Overview of Spousal Maintenance Awards in Divorce and Legal Separation
2011-02-20
In a divorce or legal separation, spousal maintenance may be ordered by the court to provide important financial support for one party or the other. Maintenance is paid by one spouse (or former spouse) to the other spouse (or former spouse). Some states refer to such support as alimony, others as spousal support. In any case, the purpose and result is the same, as we'll discuss in this article.
Historical Basis for Alimony -- Times Have Changed
There was a time when traditional marriages were entered into with the understanding and agreement that only death could ...
Tips for Keeping Children Involved with Parenting Time Activities
2011-02-20
If you could help your child live a happier life, and grow up to be a happier adult, wouldn't you try to make your parenting time more memorable? Every moment you spend with your child is an opportunity to build and strengthen your relationship. If you're wondering how to go about doing that, here are a few tips to help you along the way.
TIP #1: Stick to the Plan.
When you pick up your child at the parenting time exchange, you should have a plan on how you'll be spending your time together. Maybe you've arranged to go for a desert drive on a Saturday afternoon with ...
Before Acquiring A Business, Make Sure You Are Prepared And Protected
2011-02-20
A business purchase or acquisition may be the most significant transaction of your life. Putting a deal together is a lot like a jigsaw puzzle: to get to the point where you sign on the dotted line numerous pieces all have to fit together just right. Without proper alignment, an otherwise successful transaction can go south in a hurry. The efforts you make prior to closing will have a proportional impact on the success of the transaction: hastily thrown-together acquisitions have a much greater chance of ultimate failure.
Performing Due Diligence
Obviously, you will ...
Florida Bill Would Affect All Property Insurance Claims, Including Less Sinkhole Coverage
2011-02-20
The latest bill on the table of the Florida legislature focuses on property insurance.
According to legislators supporting the bill, SB 408 is aimed at creating more competitive pricing in the private insurance marketplace, making homeowners' insurance policies more affordable. Supporters say that premiums would be lowered because insurers would be able to lower their costs and pass on those savings to their policyholders.
But at the same time, if passed, the bill would reduce regulatory oversight on insurance companies, and actually end up harming many policyholders. ...
Injured on the Job? Protect Your Interests With These Simple Steps
2011-02-20
When workers are injured on the job, the workers' compensation system is designed to ensure that they are not forced to deal with these injuries alone. Workers' comp provides critical benefits, such as payment for medical care and wage replacement for time away from work.
To ensure access to these benefits, though, it is important for workers to follow certain procedures. Workers' compensation is a highly regulated area and the failure to follow the required processes may limit access to these benefits.
Any time you are seriously injured, the first priority must ...
Plan Ahead to Minimize Your Estate Tax Burden in New York
2011-02-20
To the surprise of many, the end of 2010 came with another temporary approach to the ongoing issue of federal estate taxes. Under the compromise legislation passed at the end of last year, estates less than $5 million are exempt from federal estate taxes, while any amount in excess of $5 million is subject to a 35 percent tax.
However, with the all of the media attention devoted to federal estate taxes, it is easy to forget that state estate taxes are far more important for many families. New York imposes an estate tax on any estate over $1 million. Many people who will ...
Government Study Finds Lack of Progress in Preventing Medical Errors
2011-02-20
Hospital errors and other forms of medical malpractice that cause serious injuries and wrongful deaths remain disturbingly frequent. The steady drum-beat from some political quarters about the supposed need for "tort reform" does not change this reality. It only seeks to obscure it.
A recent government study estimated that 15,000 Medicare patients die every month from care they were given in hospitals. Over the course of a full year, that is an astonishing 18,000 deaths -- a cascade of calamities, in a place designed to provide comfort and care.
Study of Adverse Events
The ...
Cruise Amour Unveils Network of Local Cruise Advisors
2011-02-20
Cruise Amour, the online agency, has unveiled its network of local cruise advisors.
Keen not to limit their exposure to only on-line channels, Cruise Amour made the decision in November 2010 to develop a network of local cruise advisors, each equipped to reach out to customers who are perhaps less comfortable booking on-line.
Despite tough economic times and the Christmas disruption, Cruise Amour has already recruited and trained four franchisees, with another three due to launch by the end of the month.
When asked if it had been difficult to recruit franchisees ...
British Airways is Adding an Extra Day in the Sun in Mauritius
2011-02-20
British Airways is changing its Mauritius timetable to give customers an extra day in the sun.
From November 1, flights back from the Indian Ocean isle will take off 12 hours later than at present, creating more time for relaxation before the journey home.
The better timing coincides with the route being switched from Heathrow to Gatwick, further strengthening the airline's premium leisure programme at the airport.
Currently, flights to Mauritius leave London at 4:25pm, arriving in the destination at 07:25am the following day. Flights from Mauritius to London ...
Travelzest Launches Top 11 for 2011 Competition
2011-02-20
Travelzest, the travel specialist, has announced the launch of its Top 11 for 2011 competition which will see one lucky winner receiving GBP1000 towards their next Travelzest holiday.
The Top 11 for 2011 list features what Travelzest thinks are the 11 perfect holiday experiences of 2011. The list encompasses a range of breaks that takes in the full range of luxury holiday experiences that Travelzest currently has to offer and was put together by Travelzest's team of travel experts.
The full selection of holidays available on the Top 11 for 2011 list include exploring ...
Voyages Jules Verne Adds New Itineraries to its Popular Worldwide Brochure
2011-02-20
Voyages Jules Verne, the innovative specialist tour operator, has revealed the latest edition of its 'Word of Wonders' brochure.
Offering a wide selection of tours across the globe for departures until April 2012, 'World of Wonders'' itineraries range from short breaks in Europe's cities, coast and countryside to escorted tours of Africa, the Middle East (including Jordan holidays, India, the Far East, South East Asia and the Americas.
Among the new itineraries for 2011 is a seven night walking holiday in Nepal which will allow travellers to take in the landscapes ...
Cruise Amour Launches Expanded Online Information Section
2011-02-20
Cruise Amour has announced the launch of its expanded online information and advice section, designed to provide additional information on a range of areas including cabin types, dress codes and more, in order to make booking a holiday easier and less confusing for the customer.
Historically customers who choose to book on-line do so without the benefit of a travel agent's experience and advice. In many cases knowledge is assumed and customers are expected to know which cruise lines and ships are comparable, how formal they are and how onboard facilities stack up. Cruise ...
Apes shed pounds while doubling calories, CWRU researcher finds
2011-02-18
In the U.S., even zoo gorillas need to switch to a heart-healthy diet.
"A lot are dying of heart disease, we believe like humans," said Elena Hoellein Less, a PhD candidate in biology at Case Western Reserve University.
In fact, heart disease is the number one killer of male Western lowland gorillas – the only species of gorillas in North American zoos.
After Brooks, a 21-year-old gorilla, died of heart failure at Cleveland Metroparks Zoo in 2005, Less and other researchers here took a hard look at how the animals' lifestyle affects their health. Less now leads ...
World's largest lake sheds light on ecosystem responses to climate variability
2011-02-18
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) –– Siberia's Lake Baikal, the world's oldest, deepest, and largest freshwater lake, has provided scientists with insight into the ways that climate change affects water temperature, which in turn affects life in the lake. The study is published in the journal PLoS ONE today.
"Lake Baikal has the greatest biodiversity of any lake in the world," explained co-author Stephanie Hampton, deputy director of UC Santa Barbara's National Center for Ecological Analysis & Synthesis (NCEAS). "And, thanks to the dedication of three generations of a family of ...
'Model minority' not perceived as model leader
2011-02-18
RIVERSIDE, Calif. – Asian Americans are widely viewed as "model minorities" on the basis of education, income and competence. But they are perceived as less ideal than Caucasian Americans when it comes to attaining leadership roles in U.S. businesses and board rooms, according to researchers at the University of California, Riverside.
In a groundbreaking study, researchers found that "race trumps other salient characteristics, such as one's occupation, regarding perceptions of who is a good leader," said Thomas Sy, assistant professor of psychology at UC Riverside and ...
Warm weather may hurt thinking skills in people with MS
2011-02-18
ST. PAUL, Minn. – People with multiple sclerosis (MS) may find it harder to learn, remember or process information on warmer days of the year, according to new research released today that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology's 63rd Annual Meeting in Honolulu April 9 to April 16, 2011.
"Studies have linked warmer weather to increased disease activity and lesions in people with MS, but this is the first research to show a possible link between warm weather and cognition, or thinking skills, in people with the disease," said study author Victoria Leavitt, ...
Research predicts future evolution of flu viruses
2011-02-18
New research from the University of Pennsylvania is beginning to crack the code of which strain of flu will be prevalent in a given year, with major implications for global public health preparedness. The findings will be published on February 17 in the open-access journal PLoS Genetics.
Joshua Plotkin and Sergey Kryazhimskiy, both at the University of Pennsylvania, conducted the research with colleagues at McMaster University and the Institute for Information Transmission Problems of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Plotkin believes that his group's computational ...
The brain as a 'task machine'
2011-02-18
The portion of the brain responsible for visual reading doesn't require vision at all, according to a new study published online on February 17 in Current Biology, a Cell Press publication. Brain imaging studies of blind people as they read words in Braille show activity in precisely the same part of the brain that lights up when sighted readers read. The findings challenge the textbook notion that the brain is divided up into regions that are specialized for processing information coming in via one sense or another, the researchers say.
"The brain is not a sensory machine, ...
Eggs' quality control mechanism explained
2011-02-18
To protect the health of future generations, body keeps a careful watch on its precious and limited supply of eggs. That's done through a key quality control process in oocytes (the immature eggs), which ensures elimination of damaged cells before they reach maturity. In a new report in the February 18th Cell, a Cell Press publication, researchers have made progress in unraveling how a factor called p63 initiates the deathblow.
In fact, p63 is a close relative of the infamous tumor suppressor p53, and both proteins recognize DNA damage. Because of this heritage it ...
Male fertility is in the bones
2011-02-18
Researchers have found an altogether unexpected connection between a hormone produced in bone and male fertility. The study in the February 18th issue of Cell, a Cell Press publication, shows that the skeletal hormone known as osteocalcin boosts testosterone production to support the survival of the germ cells that go on to become mature sperm.
The findings in mice provide the first evidence that the skeleton controls reproduction through the production of hormones, according to Gerard Karsenty of Columbia University and his colleagues.
Bone was once thought of as a ...
Bears uncouple temperature and metabolism for hibernation, new study shows
2011-02-18
This release is available in French, Spanish, Arabic, Japanese and Chinese on EurekAlert! Chinese.
Several American black bears, captured by the Alaska Department of Fish and Game after wandering a bit too close to human communities, have given researchers the opportunity to study hibernation in these large mammals like never before. Surprisingly, the new findings show that although black bears only reduce their body temperatures slightly during hibernation, their metabolic activity drops dramatically, slowing to about 25 percent of their normal, active rates.
This ...
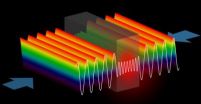
Scientists build world's first anti-laser
2011-02-18
New Haven, Conn.—More than 50 years after the invention of the laser, scientists at Yale University have built the world's first anti-laser, in which incoming beams of light interfere with one another in such a way as to perfectly cancel each other out. The discovery could pave the way for a number of novel technologies with applications in everything from optical computing to radiology.
Conventional lasers, which were first invented in 1960, use a so-called "gain medium," usually a semiconductor like gallium arsenide, to produce a focused beam of coherent light—light ...
The real avatar
2011-02-18
That feeling of being in, and owning, your own body is a fundamental human experience. But where does it originate and how does it come to be? Now, Professor Olaf Blanke, a neurologist with the Brain Mind Institute at EPFL and the Department of Neurology at the University of Geneva in Switzerland, announces an important step in decoding the phenomenon. By combining techniques from cognitive science with those of Virtual Reality (VR) and brain imaging, he and his team are narrowing in on the first experimental, data-driven approach to understanding self-consciousness.
In ...
Taking brain-computer interfaces to the next phase
2011-02-18
You may have heard of virtual keyboards controlled by thought, brain-powered wheelchairs, and neuro-prosthetic limbs. But powering these machines can be downright tiring, a fact that prevents the technology from being of much use to people with disabilities, among others. Professor José del R. Millán and his team at the Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) in Switzerland have a solution: engineer the system so that it learns about its user, allows for periods of rest, and even multitasking.
In a typical brain-computer interface (BCI) set-up, users can send ...
Skeleton regulates male fertility
2011-02-18
NEW YORK (February 17, 2011) – Researchers at Columbia University Medical Center have discovered that the skeleton acts as a regulator of fertility in male mice through a hormone released by bone, known as osteocalcin.
The research, led by Gerard Karsenty, M.D., Ph.D., chair of the Department of Genetics and Development at Columbia University Medical Center, is slated to appear online on February 17 in Cell, ahead of the journal's print edition, scheduled for March 4.
Until now, interactions between bone and the reproductive system have focused only on the influence ...
[1] ... [7849]
[7850]
[7851]
[7852]
[7853]
[7854]
[7855]
[7856]
7857
[7858]
[7859]
[7860]
[7861]
[7862]
[7863]
[7864]
[7865]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.