The Mount Sinai Hospital becomes first in NYC to offer advanced HYDROS™ Robotic System for treating enlarged prostates
2025-01-27
New York, NY [January 27, 2025]—The Mount Sinai Hospital has performed New York City’s first procedure using the HYDROS™ Robotic System, a cutting-edge technology designed to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), or an enlarged prostate. The minimally invasive procedure offers new hope for patients experiencing the symptoms of BPH, including frequent urination, incomplete bladder emptying, and nighttime urgency.
Urologists at the hospital recently performed the health system’s first three procedures, ...
FAU Engineering researchers develop new weapon against harmful algal blooms
2025-01-27
As harmful algal blooms (HABs) continue to spread across the globe, urgent research is needed to address this growing threat. Studies in Italy, China, and the Atlantic basin have shown that many water bodies have high nitrogen-to-phosphorus ratios, making phosphorus a key factor that drives these blooms. This highlights the critical need for more effective phosphorus management strategies to curb the rise of HABs and protect our ecosystems.
Recently, there’s been a growing interest in finding useful ways to repurpose troublesome algal biomass, which could be turned into valuable products like bioplastics, biofertilizers, and biofuels. Researchers have ...
Bridging critical gaps in advanced heart failure care
2025-01-27
DALLAS, January 27, 2025 — About 6.7 million American adults are living with heart failure (HF), and prevalence is expected to reach more than 8 million by 2030.[1]
While there is no cure for HF, many people with this condition can live full, enjoyable lives and disease progression can be slowed. While people with early-stage HF often can manage their condition with lifestyle modifications and medications, more advanced therapies may be needed as the disease progresses. Yet, a significant number of patients who may benefit from advanced HF specialty care don’t receive it — a gap that particularly affects populations ...
Researchers discover new way to store hydrogen using lignin jet fuel
2025-01-27
An international team of scientists has discovered a way to store and release volatile hydrogen using lignin-based jet fuel that could open new pathways for sustainable energy production.
In a new study in the International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Washington State University Professor Bin Yang and colleagues demonstrated that a type of lignin-based jet fuel they developed can chemically bind hydrogen in a stable liquid form. The research has many potential applications in fuels and transportation and could ultimately make it easier to harness ...
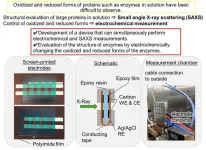
Electrochemical x-ray scattering unlocks secrets of redox enzymes
2025-01-27
Redox enzymes are proteins that catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions, which involve the transfer of electrons between molecules. Redox enzymes are crucial in bioelectrochemical devices, such as biosensors or biofuel cells. For instance, biosensors catalyze reactions that convert biochemical signals into measurable electrical signals, enabling the detection of substances like glucose. In biofuel cells, redox enzymes convert biological energy into electricity, powering small devices like medical implants. Their ability to facilitate the efficient transfer of electrons between molecules makes them indispensable ...
Unveiling Japan's geological history through volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits
2025-01-27
The Earth’s surface is constantly reshaped by the movement of tectonic plates, which make up the continental crust on which we are living. These tectonic plates are in continuous motion, and when one plate is pushed under another, it is called “subduction.” These processes play a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s landmasses, including the islands of Japan, over several hundred million years. Studying ancient mineral deposits offers a valuable way to uncover the timing of these events. However, determining the precise timing of these tectonic events has ...
Unraveling the connection between Canadian wildfires and arctic ice clouds
2025-01-27
Clouds, composed of tiny water droplets or ice crystals, play a vital role in regulating Earth’s climate by influencing the amount of solar radiation that reaches the surface. The cloud phase significantly impacts the surface energy balance as liquid water clouds reflect more radiation than ice clouds. Ice clouds typically form at temperatures below −38°C, but recent observations indicate their formation at higher temperatures in the Arctic. This phenomenon is facilitated by ice-nucleating particles (INPs), including mineral dust, organic aerosols and bioaerosols, which promote ice cloud formation above the usual freezing ...
Delayed REM sleep could be an early sign of Alzheimer’s
2025-01-27
Scientists have recently shown that both the quality and the amount of sleep we get may influence our risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
Now, a study suggests that people who take significantly longer to start the dream phase of sleep, known as rapid eye movement (REM), may be experiencing an early symptom of the disease.
REM follows three phases of non-REM sleep, each deeper than the last. The four phases take 90 minutes or more to complete, depending on age, and a person may cycle through them four or five times in a typical night. Older people take longer to reach REM.
During REM sleep the brain processes memories, ...
Weight-loss surgery lowers risk of developing complications of liver disease in patients with cirrhosis and obesity
2025-01-27
Weight-Loss Surgery Lowers Risk of Developing Complications of Liver Disease in Patients with Cirrhosis and Obesity
SPECCIAL study suggests bariatric surgery favorably influences progression of cirrhosis
UNDER EMBARGO Monday, January 27, 2025, at 05:00 AM (US Eastern Time) CLEVELAND: A Cleveland Clinic study shows that patients with obesity and fatty liver-related cirrhosis who had bariatric (weight-loss) surgery significantly lowered their future risk of developing serious ...
Heart disease remains leading cause of death as key health risk factors continue to rise
2025-01-27
Highlights:
According to the American Heart Association’s 2025 Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics Update, heart disease remains the leading cause of death in the U.S.
While medical advances have helped more people live longer with cardiovascular diseases, many of the risk factors which lead to these diseases, including high blood pressure and obesity, continue to grow at alarming rates.
Cardiovascular diseases, including heart disease and stroke, claim more lives in the U.S. than all forms of cancer and accidental deaths – the #2 and #3 causes of death – combined.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT / 5 a.m. ET Monday, Jan. 27, 2025
DALLAS, Jan. 27, 2025 — Heart ...
Preterm babies receive insufficient pain management
2025-01-27
A large proportion of babies born very early need intensive care, which can be painful. But the healthcare system fails to provide pain relief to the full extent. This is shown by the largest survey to date of pain in neonatal care, now published in the journal Pain.
Every day for 4.5 years, neonatal care staff have recorded the occurrence of pain, the causes of pain, and how pain is assessed and treated in premature babies in Sweden. The study covers 3,686 babies born between 22 and 31 weeks of gestation from 2020 to 2024. The total observation time was just over 185,000 days of care. Data were collected in the Swedish ...
Does historic redlining—a form of structural racism—affect survival in young people with cancer?
2025-01-27
A recent study indicates that children and young adults with cancer face an elevated risk of dying if they live in previously redlined neighborhoods—residential areas marked in the 1920s–1930s by lenders as undesirable for mortgage loans due to their racial demographics. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Historic redlining prevented Black households and other communities of color from accessing home mortgages for many years, leading to economic disadvantage and racial ...
How animal poop helps ecosystems adapt to climate change
2025-01-27
Climate change is melting away glaciers around the world, but in the Andes Mountains, a wild relative of the llama is helping local ecosystems adapt to these changes by dropping big piles of dung.
This finding, published Dec 30 in Scientific Reports, revealed that the activity of this animal could accelerate the time plants usually take to establish on new land by over a century, highlighting a surprising way organisms are adapting to climate change.
“It’s interesting to see how a social behavior of these animals ...
Over 1/3 of parents say their child has experienced dental problems that reflect oral hygiene habits
2025-01-27
More than one in three parents say their child has faced issues like tooth decay, cavities, stained teeth, gum concerns or tooth pain over the past two years, a national poll suggests.
And these problems were linked to children’s oral care routine, more commonly experienced among those who skipped dental hygiene recommendations or followed them less often, according to the University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health.
“Maintaining oral health from a young age, including regular brushing ...
Colorado’s parental notification law can impede adolescent access to abortion, study says
2025-01-27
AURORA, Colo. (Jan. 27, 2025) – A new study led by researchers from the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus has shed light on the burdens parental involvement laws impose on adolescents seeking abortion care, even in states like Colorado where abortion is protected. Researchers say these laws contribute to logistical barriers, heightened stress and delays in accessing care, disproportionately impacting vulnerable populations.
The study, published today in the Journal of Adolescent Health, analyzed the experiences of adolescents (ages 15-17) and young adults (18-22) who either sought or ...
Drones could be the ‘magic tools’ we need to chase bears away from people
2025-01-27
Brown bears roam across much of the northern hemisphere from the mountains of Spain to the prairies of the US. These bears are formidable carnivores that can weigh up to 751 kg (1,656 lb) and have claws 15 cm (6 in) long. With long canine teeth and a bite force of 6,800,000 pascals (1,000 psi), these bruins can easily crush bones. All these powerful features make brown bears an imposing predator that can take down prey as large and dangerous as an adult bison. Yet, while these bears eat meat, much of their diet is plant-based because they are omnivores. Brown bears have very few dietary restrictions. They are certainly not gluten intolerant ...
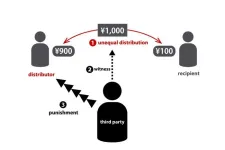
Rethinking altruistic punishment: New experimental insights
2025-01-27
How would you react if someone cut in line behind you? Some people will warn others to follow the rules, even if it does not affect them. This is known as altruistic punishment, the act of punishing others for selfish behavior without reciprocal benefit.
Previous studies on altruistic punishment often placed participants in unnatural settings where they were compelled to observe the selfishness of others and decided whether to punish them. In reality, there are times when avoidance of such a situation takes precedence over confronting unfairness. In other words, a person could pretend they did ...
Move more, age well: Prescribing physical activity for older adults as a recipe for healthy aging
2025-01-27
Can physical activity extend the lifespans of older adults? A review article published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231336 summarizes the considerable evidence supporting the important role physical activity plays in preventing or reducing the effects of diseases and discusses how to prescribe effective exercise for older adults.
Canada’s population is aging, with at least 1 in 5 people aged 65 years or older in 2025, and the number of people older than age 85 years is expected to triple in the next 20 years. However, for many people, ...
Botanic Gardens must team up to save wild plants from extinction
2025-01-27
A major study of botanic gardens around the world has revealed their struggles with one fundamental aim: to safeguard the world’s most threatened plants from extinction.
Researchers analysed a century’s worth of records - from 1921 to 2021 - from fifty botanic gardens and arboreta currently growing half a million plants, to see how the world’s living plant collections have changed over time.
The results suggest that the world’s living collections have collectively reached peak capacity, and that restrictions ...
Approaching the red planet from the kitchen
2025-01-27
Niigata, Japan - Rootless cones are small volcanic landforms ranging from several to several hundred meters in diameter, formed by continuous explosions resulting from the interaction between surface lava and water bodies like lakes and rivers (Figure 1). Unlike regular volcanoes originating from magma rising from deep underground, rootless cones form when lava covers a water-containing layer, triggering explosive reactions. Due to this process, they are also called pseudocraters. While Iceland hosts many rootless cones, they ...
How Camellias evolved with the formation of the Japanese archipelago?
2025-01-27
Niigata, Japan – The distribution of plants has been shaped by geological and climatic changes over time through repeated migration, extinction, and adaptation to new environments. The genus Camellia, comprising over 100 species mainly in East Asia, is a representative warm-temperate tree of the Sino-Japanese Floristic Region.
In Japan, four species of Camellia are found, with Camellia japonica and Camellia rusticana being the most well known. C. japonica has a broad distribution from Aomori Prefecture in the cool-temperate ...
Study succeeds in the early diagnosis of leptomeningeal disease in diffuse midline gliomas by liquid biopsy
2025-01-27
Niigata, Japan – A group led by the Department of Neurosurgery, Brain Research Institute, Niigata University succeeded in the diagnosis of leptomeningeal disease in diffuse midline gliomas by detecting H3K27M-mutant droplets from circulating tumor DNA of cerebrospinal fluid taken from these patients. In two patients, leptomeningeal disease was diagnosed earlier than with traditional methods such as MRI and cerebrospinal fluid cytology. In one patient, long term survival after the diagnosis of leptomeningeal disease by early ...
Understanding the science of meaty flavors could be key to sustainable diets, says academic
2025-01-27
Understanding the science behind meaty tastes and textures could be the key for more people switch to a planet-friendly plant diet, researchers suggest.
Ole G. Mouritsen, a professor of gastrophysics, addresses the urgent need to make changes to culinary cultures where animal-based proteins play a central role.
Replicating a little-known meaty flavour and a sensation of richness could encourage more plant-based eating, he explains.
“To ensure that there is enough food for a growing world population, to lessen the burden on the environment, and to promote healthier, sustainable eating patterns, it ...
Patients who received Ross procedure demonstrate excellent survival rates after 20 years
2025-01-26
LOS ANGELES —January 26, 2024 — Young patients who have undergone the Ross procedure for aortic valve disease have shown excellent long-term survival, the majority without the need for additional surgery two decades later.
These findings, presented today at the 61st annual meeting of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS), were the result of a 22-year study at the Narayana Institute of Cardiac Sciences in Bengaluru, India.
“The Ross operation can be performed safely with results comparable to mechanical valve replacement,” said the study’s lead author, cardiac surgeon ...
Lung volume reduction surgery for emphysema may have better outcomes than previously reported
2025-01-26
LOS ANGELES—January 26, 2025—As contemporary surgical practice continues to evolve, patients who undergo surgical lung volume reduction (LVRS) for advanced emphysema may survive longer and with fewer complications than they did in the past—and they may even fare better than those who opt for endobronchial valve (EBV) placement.
At the 2025 Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) Annual Meeting, researchers presented risk-adjusted findings that shed new light on treatments for severe emphysema. Despite having shorter hospital stays, lower hospital ...
[1] ... [707]
[708]
[709]
[710]
[711]
[712]
[713]
[714]
715
[716]
[717]
[718]
[719]
[720]
[721]
[722]
[723]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.