Women exercising in gyms often face barriers including body image and harassment
2025-01-29
When exercising in gyms, women face barriers across various domains, including physical appearance and body image, gym attire, the physical gym environment, and interactions with others, according to a study published January 29, 2025, in the open-access journal PLOS One by Emma Cowley from the SHE Research Centre, TUS, Ireland, and Jekaterina Schneider from the University of the West of England, U.K.
Exercise significantly improves physical, mental, and psychosocial health. Recent research indicates that women who engage in regular exercise experience greater health benefits than men, including lower incidence of all-cause mortality and reduced ...
SNU researchers apply the principles of mantis shrimp and fleas to create soft robots with powerful movements
2025-01-29
Seoul National University College of Engineering announced that a research team led by Professor Kyu-Jin Cho (Director of the Soft Robotics Research Center) from the Department of Mechanical Engineering took inspiration from principles found in nature and developed the "Hyperelastic Torque Reversal Mechanism (HeTRM)," which enables robots made from rubber-like soft materials to perform rapid and powerful movements. This study was published in the prestigious international journal Science Robotics on January 29.
The mantis shrimp delivers a punch ...
Quantum-inspired computing drives major advance in simulating turbulence
2025-01-29
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 19:00 GMT / 14:00 ET, WEDNESDAY 29 JANUARY 2025
Quantum-inspired computing drives major advance in simulating turbulence
Researchers at the University of Oxford have pioneered a new approach to simulate turbulent systems, based on probabilities. The findings have been published today (29 January) in the journal Science Advances.
Predicting the dynamics of turbulent fluid flows has long been a central goal for scientists and engineers. Yet, even with modern computing technology, direct and accurate simulation of all but the simplest turbulent flows remains impossible.
This is due to turbulence being ...
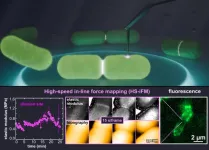
New microscopy technique reveals dynamic Escherichia coli membrane stiffness
2025-01-29
Light and electron microscopy have distinct limitations. Light microscopy makes it difficult to resolve smaller and smaller features, and electron microscopy resolves small structures, but samples must be meticulously prepared, killing any live specimens.
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is a technique originally developed to assess the physical and mechanical properties of materials at extremely high resolutions, but the imaging speeds aren’t fast enough (e.g. several minutes per frame) to capture relevant data for living biological samples. In contrast, another method, high-speed AFM (HS-AFM), is fast but cannot measure mechanical properties. Understanding ...
Bad hair bears! Greasy hair gives polar bears fur with anti-icing properties
2025-01-29
An international team of scientists has discovered the anti-icing secret of polar bear fur – something that allows one of the planet’s most iconic animals to survive and thrive in one of its most punishing climates. That secret? Greasy hair.
After some polar sleuthing, which involved scrutiny of hair collected from six polar bears in the wild, the scientists homed in on the hair “sebum” (or grease) as the all-important protectant. This sebum, which is made up of cholesterol, diacylglycerols, and fatty acids, makes it very hard for ice to attach to their fur.
While this finding ...
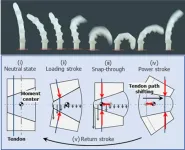
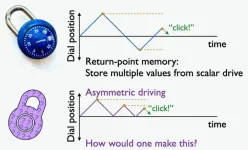
Materials can remember a sequence of events in an unexpected way
2025-01-29
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Many materials store information about what has happened to them in a sort of material memory, like wrinkles on a once crumpled piece of paper. Now, a team led by Penn State physicists has uncovered how, under specific conditions, some materials seemingly violate underlying mathematics to store memories about the sequence of previous deformations. According to the researchers, the method, described in a paper appearing today (Jan. 29) in the journal Science Advances, could inspire new ways to store information in ...
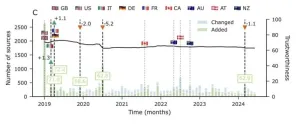
NewsGuard: Study finds no bias against conservative news outlets
2025-01-29
[Vienna, 29.01.2025]—A recent study evaluating the NewsGuard database, a leading media reliability rating service, has found no evidence supporting the allegation that NewsGuard is biased against conservative news outlets. Actually, the results suggest it’s unlikely that NewsGuard has an inherent bias in how it selects or rates right-leaning sources in the US, where trustworthiness is especially low.
“It seems unlikely that NewsGuard has an inherent bias against conservative sources, both in selecting and giving them lower ratings. Instead, the US media system is flooded with right-wing sources that tend to not adhere to professional ...
New tool can detect fast-spreading SARS-COV-2 variants before they take off
2025-01-29
By analysing millions of viral genome sequences from around the world, a team of scientists, led by the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute) and the University of Pittsburgh, uncovered the specific mutations that give SARS-CoV-2 a ‘turbo boost’ in its ability to spread.
“Among thousands of SARS-CoV-2 mutations, we identified a small number that increase the virus’ ability to spread,” said Professor Matthew McKay, a Laboratory Head at the Doherty Institute and ARC Future Fellow in the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering at the University of Melbourne, and co-lead author of the ...
Berkeley Lab helps explore mysteries of Asteroid Bennu
2025-01-29
During the past year, there’s been an unusual set of samples at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab): material gathered from the 4.5-billion-year-old asteroid Bennu when it was roughly 200 million miles from Earth.
Berkeley Lab is one of more than 40 institutions investigating Bennu’s chemical makeup to better understand how our solar system and planets evolved. In a new study published today in the journal Nature, researchers found evidence that Bennu comes from an ancient wet world, with some material from the coldest regions of the solar system, likely beyond the orbit of ...
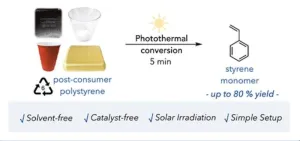
Princeton Chem discovers that common plastic pigment promotes depolymerization
2025-01-29
It turns out that the black plastic lid atop your coffee cup has a superpower. And the Stache Lab at Princeton Chemistry, which uncovered it, is exploiting that property to recycle at least two major types of plastic.
Their startling mechanism for promoting depolymerization relies on an additive that many plastics already contain: a pigment called carbon black that gives plastic its black color. Through a process called photothermal conversion, intense light is focused on plastic containing the pigment that jumpstarts the degradation.
So far, researchers have shown that carbon black can depolymerize polystyrene and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), two of the least recycled plastics in the planet’s ...
AI-driven multi-modal framework revolutionizes protein editing for scientific and medical breakthroughs
2025-01-29
Researchers from Zhejiang University and HKUST (Guangzhou) have developed a cutting-edge AI model, ProtET, that leverages multi-modal learning to enable controllable protein editing through text-based instructions. This innovative approach, published in Health Data Science, bridges the gap between biological language and protein sequence manipulation, enhancing functional protein design across domains like enzyme activity, stability, and antibody binding.
Proteins are the cornerstone of biological functions, and their precise modification holds immense potential for medical therapies, synthetic biology, and biotechnology. While traditional protein editing methods ...
Traces of ancient brine discovered on the asteroid Bennu contain minerals crucial to life
2025-01-29
A new analysis of samples from the asteroid Bennu, NASA’s first asteroid sample captured in space and delivered to Earth, reveals that evaporated water left a briny broth where salts and minerals allowed the elemental ingredients of life to intermingle and create more complex structures. The discovery suggests that extraterrestrial brines provided a crucial setting for the development of organic compounds.
In a paper published today, Jan. 29, in the journal Nature, scientists at the Smithsonian’s National Museum ...
Most mental health crisis services did not increase following 988 crisis hotline launch
2025-01-29
The launch of the nation’s 988 mental health hotline did not coincide with significant and equitable growth in the availability of most crisis services, except for a small increase in peer support services, according to a new RAND study.
Examining reports from thousands of mental health treatment facilities about the types of crisis services offered before and after the July 2022 rollout of the 988 hotline, researchers found that there was an increase in peer support services, a significant decrease in psychiatric walk-in services, and small declines in mobile crisis response and suicide prevention services.
Significant ...
D-CARE study finds no differences between dementia care approaches on patient behavioral symptoms or caregiver strain
2025-01-29
New research comparing different approaches to dementia care for people with Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias found no significant differences in patient behavioral symptoms or caregiver strain, whether delivered through a health system, provided by a community-based organization, or as usual care over an 18-month period.
However, the Dementia Care Study, also known as D-CARE, also found that caregiver self-efficacy—a measurement of caregivers’ confidence in managing dementia-related challenges and accessing support — improved in both the health-system and community-based ...
Landmark genetic study: Fresh shoots of hope on the tree of life
2025-01-29
In the most comprehensive global analysis of genetic diversity ever undertaken, an international team of scientists has found that the genetic diversity is being lost across the globe but that conservation efforts are helping to safeguard species.
The landmark study, published in the pre-eminent scientific journal Nature, was led by Associate Professor Catherine Grueber from the School of Life and Environmental Sciences and a team of researchers from countries including the UK, Sweden, Poland, Spain, Greece and China.
The data spans more than three decades (from 1985-2019) and looks at 628 species of animals, plants and fungi across all terrestrial ...
Discovery of a unique drainage and irrigation system that gave way to the “Neolithic Revolution” in the Amazon
2025-01-29
A pre-Columbian society in the Amazon developed a sophisticated agricultural engineering system that allowed them to produce maize throughout the year, according to a recent discovery by a team of researchers from the Institute of Environmental Science and Technology (ICTA-UAB) and the Department of Prehistory at the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, (Spain); the Universities of Exeter, Nottingham, Oxford, Reading and Southampton (UK); the University of São Paulo (Brazil) and Bolivian collaborators. This finding contradicts previous theories that dismissed the possibility of intensive monoculture agriculture in the region.
The study, published today ...
Racial and ethnic disparities in pediatric counseling on nutrition, lifestyle, and weight
2025-01-29
About The Study: This secondary analysis of the BP-CATCH trial found that among children with high blood pressure measurements, racial and ethnic disparities in receiving nutrition, lifestyle, and all 3 counseling topics were significant, although no significant disparities in receipt of weight counseling were noted. Racial disparities in receipt of counseling were not observed in participants with and without obesity.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Moonseong Heo, PhD, email mheo@clemson.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.56238)
Editor’s ...
Longitudinal analysis of obesity drug use and public awareness
2025-01-29
About The Study: This repeated cross-sectional study including 69.2 million obesity management drug dispensed prescriptions revealed an increase from 0.76 million in July 2017 to 1.5 million in February 2024, with an upward trend in monthly phentermine and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist prescriptions. There was a robust positive correlation between public online search activity for semaglutide and tirzepatide and their prescription trends. The joint surge in prescriptions and online searches ...
Mental health disparities by sexual orientation and gender identity in the All of Us Research Program
2025-01-29
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study of participants in the All of Us Research Program, there were significant mental health disparities between participants in sexual and gender minority (SGM) and cisgender heterosexual (non-SGM) groups. These findings underscore the need for tailored mental health interventions to improve the well-being of SGM populations, while noting that the associations do not imply causality but reflect the stigma and minority stress experienced by these individuals.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Marvin E. Langston, PhD, email marvlang@stanford.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Research contrasts drought sensitivity of Eurasian and North American grasslands
2025-01-29
EMBARGO: THIST CONTENT IS UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 11 AM U.S. EASTERN STANDARD TIME ON JANUARY 29, 2025. INTERESTED MEDIA MAY RECIVE A PREVIEW COPY OF THE JOURNAL ARTICLE IN ADVANCE OF THAT DATE OR CONDUCT INTERVIEWS, BUT THE INFORMATION MAY NOT BE PUBLISHED, BROADCAST, OR POSTED ONLINE UNTIL AFTER THE RELEASE WINDOW.
Grasslands in Asia and North America differ in their responses to drought, according to a new paper in the journal Nature led by faculty at Colorado State University. The findings show that differences in the dominant grasses and lower species diversity in the Eurasian Steppe grasslands may make it more vulnerable to drought ...
Life’s building blocks in Bennu samples
2025-01-29
Japanese collaborators detected all five nucleobases — building blocks of DNA and RNA — in samples returned from asteroid Bennu by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission.
Asteroids, small airless bodies within the inner Solar System, are theorized to have contributed water and chemical building blocks of life to Earth billions of years ago. Although meteorites on Earth come from asteroids, the combination of exposure to moisture in the atmosphere and to an uncontrolled biosphere means that interpreting the data from them is challenging. Pristine samples collected from asteroids in space would be the ideal candidates, and successful sample ...
Pairing old and new technologies could unlock advances in plankton science
2025-01-29
Advances in technology – such as microscopic imaging and molecular techniques – have the potential to transform our understanding of global ocean health, according to the authors of a new study.
However, they should not be employed at the expense of long-term plankton monitoring programmes, which continue to provide an essential role in tracking how our seas are shifting in the face of a changing global climate and are essential for informing routine assessments of marine biodiversity required by ...
Pristine asteroid samples reveal secrets of the ancient solar system
2025-01-29
Curtin University researchers have gained an unprecedented glimpse into the early history of our solar system through some of the most well-preserved asteroid samples ever collected, potentially transforming our understanding of planetary formation and the origins of life.
Experts from Curtin’s School of Earth and Planetary Sciences were selected to be amongst the first in the world to inspect samples collected during NASA’s seven-year, OSIRIS-REx mission to the ancient asteroid Bennu.
Asteroid Bennu is thought to be made of rubble fragments from a 4.5-billion-year-old parent body, containing materials that originated ...
ISarcoPRM algorithm: advancing global sarcopenia diagnosis
2025-01-29
“One of the most commonly used diagnostic methods, appendicular lean mass (ALM) measured by dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) has been reported to fail to precisely detect age-related loss of muscle mass […]”
BUFFALO, NY- January 29, 2025 – A new editorial was published in Volume 16, Issue 22 of Aging (Aging-US) on December 11, 2024, titled “ISarcoPRM algorithm for global operationalization of sarcopenia diagnosis.”
In this editorial, Pelin ...
Pathogenic variants in retinoblastoma suggest a potential gain-of-function mutation
2025-01-29
“In other words, the pR552* mutant behaves more like a gain-of-function or oncogenic mutant. Indeed, a family carrying this mutation showed complete penetrance and high expressivity.”
BUFFALO, NY- January 29, 2025 – A new research paper was published in Volume 16 of Genes & Cancer on January 20, 2025, entitled, “Analysis of pathogenic variants in retinoblastoma reveals a potential gain of function mutation.”
Researchers from Instituto de Física Universidad Autónoma de San Luis Potosí and Hospital Central “Ignacio Morones Prieto” have found a new way a gene mutation might contribute ...
[1] ... [701]
[702]
[703]
[704]
[705]
[706]
[707]
[708]
709
[710]
[711]
[712]
[713]
[714]
[715]
[716]
[717]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.