AAAS enters pilot with ProRata to bolster standards for transparency and reliability in AI searches
2025-01-29
The American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS), the nonprofit publisher of the Science family of journals, is conducting a pilot with ProRata as part of its commitment to communicate trusted scientific findings broadly. ProRata is an AI company guided by the belief that content creators should receive attribution for their work. Partnering with AAAS will strengthen ProRata’s new AI-driven search engine, Gist.ai, while showing how content that powers AI-driven searches can be sustainably attributed.
The pilot – ProRata’s first with a scientific publisher – ...
Improving the way flash memory is made
2025-01-29
To store ever more data in electronic devices of the same size, the manufacturing processes for these devices need to be studied in greater detail. By investigating new approaches to making digital memory at the atomic scale, researchers engaged in a public-private partnership are aiming to address the endless demand for denser data storage.
One such effort has focused on developing the ideal manufacturing process for a type of digital memory known as 3D NAND flash memory, which stacks data vertically to increase storage density. The narrow, deep holes required for this type of memory can be etched ...
NFL PLAY 60 Fitness Break broadcast delivers movement minutes in advance of Super Bowl LIX
2025-01-29
DALLAS, Jan. 29, 2025 — The American Heart Association, a global force changing the future of health for all, and the National Football League (NFL), in collaboration with its 32 NFL clubs, are challenging kids to get moving and PLAY 60 in advance of Super Bowl LIX with the latest installment of the NFL PLAY 60 Fitness Break school broadcast series. On Thursday, Feb. 5 at 1 p.m. ET/ 12 p.m. CT/ 10 a.m. PT the Association and the NFL will deliver an action-packed, 15-minute synchronous streaming broadcast to help elementary school students ...
Blood-powered toes give salamanders an arboreal edge
2025-01-29
PULLMAN, Wash. — Wandering salamanders are known for gliding high through the canopies of coastal redwood forests, but how the small amphibians stick their landing and take-off with ease remains something of a mystery.
A new study in the Journal of Morphology reveals the answer may have a lot to do with a surprising mechanism: blood-powered toes. The Washington State University-led research team discovered that wandering salamanders (Aneides vagrans) can rapidly fill, trap, and drain the blood in their toe tips to optimize attachment, detachment and general locomotion through their arboreal environment.
The research not only uncovers a previously ...
Better nurse staffing linked to fewer C-sections
2025-01-29
Labor and delivery units that are adequately staffed by nurses have lower cesarean birth rates, according to new research published in the journal Nursing Outlook.
“Our findings highlight how crucial nurse staffing is for optimal maternal outcomes,” said Audrey Lyndon, the Vernice D. Ferguson Professor in Health Equity and executive vice dean at NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing.
C-sections account for nearly a third of births in the US and are the most common surgery performed in hospitals. While C-sections can be lifesaving and some are necessary for the health of the mother and child, the surgery carries more risks and a longer recovery ...
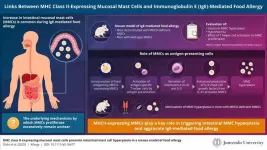
Role of specialized mucosal mast cells in IgE-mediated food allergy
2025-01-29
Food allergy, or the aggressive immune system reaction following the consumption of a certain food or food ingredient, typically involves immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies and can be potentially life-threatening. Often, the immune response to a food protein can be rapid and severe, requiring emergency care. In recent years, scientific studies have revealed that mucosal mast cells (MMCs), which are immune cells that arise from bone marrow, are excessively produced and play a key role in the severity and sudden onset ...
Study reveals how microbes help detoxify our atmosphere
2025-01-29
Melbourne researchers have discovered crucial new information about how microbes consume huge amounts of carbon monoxide (CO) and help reduce levels of this deadly gas.
Over two billion tonnes of carbon monoxide are released into the atmosphere globally each year. Microbes consume about 250 million tonnes of this, reducing CO to safer levels.
The Monash University-led Study, published in Nature Chemical Biology, reveals at an atomic level how microbes consume CO present in the atmosphere. They use a special enzyme, called the CO dehydrogenase, ...
White blood cell count could predict severity of COVID-19 symptoms
2025-01-29
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Jan 29, 2025)—Thanks to advances in treatment options, a COVID-19 diagnosis is no longer as scary as it once was, at least for most people. A new study, however, suggests that it may now be easier to predict who is most likely to suffer with more serious disease symptoms based on leukocyte (white blood cell) count. Results of the study are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The Menopause Society.
Millions of people worldwide suffer from the ongoing effects of COVID-19—which is caused by the SARs-CoV-2 ...
Moderate exercise keeps appetite at bay
2025-01-29
A recent study involving researchers at Murdoch University’s Health Futures Institute has revealed that moderate-intensity exercise can significantly influence appetite-related hormones and perceptions in males with obesity.
The study, titled “Acute effect of exercise on appetite-related factors in males with obesity,” provides new insights into how exercise can aid appetite control and weight management.
One of the study authors, Associate Professor Timothy Fairchild from Murdoch’s School ...
Cancer drugs linked to severe chronic peripheral nerve pain for 4 in every 10 patients
2025-01-29
Worldwide, cancer chemotherapy is linked to persistent severe peripheral nerve pain (neuropathy) for around 4 in every 10 patients treated with these drugs, suggests a pooled data analysis of the available evidence, published in the open access journal Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine.
Notwithstanding wide regional variations, platinum based drugs, taxanes, and lung cancer seem to be associated with the highest rates of persistent painful neuropathy, lasting at least 3 months, the findings suggest, prompting the researchers to call for tailored approaches to pain ...
Lack of essential vitamins and minerals common in people with type 2 diabetes
2025-01-29
Micronutrient deficiency, whereby levels of vitamins and minerals essential for healthy bodily function are far too low, is common in people with type 2 diabetes, finds a pooled data analysis of the available evidence, published in the open access journal BMJ Nutrition Prevention & Health.
A lack of vitamin D is the most common ‘missing’ micronutrient, overall, the findings indicate, with women at greater risk than men of these deficiencies, dubbed 'hidden hunger.'
Genetic predisposition, various environmental factors, sedentary ...
Calorie labels on menus could make eating disorders worse
2025-01-29
Calorie labels on restaurant menus are negatively impacting people with eating disorders, according to a new study published today in the BMJ Public Health.
The review, which is the first of its kind, is led by researchers at King’s College London. It found that individuals who have been diagnosed with an eating disorder changed their behaviours if presented with a menu featuring calorie labels.
This included avoiding restaurants, triggering eating disorder thoughts and paying more attention to calorie labels as identified by eye tracking research.
The research found that some people with eating disorders reported that seeing menu labels reinforced ...
Artificial intelligence model identifies potential risk genes for Parkinson’s disease
2025-01-28
Researchers from the Cleveland Clinic Genome Center have successfully applied advanced artificial intelligence (AI) genetics models to Parkinson’s disease. Researchers identified genetic factors in progression and FDA-approved drugs that can potentially be repurposed for PD treatment.
The npj Parkinson’s Disease report uses an approach called “systems biology,” which uses AI to integrate and analyze multiple different forms of information from genetic, proteomic, pharmaceutical and patient datasets to identify patterns that may not be obvious from analyzing ...
A new register with thousands of entangled nuclei to scale quantum networks
2025-01-28
In a groundbreaking achievement for quantum technologies, researchers at the Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge, have created a functional quantum register using the atoms inside a semiconductor quantum dot.
Published in Nature Physics, the work demonstrates the introduction of a new type of optically connected qubits—a critical advance in the development of quantum networks, where stable, scalable, and versatile quantum nodes are essential.
Quantum dots are nanoscale objects with unique optical and electronic properties that come from quantum mechanical effects. These systems are already used in technologies ...
New avenues in quantum research: supramolecular qubit candidates detected
2025-01-28
Qubits are the basic building blocks of information processing in quantum technology. An important research question is what material they will actually consist of in technical applications. Molecular spin qubits are considered promising qubit candidates for molecular spintronics, in particular for quantum sensing. The materials studied here can be stimulated by light; this creates a second spin centre and, subsequently, a light-induced quartet state. Until now, research has assumed that the interaction between two spin centres can only be strong enough for ...
2024 ISS National Lab Annual Report highlights momentum in space-based R&D
2025-01-28
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER (FL), January 28, 2025 – The International Space Station (ISS) National Laboratory highlighted the rapid growth of space-based R&D in its annual report, released today by the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space® (CASIS®). Over the past fiscal year, the ISS National Lab sponsored more than 100 payloads delivered to the orbiting laboratory—the second-highest annual total to date. Also this year, ISS National Lab-related results were published in 51 peer-reviewed articles—the most ever in a year—underscoring the vital role of the ISS National Lab in advancing scientific discovery and innovation.
Since 2011, ...
New clues to the mechanism behind food tolerance and allergies
2025-01-28
With every bite of food we take, our intestinal immune system must make a big decision. Tasked with defending us from foreign pathogens, these exquisitely sensitive cells somehow distinguish friend from foe—destroying invaders while tolerating food and helpful bacteria. How the gut separates the good from the bad has long puzzled scientists.
Now, new research identifies specific gut cell types that communicate with T cells—prompting them to tolerate, attack, or simply ignore—and explains how these opposing responses are triggered. The findings, published in Science, give scientists ...
Leveraging artificial intelligence for vaccine development: A Ragon-MIT advancement in T cell epitope prediction
2025-01-28
Cambridge, Mass.— An exciting collaboration between the Ragon Institute and the Jameel Clinic at MIT has achieved a significant milestone in leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to aid the development of T cell vaccine candidates.
Ragon faculty member Gaurav Gaiha, MD, DPhil, and MIT Professor Regina Barzilay, PhD, AI lead of the Jameel Clinic for AI and Health, have published research in Nature Machine Intelligence introducing MUNIS—a deep learning tool designed to predict CD8+ T cell epitopes with unprecedented accuracy. This advancement has the potential to accelerate vaccine development against various ...
Moffitt Research advocates for routine brain MRI screening in asymptomatic late stage breast cancer patients
2025-01-28
TAMPA, Fla. (Jan. 28, 2025) — A new study led by researchers at Moffitt Cancer Center shows that asymptomatic brain metastasis is more common in stage 4 breast cancer patients than previously believed. The study, published in Neuro-Oncology, suggests that doctors may need to rethink current screening guidelines for detecting brain metastasis in patients without symptoms.
Researchers examined 101 asymptomatic patients diagnosed with stage 4 breast cancer, including triple-negative, HER2-positive and hormone receptor-positive/HER2-negative ...
More primary care physicians are affiliated with hospitals, leading to increased patient costs
2025-01-28
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — A study by researchers at the Brown University School of Public Health shows that nearly half of all primary care providers (PCPs) in the United States are affiliated with hospitals, while the number of PCPs affiliated with private equity firms is growing and concentrated in certain regional markets.
Compared with PCPs at independent practices, those affiliated with hospitals or private equity firms charged higher prices for the same services.
The findings were published in JAMA Health Forum.
Health care consolidation is a driving force behind ...
Can you really have it all? New study reveals how to succeed at work without sacrificing your free time
2025-01-28
New INFORMS Organization Science Study Key Takeaways:
Integrating work-related learning into leisure activities can enhance confidence, build new skills and support professional growth.
Leisure-work synergizing is most effective for individuals who prefer blending work and personal life rather than keeping them separate.
Overdoing leisure-work synergizing may lead to fatigue, emphasizing the importance of balance to maintain its benefits.
BALTIMORE, MD, January 28, 2025 – Could your favorite hobbies help you get ahead at work? New research published in the INFORMS journal Organization Science explores “leisure-work ...
Western Kenyan farmers favor restoring land with native trees. Yet barriers remain
2025-01-28
African nations have grand ambitions to green up landscapes with trees; the Kenyan government, for example, launched an initiative to plant 15 billion trees by 2032. The hope is that new trees could help fight desertification, create opportunities for livelihood diversification, support nutritional diets, restore biodiversity in highly degraded land and capture planet-heating carbon. Restoring lands using trees could empower millions whose livelihoods depend on working the land while generating multiple environmental and social benefits.
Yet tree planting projects often fall short because ...
Inherited gene elevates prostate cancer risk in affected families
2025-01-28
A study of men with a family history of prostate cancer has discovered an inherited form of prostate cancer.
The inherited mutated gene WNT9B, which functions normally in embryonic prostate development, increases risk of adult prostate cancer, according to the Vanderbilt University Medical Center study published in JCO Precision Oncology.
This discovery was replicated in five independent study populations collectively encompassing one-half million patients from the U.S. and Europe, with the increased prostate cancer risk estimates ranging from two- to 12-fold, according to lead author Jeffrey Smith, MD, PhD, associate ...
Rice SynthX and MD Anderson team awarded Kleberg medical grant for brain metastasis research
2025-01-28
Rice University chemist and director of the university’s Synthesis X Center Han Xiao and cancer biologist Dihua Yu of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have received a three-year, $1.5 million grant from the Robert J. Kleberg Jr. and Helen C. Kleberg Foundation, allowing them to do further research on overcoming the blood-brain barrier (BBB) for the treatment of brain metastasis. This hurdle blocks most cancer therapies from reaching the brain, but the scientists’ innovative approach could transform the treatment of brain ...
Microbial therapy offers new hope for vitiligo patients
2025-01-28
‘Astonishing’ findings in mice suggest microbial product could restore skin pigmentation
Offers hope for a disease that affects all skin tones, but is more visible and severe in darker skin
Vitiligo affects 0.5% to 2% of the global population
Patients available for interviews upon request
CHICAGO --- A natural compound derived from gut-friendly bacteria significantly slows the progression of vitiligo and may restore pigmentation, reports a new Northwestern University pre-clinical study in mice.
The findings could offer hope to millions affected by the autoimmune ...
[1] ... [702]
[703]
[704]
[705]
[706]
[707]
[708]
[709]
710
[711]
[712]
[713]
[714]
[715]
[716]
[717]
[718]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.