With a little help from their friends: Poll shows role of close friendships in older adults’ health
2024-12-12
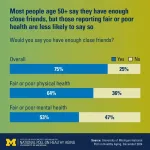
Whether they’re lifelong buddies or recently connected, close to home or miles away, a new poll shows the key role that friends play in the lives and wellbeing of adults aged 50 and older.
But it also reveals some challenges for those who have physical health or mental health issues – suggesting it may be important for them connect with existing friends or make new friends.
In all, 90% of people aged 50 and older say they have at least one close friend, and 75% say they have enough close friends, ...
Too much screen time can reduce sleep quality in preschool-age children, making behavioral problems worse
2024-12-12
Excessive screen use by preschool-age children can lead to reduced sleep quality, exacerbating problems such as poor attention, hyperactivity and unstable mood, a new study suggests.
Peer-reviewed findings published in Early Child Development and Care show how screen time is “significantly” correlated with increased hyperactive attention problems and emotional symptoms, and with decreased sleep quality.
Additionally, the research – carried out by experts in China and Canada – demonstrates how sleep quality is also extensively correlated with decreased hyperactive attention problems, emotional symptoms and peer problems.
The findings ...
Study reveals role of allele dosage in improving sweetpotato traits
2024-12-12
Sweetpotatoes are an agricultural powerhouse that feeds millions globally. However, their complex genetics make it challenging for breeders to understand and improve traits like yield, disease resistance, and nutritional content. A new study reveals insights into the significance of leveraging “allele dosages” in sweetpotato breeding practices.
“Sweetpotatoes are hexaploid, meaning they have six copies of each chromosome, unlike diploid crops like tomato or rice, which have two," explained Zhangjun Fei, a professor at the Boyce Thompson Institute and one of the study's lead authors. “This genetic ...
Dan M. Frangopol and Sunyong Kim co-author third book on structural performance
2024-12-12
Dan M. Frangopol, the inaugural Fazlur R. Khan Endowed Chair of Structural Engineering and Architecture at Lehigh University, has co-authored a new book on probabilistic structural performance assessments.
System Reliability, Risk, Longevity, Sustainability and Optimal Decision-Making: Emphasis on Marine Structures (available April 11, 2025) offers a comprehensive framework for analyzing and predicting the time-dependent performance of deteriorating structures. The book emphasizes marine infrastructure, addressing system reliability, risk, longevity, sustainability, and optimal decision-making processes. It is a valuable resource for students, engineers, researchers, decision-makers, ...
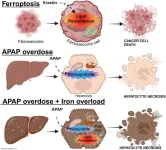
Ferroptosis and intrinsic drug-induced liver injury by acetaminophen and other drugs: a critical evaluation and historical perspective
2024-12-12
DILI is broadly categorized into intrinsic and idiosyncratic types. Intrinsic hepatotoxins, such as APAP, cause dose-dependent injury, while idiosyncratic DILI involves complex immune and metabolic interactions that remain poorly understood. Mechanistic studies of intrinsic hepatotoxins have revealed oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction as key contributors to injury. Historically, LPO and iron-catalyzed free radical generation were central to understanding DILI, but the focus shifted toward apoptosis in the late 20th century.
The discovery of ferroptosis—a regulated form of cell death characterized ...
Reiki therapy demonstrates significant symptom relief for cancer patients receiving infusion treatments
2024-12-12
CLEVELAND - A recent study conducted at University Hospitals Connor Whole Health has evaluated a Reiki program designed for outpatients with cancer and receiving infusion treatments at two University Hospitals infusion centers.
The study, entitled “Evaluation of a Reiki Volunteer Program within Two Cancer Infusion Centers,” was recently published in the Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, a peer-reviewed journal that serves as an interdisciplinary audience of professionals. This retrospective review, conducted between March 2022 and February 2024, evaluated the effects of Reiki on outpatients receiving infusion treatments such as chemotherapy. During Reiki sessions, a ...
Long-term exposure to air pollution linked to blood clots in veins that bring blood to the heart
2024-12-12
WHAT: A large study found that greater exposure to long-term air pollution was linked with increased risks for blood clots that can occur in deep veins, which, if untreated, can block blood flow and cause serious complications, even death.
These findings came from a longitudinal study funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) that included 6,651 U.S. adults who were followed for an average of 17 years between 2000 and 2018. Participants lived in or near one of six major metropolitan areas: New York, Baltimore, Chicago, Los Angeles, Minneapolis, and Winston-Salem, North Carolina.
Throughout the study, 248 adults, 3.7% of the study sample, developed blood clots ...
National Academy of Inventors partners with PMU to recognize three exceptional innovators
2024-12-12
The National Academy of Inventors (NAI) is proud to announce the recipients of the inaugural Prince Mohammad bin Fahd University (PMU)-National Academy of Inventors International Patent Award. This year’s recipients will be honored at a special ceremony on December 12th, 2024 at PMU’s campus in Al-Khobar, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
The PMU-NAI International Patent Award was created to recognize and honor distinguished scientists, research institutions, research centers, and universities across the globe for their outstanding patents and inventions that create positive societal ...
Deep learning model accurately diagnoses COPD
2024-12-12
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Using just one inhalation lung CT scan, a deep learning model can accurately diagnose and stage chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), according to a study published today in Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
COPD is a group of progressive lung diseases that impair a person’s ability to breathe. Symptoms typically involve shortness of breath and fatigue. There currently is no cure for COPD, and it is the third leading cause of death worldwide, according to the World Health Organization.
A ...
Alliance Foundation Trials phase III PATINA study shows promise for patients with HR+, HER2+ metastatic breast cancer
2024-12-12
Alliance Foundation Trials, LLC (AFT) and Pfizer Inc. today announced results from the phase III PATINA trial demonstrating that the addition of palbociclib (IBRANCE®) to current standard-of-care first-line maintenance therapy (following induction chemotherapy) resulted in statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) by investigator assessment in patients with hormone receptor-positive (HR+), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive (HER2+) metastatic ...
COMET trial finds quality of life similar among patients with low- risk DCIS whether they received active monitoring or surgery
2024-12-12
SAN ANTONIO – Patients with low-risk ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) who underwent active monitoring reported comparable physical, emotional, and psychological outcomes to patients who received upfront treatment, according to results from the COMET clinical trial presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS), held December 10-13, 2024.
The results of this study were simultaneously published in JAMA Oncology.
“Active monitoring” is a strategy in which patients are monitored closely, with surgery reserved for those patients who ...
Adjuvant tamoxifen may reduce recurrence risk for patients with ‘good-risk’ DCIS who forgo radiation
2024-12-12
SAN ANTONIO – For patients with “good-risk” ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) who underwent breast- conserving surgery and did not receive radiotherapy, tamoxifen significantly decreased the risk of recurrence in the same breast, according to results presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS), held December 10-13, 2024.
“Good-risk” DCIS was defined as grade 1 or 2, 2.5 cm or smaller, and having clear surgical margins of 3 mm or greater.
Current guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) advise that patients who undergo breast-conserving surgery after a diagnosis ...
COMET trial finds active monitoring is a viable option for some patients with low-risk DCIS
2024-12-12
SAN ANTONIO – Among patients with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, HER2-negative, low-risk ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), those who underwent active monitoring had similar two-year invasive ipsilateral breast cancer recurrence rates as those who underwent guideline-concordant treatment, according to results from the COMET clinical trial presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS), held December 10-13, 2024.
The results of this study were simultaneously published in JAMA.
“Active monitoring” is a strategy in which patients are monitored closely, with surgery reserved for those patients who develop cancer.
A steady increase ...
Most patients with intermediate-risk breast cancer may safely avoid chest wall irradiation after mastectomy
2024-12-12
SAN ANTONIO – Patients with intermediate-risk breast cancer had similar rates of 10-year overall survival whether or not they underwent chest wall irradiation (CWI) after mastectomy, according to results from the BIG 2-04 MRC SUPREMO clinical trial presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS), held December 10-13, 2024.
“While post-mastectomy CWI is the standard of care for most patients with early-stage breast cancer who have four or more positive axillary lymph nodes, its role in patients with fewer positive lymph nodes or node-negative disease remains controversial,” ...
Active monitoring with or without endocrine therapy for low-risk ductal carcinoma in situ
2024-12-12
About The Study: Women with low-risk ductal carcinoma in situ randomized to active monitoring did not have a higher rate of invasive cancer in the same breast at 2 years compared with those randomized to guideline-concordant care.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, E. Shelley Hwang, MD, MPH, email shelley.hwang@duke.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.26698)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
Patient-reported outcomes for low-risk ductal carcinoma in situ
2024-12-12
About The Study: In this prespecified secondary analysis of the Comparing an Operation to Monitoring, With or Without Endocrine Therapy (COMET) prospective randomized trial, the overall lived experience of women randomized to undergo active monitoring for low-risk ductal carcinoma in situ was similar to that of women randomized to guideline-concordant care during the 2 years following diagnosis.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Ann H. Partridge, MD, MPH, email ann_partridge@dfci.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
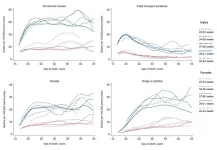
Women born prematurely are at greater risk of committing suicide
2024-12-12
Not only are they the smallest among us, premature children also face health and life challenges that make them the most vulnerable. Generally speaking, they have a slightly higher risk of mortality due to illness. It is now apparent that they also have a higher risk of unexpected death from so-called external causes: road traffic accidents, substance abuse and suicide.
This has been revealed in a major Nordic study led by Professor Kari Risnes from the Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU). The researchers have analyzed birth data and causes of death for nearly 37,000 individuals aged between 15 ...
Bovhyaluronidaze azoximer significantly reduces exercise intolerance in patients with long-term pulmonary sequelae of COVID-19
2024-12-12
Petrovax announced today the positive results from “Long-CoV-III-21,” a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of bovhyaluronidase azoximer in adult patients with pulmonary sequelae of COVID-19. Bovhyaluronidase azoximer, marketed under the brand name Longidaza, is a polymer-conjugated hyaluronidase with an extended half-life. The study drug and placebo were administered for 71 days, with an observation period extending to Day 180.
Longidaza demonstrated a statistically significant 62% reduction in the proportion of patients with exertional desaturation ...
New insights into the evolution and paleoecology of mosasaurs: most comprehensive study to date
2024-12-12
Mosasaurs are extinct marine lizards, spectacular examples of which were first discovered in 1766 near Maastricht in the Netherlands, fueling the rise of the field of vertebrate palaeontology (the study of fossil remains of animals with backbones). Palaeontologist Michael Polcyn presented the most comprehensive study to date on the early evolution and ecology of these extinct marine reptiles. On 16 December, Polcyn will receive his PhD from Utrecht University for his research into the evolution of the mosasaurs. "Mosasaurs are a textbook example of macroevolution, ...
New insights into brain mechanisms underlying empathy
2024-12-12
Genova (Italy), 12th December 2024 – A specific brain mechanism modulates how animals respond empathetically to others’ emotions. This is the latest finding from the research unit Genetics of Cognition, led by Francesco Papaleo, Principal Investigator at the Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT - Italian Institute of Technology) and affiliated with IRCCS Ospedale Policlinico San Martino in Genova. The study, recently published in Nature Neuroscience, provides new insights into psychiatric ...
Semiconductor device technology recognized by the "Olympics of Semiconductors"
2024-12-12
The Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS) announced that Dr. Yong-Hun Kim from the Energy & Environment Materials Research Division and Dr. Kyung Song from the Material Characterization Center, in collaboration with Professor Hyun-Sang Hwang's team from POSTECH, have successfully developed a groundbreaking heterojunction technology. This technology integrates tungsten disulfide (WS₂), a two-dimensional (2D) material, with hafnium zirconium oxide (HZO), a ferroelectric material, achieving both interfacial stability and superior crystallinity. The results have been accepted by the International Electron Devices Meeting 2024 (IEDM 2024), ...
What brings richness to sparkling wines?
2024-12-12
“Rich” and “full-bodied” are terms that people often use to describe the taste of wine. They are also the properties that kokumi compounds bring to foods like mature Gouda cheese, though scientists haven’t widely explored them in wines. In ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, researchers now connect the dots and report 11 probable kokumi compounds in sparkling wines.
Kokumi is often confused with the better-known term umami. Umami is a savory, meaty flavor and is one of the basic five tastes, along with sweet, ...
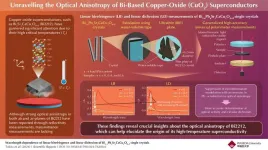
Towards room-temperature superconductivity: Insights into optical properties of bi-based copper-oxide superconductors
2024-12-12
Superconductors are materials which conduct electricity without any resistance when cooled down below a critical temperature. These materials have transformative applications in various fields, including electric motors, generators, high-speed maglev trains, and magnetic resonance imaging. Among these materials, CuO2 superconductors like Bi2212 stand out due to their high critical temperatures that surpass the Bardeen–Cooper–Schrieffer limit, a theoretical maximum temperature limit for superconductivity. However, ...
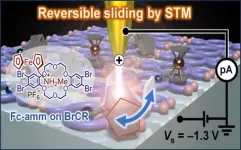
World’s smallest molecular machine: reversible sliding motion in ammonium-linked ferrocene
2024-12-12
Artificial molecular machines, nanoscale machines consisting of a few molecules, offer the potential to transform fields involving catalysts, molecular electronics, medicines, and quantum materials. These machines operate by converting external stimuli, like electrical signals, into mechanical motion at the molecular level. Ferrocene, a special drum-shaped molecule composed of an iron (Fe) atom sandwiched between two five-membered carbon rings, is a promising foundational molecule for molecular machinery. Its discovery earned the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1973, and it has since ...
Researchers reveal key factors behind Japan’s plastic waste removal rates in rivers
2024-12-12
Plastic pollution is an ever-growing problem in today’s world, as most societies have become overly dependent on plastics for packaging, medical supplies, and general goods. Plastic litter accumulation in the ocean, either through deliberate dumping or by being transported from a river, poses significant environmental challenges. Additionally, this plastic eventually degrades into small fragments called microplastics, which then impact diverse marine and land ecosystems by working their way up the food chain and into most living organisms. Though their negative effects on cell health are still under study, many nations have taken a cautionary stance, ...
[1] ... [768]
[769]
[770]
[771]
[772]
[773]
[774]
[775]
776
[777]
[778]
[779]
[780]
[781]
[782]
[783]
[784]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.