Adverse childhood experiences in firstborns associated with poor mental health of siblings
2025-02-04
Children are nearly three-quarters (71%) more likely to develop mental health problems between the ages of five and 18, if the firstborn child in their family experienced adversity during their first 1,000 days, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The first-of-its-kind study, published in The Lancet Public Health and funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research Policy Research Programme, found that mothers whose firstborns had experienced adverse childhood experiences had a 71% increased risk of having children (aged five -18) with mental health problems, compared to mothers whose firstborn did not experience adversity.
This ...
Montana State scientists publish new research on ancient life found in Yellowstone hot springs
2025-02-04
BOZEMAN – In a new publication in the journal Nature Communications, Montana State University scientists in College of Agriculture highlight fresh knowledge of how ancient microorganisms adapted from a low-oxygen prehistoric environment to the one that exists today. The work builds on more than two decades of scientific research in Yellowstone National Park by MSU professor Bill Inskeep.
The article, titled “Respiratory Processes of Early-evolved Hyperthermophiles in Sulfidic and Low-oxygen Geothermal Microbial Communities” was published Jan. 2. Authors Inskeep, a professor in the Department of Land Resources and Environmental Sciences, and Mensur ...
Generative AI bias poses risk to democratic values
2025-02-04
Generative AI, a technology that is developing at breakneck speed, may carry hidden risks that could erode public trust and democratic values, according to a study led by the University of East Anglia (UEA).
In collaboration with researchers from the Getulio Vargas Foundation (FGV) and Insper, both in Brazil, the research showed that ChatGPT exhibits biases in both text and image outputs — leaning toward left-wing political values — raising questions about fairness and accountability in its design.
The study revealed ...
Study examines how African farmers are adapting to mountain climate change
2025-02-03
A new international study highlights the severity of climate change impacts across African mountains, how farmers are adapting, and the barriers they face – findings relevant to people living in mountain regions around the world.
"Mountains are the sentinels of climate change,” said Julia Klein, a Colorado State University professor of ecosystem science and sustainability and co-author of the study. “Like the Arctic, some of the first extreme changes we're seeing are happening in mountains, from glaciers melting to extreme events. There's greater warming at higher elevations, so what's happening in mountains is foreshadowing what's going ...
Exposure to air pollution associated with more hospital admissions for lower respiratory infections
2025-02-03
Air pollution is a well-known risk factor for respiratory diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). However, its contribution to lower respiratory infections —those that affect the lower respiratory tract, including the lungs, bronchi and alveoli— is less well documented, especially in adults. To fill this gap in knowledge, a team from the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the ”la Caixa” Foundation, assessed the effect of air pollution ...
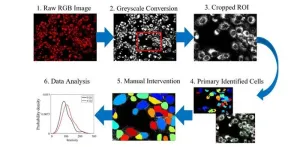
Microscopy approach offers new way to study cancer therapeutics at single-cell level
2025-02-03
Understanding how tumors change their metabolism to resist treatments is a growing focus in cancer research. As cancer cells adapt to therapies, their metabolism often shifts, which can help them survive and thrive despite medical interventions. This process, known as metabolic reprogramming, is a key factor in the development of treatment resistance. However, current methods to study these changes can be costly, complex, and often destructive to the cells being studied. Researchers at the University of Kentucky have developed a new, simpler approach to observe these metabolic shifts in cancer cells, offering a more accessible and effective tool for cancer research.
As ...
How flooding soybeans in early reproductive stages impacts yield, seed composition
2025-02-03
FAYETTEVILLE, Ark. — With an increasing frequency and intensity of flooding events and an eye to capitalize on a common rice production technique, soybean breeders are on a quest to develop varieties with flood tolerance at any stage in the plant’s development.
Farmers who use zero-grade fields for rice as their main production system are also interested in flood-tolerant soybean varieties for crop rotation, said Caio Vieira, assistant professor of soybean breeding and a researcher for the Arkansas Agricultural Experiment Station, the University of Arkansas ...
Gene therapy may be “one shot stop” for rare bone disease
2025-02-03
For the last 10 years, the only effective treatment for hypophosphatasia (HPP) has been an enzyme replacement therapy that must be delivered by injection three-to-six times each week.
“It's been a tremendous success and has proven to be a lifesaving treatment,” said José Luis Millán, PhD, professor in the Human Genetics Program at Sanford Burnham Prebys. “Many children who have been treated otherwise would have died shortly after birth, and they are now able to look forward to long lives.
“It is, however, a very invasive treatment. Some patients have reactions from frequent injections and discontinue ...
Protection for small-scale producers and the environment?
2025-02-03
Sustainability certificates such as Fairtrade, Rainforest Alliance and Cocoa Life promise to improve the livelihoods of small-scale cocoa producers while preserving the biodiversity on their plantations. Together with the European Commission's Joint Research Centre, researchers from the University of Göttingen have investigated whether sustainability certificates actually achieve both these goals. To find out, they carried out an analysis within the Ghanaian cocoa production sector. Their results show that although certification improves both cocoa yield and cocoa income for small-scale producers, they were unable to ...
Researchers solve a fluid mechanics mystery
2025-02-03
What began as a demonstration of the complexity of fluid systems became an art piece in the American Physical Society’s Gallery of Fluid Motion, and ultimately its own puzzle that the researchers just solved. Their new study is published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
“We came up with this experiment because we were having a hard time convincing people of certain effects happening for the problem of drag reduction,” said assistant
professor Paolo Luzzatto-Fegiz, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering, whose research specialties include modeling flow and investigating drag — as ...
New grant funds first-of-its-kind gene therapy to treat aggressive brain cancer
2025-02-03
The California Institute for Regenerative Medicine has awarded a $6 million grant to USC investigators pioneering a new first-of-its-kind genetic therapy for glioblastoma, a severe form of brain cancer. The treatment would be the first gene therapy for glioblastoma to use a novel, more precise delivery system that is less likely to harm non-cancerous cells.
Glioblastoma is an aggressive and fast-growing cancer originating in the brain that occurs primarily in adults and has no known cure. Patients diagnosed with this type of tumor have a five-year survival rate of just 5 percent. The cancer’s location—in the sensitive brain—combined ...
HHS external communications pause prevents critical updates on current public health threats
2025-02-03
The Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) is concerned that two weeks have passed since the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) announced a pause on mass communications and public appearances that are not directly related to emergencies or critical to preserving health. With the order remaining in effect until a new HHS secretary is confirmed, this unpredictable timeline prolongs uncertainty for both healthcare professionals and the public, and endangers the nation by hindering our ability to detect and respond to public health threats, such as avian influenza (H5N1). Public ...
New ACP guideline on migraine prevention shows no clinically important advantages for newer, expensive medications
2025-02-03
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 3 February 2025
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
New ...
Revolutionary lubricant prevents friction at high temperatures
2025-02-03
Through a multi-university collaboration, researchers at Virginia Tech have discovered a new, solid lubricating mechanism that can reduce friction in machinery at extremely high temperatures. It works well beyond the breakdown temperature of traditional solid lubricants such as graphite, and the findings were published in Nature Communications.
“This breakthrough solid-state lubricant could change how we design materials for high-tech engines, making them last longer and work better under extreme conditions,” said Rebecca Cai, associate professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and one of the ...
Do women talk more than men? It might depend on their age
2025-02-03
The stereotype that women are much more talkative than men is pervasive across many cultures, but a widely reported study by University of Arizona researchers in 2007 refuted the claim, finding that men and women speak roughly the same number of words per day – around 16,000.
A new, larger follow-up to that study paints a more nuanced picture, suggesting that women may be the chattier gender, but only during a certain period of life.
"There is a strong cross-cultural assumption that women talk a lot more than men," said ...
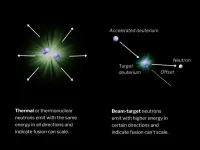
The right kind of fusion neutrons
2025-02-03
In physics, the term “isotropy” means a system where the properties are the same in all directions. For fusion, neutron energy isotropy is an important measurement that analyzes the streams of neutrons coming from the device and how uniform they are. This is critical because so-called isotropic fusion plasmas suggest a stable, thermal plasma that can be scaled to higher fusion energy gains, whereas anisotropic plasmas, those emitting irregular neutron energies, can lead to a dead end.
A new Zap research paper, published last week ...
The cost of preventing extinction of Australia’s priority species
2025-02-03
A new study has estimated it would cost $15.6 billion per year for 30 years to prevent extinction for 99 of Australia’s priority species.
The research, led by Griffith University’s Centre for Planetary Health and Food Security with WWF-Australia and the University of Queensland, highlights the urgent need for increased funding to combat threats such as habitat destruction, invasive species and climate change.
Australia has already lost more than 100 endemic species in the past three centuries, placing it at the forefront of the global extinction crisis.
The ...
JMIR Publications announces new CEO
2025-02-03
(Toronto, February 3, 2025) JMIR Publications, the leading open access publisher in digital health and open science, announced today that Sean Jeong has been appointed as its new chief executive officer (CEO), effective January 23, 2025. Dr Gunther Eysenbach, founder of JMIR Publications, will be stepping down as CEO after over two decades of transformative leadership to focus on new opportunities for innovation in academic publishing, including artificial intelligence (AI)–driven solutions and the advancement of Plan P. He will continue to serve as the editor in chief of the Journal of Medical ...
NCSA awards 17 students Fiddler Innovation Fellowships
2025-02-03
The National Center for Supercomputing Applications awarded Fiddler Innovation Fellowships to 17 University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and NCSA graduate students in a ceremony January 28 honoring the outstanding achievements and interdisciplinary contributions to NCSA programs Students Pushing Innovation (SPIN) and Design for America during the 2023-24 academic year.
The awards are part of a $2 million endowment from Jerry Fiddler and Melissa Alden to Illinois in support of student ...
How prenatal alcohol exposure affects behavior into adulthood
2025-02-03
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD), characterized by symptoms of cognitive decline, such as worsened memory and impaired decision-making, are alarmingly prevalent globally. In a new study in JNeurosci led by Amy Griffin at the University of Delaware, researchers used rats to find brain circuits that may contribute to the cognitive issues that FASD patients experience, with the end goal of informing treatment strategies. Brain regions linked with working memory and decision-making were damaged in baby rats following exposure to alcohol during the age equivalent of the third trimester ...
Does the neuron know the electrode is there?
2025-02-03
Overview:
A research group from the Institute for Research on Next-generation Semiconductor and Sensing Science (IRES²) at Toyohashi University of Technology developed an innovative in vivo electrophysiological neural recording technology that minimizes neuronal death and allows stable recordings for over a year.
This breakthrough involves a 5-µm-diameter microneedle electrode fabricated on a flexible film using silicon-growth technology. Through experiments using mice, the team demonstrated significantly reduced neuronal death and stable neuronal activity recordings compared with traditional electrode technologies, overcoming long-standing challenges in neural recording.
Details:
Long-term ...
Vilcek Foundation celebrates immigrant scientists with $250,000 in prizes
2025-02-03
New York, NY, February 3, 2025 — The Vilcek Foundation has announced $250,000 in awards recognizing immigrant scientists. The 2025 Vilcek Foundation Prizes in Biomedical Science are bestowed as part of the foundation’s annual prizes program in support of its mission.
The Vilcek Foundation Prizes in Biomedical Science are a tribute to Vilcek Foundation co-founder Jan Vilcek, biomedical scientist and philanthropist. Born in Slovakia, Vilcek excelled as a researcher and immunologist, publishing his first single-author paper in Nature at 26. In 1965, with his wife, Marica, he immigrated to the United States ...
Age and sex differences in efficacy of treatments for type 2 diabetes
2025-02-03
About The Study: This systematic review and network meta-analysis of 601 eligible trials found that sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1 receptor agonists were associated with lower risk of major adverse cardiovascular events. Analysis of age × treatment interactions suggested that SGLT2 inhibitors were more cardioprotective in older than in younger people despite smaller reductions in hemoglobin A1c; GLP-1 receptor agonists were more cardioprotective in younger people.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Peter Hanlon, PhD, email peter.hanlon@glasgow.ac.uk.
To access the ...
Octopuses have some of the oldest known sex chromosomes
2025-02-03
The octopus just revealed another one of its secrets: what determines its sex.
University of Oregon researchers have identified a sex chromosome in the California two-spot octopus. This chromosome has likely been around for 480 million years, since before octopuses split apart from the nautilus on the evolutionary tree. That makes it one of the oldest known animal sex chromosomes.
The finding also is evidence that octopuses and other cephalopods, a class of sea animals that includes squid and nautiluses, do use chromosomes to determine their sex, answering a longstanding mystery among biologists.
“Cephalopods are already such interesting creatures, ...
High-yield rice breed emits up to 70% less methane
2025-02-03
Rice cultivation is responsible for around 12% of global methane emissions, and these emissions are expected to increase with global warming and as the human population continues to grow. Now, scientists have identified chemical compounds released by rice roots that determine how much methane the plants emit. On February 3 in the Cell Press journal Molecular Plant, they report that this information enabled them to breed a new strain of rice that emits up to 70% less methane.
“This study shows that you can have low methane and ...
[1] ... [705]
[706]
[707]
[708]
[709]
[710]
[711]
[712]
713
[714]
[715]
[716]
[717]
[718]
[719]
[720]
[721]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.