Breakthrough AI model can translate the language of plant life
2024-12-09
A pioneering Artificial Intelligence (AI) powered model able to understand the sequences and structure patterns that make up the genetic “language” of plants, has been launched by a research collaboration.
Plant RNA-FM, believed to be the first AI model of its kind, has been developed by a collaboration between plant researchers at the John Innes Centre and computer scientists at the University of Exeter.
The model, say its creators, is a smart technological breakthrough that can drive discovery and innovation in plant science and potentially across the study of invertebrates ...
MASH discovery redefines subtypes with distinct risks: shaping the future of fatty liver disease treatment
2024-12-09
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), formerly referred to as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), impacts roughly 30% of the global adult population. The disease spans from benign fat accumulation in the liver (steatosis) to its more severe form, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH, formerly nonalcoholic steatohepatitis or NASH). MASH represents a dangerous progression, with the potential to cause cirrhosis, liver cancer, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
Despite ...
Three-quarters of Earth’s land became permanently drier in last three decades: UN
2024-12-09
Even as dramatic water-related disasters such as floods and storms intensified in some parts of the world, more than three-quarters of Earth’s land became permanently drier in recent decades, UN scientists warned today in a stark new analysis.
Some 77.6% of Earth’s land experienced drier conditions during the three decades leading up to 2020 compared to the previous 30-year period, according to the landmark report from the UN Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD).
Over the same period, drylands expanded by about 4.3 million km2 – an area nearly a third larger than India, the world’s ...
Lower-quality public housing is at high risk of flood damage
2024-12-09
AUSTIN, TX, Dec 09, 2024 – Hurricane Helene highlighted the increasing intensity of extreme weather events and the catastrophic flooding they can bring. A new study finds that many Americans residing in lower-quality public housing face a high risk of experiencing flood-related damages as their homes are disproportionately located in areas of high flood risk.
A study by scientists from the Ohio State University and Texas A&M University has combined HUD’s physical inspection scores of public housing units across the country (from 2013-2020) with ...
Study compares soft tissue sarcoma rates among U.S. military servicemen and men in the general population
2024-12-09
A recent analysis reveals that the incidence rates of soft tissue sarcomas—cancers in muscle, fat, blood vessels, nerves, and tendons—are lower in young U.S. active-duty military servicemen compared with those in the general population, but higher in middle-aged servicemen, perhaps due to greater cumulative exposure to toxins. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Soft tissue sarcomas are rare cancers arising all over the body, in various organs and tissues such as muscle, fat, and viscera. Most sarcomas arise sporadically, but a small subset arise from exposure to ...
Toxic air in Texas high schools
2024-12-09
AUSTIN, TX, Dec 9, 2024 – Semivolatile organic compounds (SVOCs) are found in building materials and consumer products like carpeting, furniture and electronics. Gases released by these chemicals in homes, offices and schools pose potential human health risks such as cancers, reproductive disorders, and nervous system damage.
A recent study of the indoor air in central Texas high schools revealed that two groups of SVOCs, phthalates and PBDEs, are prevalent in high school environments. The ...
What motivates Americans to eat less red meat?
2024-12-09
AUSTIN, TX, Dec 9, 2024 – Limiting red meat consumption is key to a sustainable and healthy diet, yet Americans are among the world’s largest consumers of red meat. A new study reveals the demographics of American adults who choose not to eat red meat and finds that environmental concerns may matter more to them than health risks.
Researchers at Baruch College and the University of Southern California (USC) surveyed more than 7,500 adults as part of the Understanding America Study – a probability-based Internet panel of individuals 18 and older. They will present ...
Sugary drinks significantly raise cardiovascular disease risk, but occasional sweet treats don’t, scientists find
2024-12-09
A little of what you fancy does you good… unless it’s a fizzy drink. Scientists studying the impact of sugar on the risk of cardiovascular disease have found that eating too much added sugar increases your risk of stroke or aneurysm, but eating a few treats is associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases. Meanwhile, drinking sweetened beverages raises your risk of stroke, heart failure, and atrial fibrillation.
“The most striking finding from our study is the divergent relationship between different sources of added sugar and cardiovascular ...
Falsifying anthropics
2024-12-09
In short:
“We exist, therefore the universe is made to host us”: the anthropic principle has sparked intense debate in cosmology since its first formulation. A new paper published in JCAP proposes a way to test it. To falsify it, all three of the following conditions must be confirmed by observations:
• Cosmic inflation occurred
• Axions exist
• Dark matter is not made of axions
If all these conditions are proven true, the anthropic principle would lose its validity, and our universe would appear ...
New West Health-Gallup poll reveals most Americans worried about often hidden healthcare fees
2024-12-09
WASHINGTON, DC – Monday, December 9, 2024 – More than half of Americans (52%) worry about affording the cost of often hidden healthcare fees, increasingly pervasive charges that could add hundreds or even thousands of dollars to their medical bills a new West Health-Gallup poll finds.
Hospitals typically add these fees on top of charges for routine medical services like lab tests or physical examinations provided at outpatient centers, clinics, and medical offices that they own. This means patients end up paying more for the same medical service than they would at independent providers or freestanding clinics – and some may not even ...
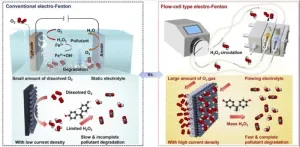
Developing wastewater treatment units that treat right where it's generated
2024-12-09
Conventional wastewater treatment involves the centralized collection of wastewater from sources through pipes to large-scale treatment plants, where it is treated in bulk. However, this is not feasible in small, decentralized areas such as rural areas. Simple treatment units installed at small non-point sources of pollution mainly focus on disinfection and turbidity improvement, and do not properly decompose the recalcitrant organic matter in wastewater. In addition, even if industrial wastewater is treated in-house, the treatment efficiency is low, and highly ...
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers find rotavirus vaccine is safe for use in NICU babies
2024-12-09
Philadelphia, December 9, 2024 – Researchers from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) found that transmission of rotavirus vaccine strains in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) is rare and without clinical consequences, strongly suggesting that giving the rotavirus vaccine to eligible infants during their hospitalization provides immune benefits that outweigh any risks. The findings, published today in the journal Pediatrics, could serve as the basis for a change in clinical practice.
Rotavirus is a virus that infects the lining of the intestines and is typically ...
New international guidelines announced for Premature Ovarian Insufficiency (POI)
2024-12-09
New guidelines on the diagnosis and management of premature ovarian insufficiency (POI) – developed by the Centre for Research Excellence in Women’s Health in Reproductive Life (CRE-WHiRL) at Monash University, and key international women’s health organisations with an international team of experts including women with lived experience – will be published today (TBC) simultaneously in three leading journals.
POI is defined as loss of ovarian function before 40 years. This is much earlier than the usual age of menopause; occurring at an average age of 48-51 years in women globally.
POI affects approximately 4 per cent ...
Supporting parents through “unimaginable pain” of losing child – new toolkit developed for clinicians involved in Child Death Review
2024-12-08
Parents who face the heartbreaking loss of their child should get a specific keyworker to support them through bereavement, wherever they are in the country, according to a set of recommendations informed by new research.
In an academic paper published in Archives of Disease in Childhood today, bereaved parents and academic experts from the University of Birmingham, University of Bristol and Birmingham Community Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust have outlined their recommendations for support that all bereaved parents ...
Could online technology be a clue as to why boys in Norway are outperforming girls in learning English as a second language?
2024-12-08
Bucking conventionality, boys in Norway are making early gains in reading English as a second language and even outperforming girls at age 10 and 13 – a new a study of more than one million students suggests.
Publishing their findings in the peer-reviewed journal Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy & Practice, experts from the University of Oslo propose the perhaps unexpected results might be explained by online gaming and experiences with other digital technologies such as YouTube – with English being the language of the internet.
“Our ...
A healthy diet helps the weighty battle with chronic pain
2024-12-08
Chronic pain is an acute and debilitating condition that affects millions of people worldwide. And while pain interventions are available, many people struggle without treatment at all.
Now new research from the University of South Australia shows that adopting a healthy diet can reduce the severity of chronic pain, presenting an easy and accessible way for sufferers to better manage their condition.
Exploring associations between body fat, diet, and pain, researchers found that a greater consumption of foods within the Australian Dietary Guidelines was directly associated with lower levels of body ...
ASH 2024: Antibody shows encouraging results for treating high-risk follicular lymphoma and marginal zone lymphoma
2024-12-08
MIAMI, FLORIDA (STRICTLY EMBARGOED UNTIL DEC. 8, 2024, AT 12 NOON EST) – Two clinical trials testing the antibody loncastuximab tesirine (Zynlonta) showed encouraging results in patients with high-risk forms of two blood cancers – follicular lymphoma and marginal zone lymphoma. The findings, led by physician-scientists at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, part of the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, will be presented at the American Society of Hematology’s 2024 meeting in San Diego.
One study, a phase 2 clinical trial led by Juan Alderuccio, M.D., ...
Observation of new electric field signals strong potential for assorted devices: new research at City University of Hong Kong
2024-12-08
HONG KONG (8 December 2024)—A new vortex electric field with the potential to enhance future electronic, magnetic and optical devices has been observed by researchers from City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) and local partners.
The research, published in Science, is highly valuable as it can upgrade the operation of many devices, including strengthening memory stability and computing speed. With further research, the discovery of the vortex electric field can even later impact the fields of quantum computing, spintronics, and nanotechnology.
“Previously, generating a vortex electric field required expensive thin film deposition techniques and complex procedures. However, our ...
A sickle cell first: Base editing, a new form of gene therapy, leaves patient feeling ‘more than fine’
2024-12-07
Though he doesn’t remember it, Branden Baptiste had his first sickle cell crisis at age 2. Through elementary school, he was in and out of the hospital with pain episodes, not knowing why. As he got older, he learned he had sickle cell disease: His red blood cells were forming sickle shapes and getting stuck in his blood stream, preventing oxygen from reaching his tissues.
“From age 12, things skyrocketed,” says Branden, now 20. “I was in the hospital every other month with crises.” He estimates he missed 60 days of school every year.
In sixth grade, Branden had to have his left hip replaced ...
Keto diet metabolite may power up CAR T cells to kill cancer
2024-12-07
SAN DIEGO – A simple dietary supplement may provide a new approach to boost CAR T cell function, according to a study from researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and Penn Medicine’s Abramson Cancer Center. While the approach needs to be assessed in clinical trials, the early research, shared in a press briefing today at the 66th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition (Abstract 4), hints at a potentially cost-effective strategy to improve CAR T cell function and cancer-fighting abilities.
CAR T cell therapy is a ...
New study reveals a fiber diet may delay a type of blood cancer
2024-12-07
Today researchers at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) reported results from the first ever clinical trial to show that a high fiber plant based dietary intervention may delay progression to multiple myeloma, a type of rare, incurable blood cancer affecting the bone marrow. The study enrolled 20 participants with a precancerous blood disorder and an elevated body mass index (BMI) at risk for developing multiple myeloma. They received 12 weeks of high fiber plant-based meals and 24 weeks of coaching. Two participants with progressing disease prior to study showed a significant improvement of their disease progression trajectory. Additionally, at one year ...
Global clinical trial shows improved survival rates for common childhood leukemia
2024-12-07
Just days before his fourth birthday, Santiago was diagnosed with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), the most common cancer in children.
He began chemotherapy the next day, and the outlook was promising – disease-free survival rates for B-ALL are among the highest for paediatric cancers, at 80 to 85 per cent. However, limited progress has been made over the last 15 years, and relapsed B-ALL remains a leading cause of cancer death among children.
Seeking to explore all options, Santiago’s parents enrolled him in a Children’s Oncology Group clinical trial led by scientists ...
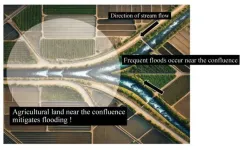
Agricultural land near where rivers meet can mitigate floods
2024-12-07
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University showed that agricultural land preserved around river confluences can help mitigate floods. They make a case for Eco-DRR, an approach that uses existing environmental resources to improve resilience against flooding. Statistical analysis showed that municipalities with agricultural land in areas with high water storage potential suffered fewer floods, with stronger correlation when agricultural land was situated near river confluences. The team hope their findings inform effective land usage.
Climate change has brought ...
Hybrid theory offers new way to model disturbed complex systems
2024-12-06
In fields ranging from immunology and ecology to economics and thermodynamics, multi-scale complex systems are ubiquitous. They are also notoriously difficult to model. Conventional approaches take either a bottom-up or top-down approach. But in disturbed systems, such as a post-fire forest ecosystem or a society in a pandemic, these unidirectional models can’t capture the interactions between the small-scale behaviors and the system-level properties. SFI External Professor John Harte (UC Berkeley) and his collaborators have worked to resolve this challenge by building a hybrid method that links bottom-up behaviors and top-down causation in a single theory.
Harte et ...
MRI could be key to understanding the impact a gluten free diet has on people with coeliac disease
2024-12-06
Experts have used magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to better understand the impact a gluten free diet has on people with coeliac disease, which could be the first step towards finding new ways of treating the condition.
The MARCO study – MAgnetic Resonance Imaging in COliac disease – which is published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology (CGH), was led by experts from the School of Medicine at the University of Nottingham, alongside colleagues at the Quadram Institute.
Coeliac disease is a chronic condition affecting around one person in every 100 in the general population. When people with coeliac ...
[1] ... [790]
[791]
[792]
[793]
[794]
[795]
[796]
[797]
798
[799]
[800]
[801]
[802]
[803]
[804]
[805]
[806]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.