potentially eliminated a lifetime drug prescription that two children with a previously unknown type of adrenal insufficiency had been receiving for 14 years. Over a lifespan, the adjustment in treatment represents an approximate saving of $10,000 in drug and test costs per patient. Moreover, the less invasive treatment regime can potentially reduce the lifetime risk of hypertension in the patients. ...
Nanomaterials key to developing stronger artificial hearts
2013-01-31
On January 30, 2013 ACS Nano published a study by Ali Khademhosseini, PhD, MASc, Brigham and Women's Hospital Division of Biomedical Engineering, detailing the creation of innovative cardiac patches that utilize nanotechnology to enhance the conductivity of materials to induce cardiac tissue formation. Creation of these ultra-thin cardiac patches put medicine a step closer to durable, high-functioning artificial tissues that could be used to repair damaged hearts and other organs.
The cardiac tissue patches utilize a hydrogel scaffolding reinforced by nanomaterials called ...
Pediatric orthopaedic surgeons show age-related patterns of spine injury in ATV injuries
2013-01-31
Memphis, Tenn. – Children continue to account for a disproportionate percentage of morbidity and mortality from ATV-related accidents – up 240 percent since 1997, according to a Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics report published by pediatric orthopaedic surgeons at Le Bonheur Children's Hospital.
The surgeons – who studied data from the Kids' Inpatient Database – found spine-related injuries from all-terrain vehicles (ATVs) in the United States are more common in older children and in females, unlike males in most trauma studies. ATV-related spine injuries in children ...
Researcher uncovers potential cause, biomarker for autism and proposes study to investigate theory
2013-01-31
NEW YORK, NY — A New York-based physician-researcher from Touro College of Osteopathic Medicine, best known for his research into fertility and twinning, has uncovered a potential connection between autism and a specific growth protein that could eventually be used as a way to predict an infant's propensity to later develop the disease. The protein, called insulin-like growth factor (IGF), is especially involved in the normal growth and development of babies' brain cells. Based on findings of prior published studies, Touro researcher Gary Steinman, MD, PhD, proposes that ...
Working alone won't get you good grades
2013-01-31
Students who work together and interact online are more likely to be successful in their college classes, according to a study published Jan. 30 in the journal Nature Scientific Reports and co-authored by Manuel Cebrian, a computer scientist at the Jacobs School of Engineering at the University of California San Diego.
Cebrian and colleagues analyzed 80,000 interactions between 290 students in a collaborative learning environment for college courses. The major finding was that a higher number of online interactions was usually an indicator of a higher score in the class. ...
Adding new members to group increases distrust among older members, impacts coordination
2013-01-31
Adding a new member to a working group can create distrust between members and hinder group functions, but a new study suggests that the distrust created is between older group members rather than about the newcomers- especially when previous group performance with just the older group members is poor. The results are part of a study published January 30 in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Matthew McCarter and Roman Sheremeta from Chapman University (U.S).
Previous studies report that changing members in an existing group hurts group performance, but the underlying ...
Leading by the nose: Star-nosed mole reveals how mammals perceive touch, pain
2013-01-31
The most sensitive patch of mammalian skin known to us isn't human but on the star-shaped tip of the star-nosed mole's snout. Researchers studying this organ have found that the star has a higher proportion of touch-sensitive nerve endings than pain receptors, according to a study published January 30 in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Diana Bautista and colleagues from the University of California, Berkeley and Vanderbilt University.
Touch and pain are closely intertwined sensations, but very little is known about how these sensations are detected in our cells. In ...
Chimp see, chimp learn: First evidence for chimps improving tool use techniques by watching others
2013-01-31
VIDEO:
This video shows the "dipping " technique performed by chimpanzee Ayumu. Note that he uses his mouth to insert the tube into the bottle. In form, his technique is identical to...
Click here for more information.
Chimps can learn more efficient ways to use a tool by watching what others do, according to research published January 30 in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Shinya Yamamoto and colleagues from Kyoto University and Kent University, UK. Their study ...
Tapeworm eggs discovered in 270 million year old fossil shark feces
2013-01-31
A cluster of tapeworm eggs discovered in 270-million-year-old fossilized shark feces suggests that intestinal parasites in vertebrates are much older than previously known, according to research published January 30 in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Paula Dentzien-Dias and colleagues from the Federal University of Rio Grande, Brazil.
Remains of such parasites in vertebrates from this era are rare- of 500 samples examined, only one revealed the tapeworm eggs. This particular discovery helps establish a timeline for the evolution of present-day parasitic tapeworms ...
Pact invests US $109 million to secure critical genetic material, maintain global food production
2013-01-31
Contact: Michelle Geis
mgeis@burnesscommunications.com
301-280-5712
Contact: Susan Tonassi
301-280-5711
stonassi@burnesscommunications.com
Pact invests US $109 million to secure critical genetic material, maintain global food production
CGIAR consortium partners with global crop diversity trust to revitalize genebanks housing scores of crops considered essential to food security
BONN, GERMANY (31 JANUARY 2013)—Concerned that inconsistent funding eventually could weaken a global network of seed banks at a time when farmers face unprecedented challenges, two ...
Forsyth scientists gain new understanding of latent tuberculosis
2013-01-31
Scientists at the Forsyth have gained new insight on how Tuberculosis (TB) remains a global epidemic. Although drugs have been available to fight TB for 50 years, the disease still infects nearly 2.2 billion people worldwide and causes 1.7 million annual deaths. This is largely attributed to the bacteria's ability to stay dormant in the human body and later resurface as active disease. The Forsyth team, and its collaborators from Stanford University, has recently discovered that Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacteria that causes TB, can lay dormant and thrive within ...
Itching for new help for eczema: Recently identified immune cells possible therapeutic target
2013-01-31
PHILADELPHIA - The increasing incidence of allergic skin diseases, and the accompanying economic burden and heightened risk of developing other allergic conditions, have spurred researchers to look for better ways to control these immune system-based disorders.
Atopic dermatitis, more commonly called eczema, now affects 10 to 20 percent of children in the United States and direct health-care costs exceed $3 billion, according to the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. What's more, up to 50 percent of children with atopic dermatitis ...
Scientists may have received millions in duplicate funding
2013-01-31
Big Data computation at the Virginia Bioinformatics Institute at Virginia Tech reveals that over the past two decades funding agencies may have awarded millions and possibly billions of dollars to scientists who submitted the same grant request multiple times — and accepted duplicate funding.
An analysis led by Harold R. Garner, a professor at Virginia Tech, not only indicates that millions in funding may have been granted and used inappropriately, it points to techniques to uncover existing instances of duplicate funding and ways to prevent it in the future. The analysis ...
Setting the stage for a new paradigm in treatment of heart failure
2013-01-31
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Despite a substantial increase in the number of people suffering the debilitating and often deadly effects of heart failure, treatments for the condition have not advanced significantly for at least 10 years. An analysis by researchers at the University of North Carolina School of Medicine shows new breakthroughs could be closer than we thought.
The analysis points to striking similarities between heart cells in patients with heart failure and brain cells in patients with Alzheimer's disease, raising the possibility that some treatment approaches being ...
[1] ... [5280]
[5281]
[5282]
[5283]
[5284]
[5285]
[5286]
[5287]
5288
[5289]
[5290]
[5291]
[5292]
[5293]
[5294]
[5295]
[5296]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.