New insights into low-temperature densification of ceria-based barrier layers for solid oxide cells
2024-11-27
Solid oxide cells (SOCs), including solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) and solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOECs), are among the most promising energy conversion technologies due to their high efficiency and fuel flexibility. However, the high-temperature sintering required for their manufacture often leads to undesirable reactions at the electrolyte and electrode interface, degrading cell performance. A thin, dense ceria-based barrier layer, typically composed of gadolinium-doped ceria (GDC), is widely used to prevent these reactions. Achieving sufficient densification ...
AI Safety Institute launched as Korea’s AI Research Hub
2024-11-27
The Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), headed by Minister Yoo Sang-im, held the launch ceremony for the "AI Safety Institute" (AISI) on Wednesday, November 27, at the Pangyo Global R&D Center.
At the "AI Seoul Summit"last May, leaders from 10 countries recognized safety as a key component of responsible AI innovation and emphasized the importance of establishing AI safety institutes and fostering global collaboration for safe AI. President Yoon Suk Yeol also expressed his commitment, stating, "We will work towards establishing an AI safety institute in Korea and actively participate ...
Air pollution linked to longer duration of long-COVID symptoms
2024-11-27
Exposure to air pollutants (PM2.5 and PM10) is associated with an increased risk of persistent long-COVID symptoms, partly due to its impact on the severity of the acute infection. This is the main conclusion of a study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by “la Caixa” Foundation, in collaboration with the Germans Trias i Pujol Research Institute (IGTP), and published in Environmental Health Perspectives.
Long-COVID is a heterogeneous condition in which symptoms like fatigue, breathlessness, and cognitive issues persist for months after ...
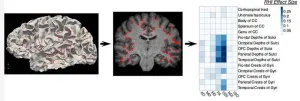
Soccer heading damages brain regions affected in CTE
2024-11-27
CHICAGO – Soccer heading may cause more damage to the brain than previously thought, according to a study being presented next week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Heading is a widely used technique in soccer where the players control the direction of the ball by hitting it with their head. In recent years, research has been done that suggests a link between repeated head impacts and neurodegenerative diseases, such as chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE).
“The potential effects of repeated head impacts in sport are ...
Autism and neural dynamic range: insights into slower, more detailed processing
2024-11-27
A new study has linked distinct neural and behavioral characteristics in autism spectrum disorder to a simple computational principle. Centered on the “dynamic range” of neurons, which reflects how gradually or sharply they respond to input, the study suggests that individuals with autism spectrum disorder have an increased dynamic range in their neuronal response, resulting in a more detailed but slower response to changes. This research defies previous descriptions of ASD as a “broken cog in the machine” and provides a deeper, richer account of the computational basis of ASD.
[Hebrew University of Jerusalem]– Researchers Dr. Yuval Hart and Oded ...
AI can predict study results better than human experts
2024-11-27
Large language models, a type of AI that analyses text, can predict the results of proposed neuroscience studies more accurately than human experts, finds a new study led by UCL (University College London) researchers.
The findings, published in Nature Human Behaviour, demonstrate that large language models (LLMs) trained on vast datasets of text can distil patterns from scientific literature, enabling them to forecast scientific outcomes with superhuman accuracy.
The researchers say this highlights ...
Brain stimulation effectiveness tied to learning ability, not age
2024-11-27
As we age, our cognitive and motor functions deteriorate, which in turn affects our independence and overall quality of life. Research efforts to ameliorate or even completely abolish this have given rise to technologies that show a lot of promise.
Among these is non-invasive brain stimulation: a term encompassing a set of techniques that can affect brain functions externally and noninvasively, without the need for surgery or implants. One such promising technique, in particular, is anodal transcranial direct current stimulation (atDCS), which uses ...
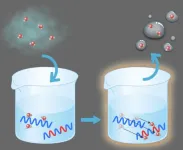
Making a difference: Efficient water harvesting from air possible
2024-11-27
Harvesting water from the air and decreasing humidity are crucial to realizing a more comfortable life for humanity. Water-adsorption polymers have been playing a key part in atmospheric water harvesting and desiccant air conditioning, but desorption so that the polymers can be efficiently reused has been an issue. Now, Osaka Metropolitan University researchers have found a way to make desorption of these polymers more efficient.
Usually, heat of around 100°C is required to desorb these polymers, but Graduate School of Engineering student Daisuke Ikegawa, Assistant Professor Arisa Fukatsu, ...
World’s most common heart valve disease linked to insulin resistance in large national study
2024-11-27
A large new population study of men over 45 indicates insulin resistance may be an important risk factor for the development of the world’s most common heart valve disease – aortic stenosis (AS).
Published today in the peer-reviewed journal Annals of Medicine, the findings are believed to be the first to highlight this previously unrecognised risk factor for the disease.
It is hoped that by demonstrating this link between AS and insulin resistance – when cells fail to respond effectively to insulin and the body makes more than necessary to maintain normal glucose ...
Study unravels another piece of the puzzle in how cancer cells may be targeted by the immune system
2024-11-27
Effective immunity hinges on the ability to sense infection and cellular transformation. In humans, there is a specialised molecule on the surface of cells termed MR1. MR1 allows sensing of certain small molecule metabolites derived from cellular and microbial sources; however, the breadth of metabolite sensing is unclear.
Published in PNAS, researchers at the Monash University Biomedicine Discovery Institute have identified a form of Vitamin B6 bound to MR1 as a means of engaging tumour-reactive immune cells. The work involved an international collaborative team co-led by researchers from the University of Melbourne.
According ...
Long-sought structure of powerful anticancer natural product solved by integrated approach
2024-11-27
A collaborative effort by the research groups of Professor Haruhiko Fuwa from Chuo University and Professor Masashi Tsuda from Kochi University has culminated in the structure elucidation and total synthesis of anticancer marine natural products, iriomoteolide-1a and -1b. These natural products were originally isolated from the marine dinoflagellate collected off the Iriomote Island, Okinawa, Japan.
Because of its potent anticancer activity, iriomoteolide-1a is an intriguing natural product that attract immense attention from the chemical community around the globe. ...
World’s oldest lizard wins fossil fight
2024-11-27
A storeroom specimen that changed the origins of modern lizards by millions of years has had its identity confirmed.
The tiny skeleton, unearthed from Triassic-aged rocks in a quarry near Bristol, is at least 205 million years old and the oldest modern-type lizard on record.
Recently, the University of Bristol team’s findings came under question, but fresh analysis, published today in Royal Society Open Science, proves that the fossil is related to modern anguimorphs such as anguids and monitors. The discovery ...
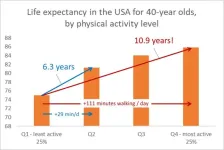
Simple secret to living a longer life
2024-11-27
If everyone in the United States population was as active as the top 25 per cent, individuals over the age of 40 could add five years to their life, according to a new study led by Griffith University researchers.
Physical activity has long been known to be good for health, however estimates have varied regarding how much benefit could be gained from a defined amount of activity, both for individuals and for populations.
This latest study used accelerometry to gain an accurate view of the population’s physical activity levels instead of relying on survey responses as per other studies, and found the benefits were around twice as strong ...
Same plant, different tactic: Habitat determines response to climate
2024-11-27
Plants need light to grow, but too much light can induce damage to the photosynthetic complex known as photosystem II. It is known that plants adapted to growing under full sun repair this light-induced damage more. But this repair activity slows down in colder temperatures. An Osaka Metropolitan University-led international research team has now found some clues to how plants survive in colder regions.
Graduate School of Science Associate Professor Riichi Oguchi and colleagues from Australia, Austria, and Japan grew Arabidopsis thaliana (commonly ...
Drinking plenty of water may actually be good for you
2024-11-27
Public health recommendations generally suggest drinking eight cups of water a day. And many people just assume it’s healthy to drink plenty of water.
Now researchers at UC San Francisco have taken a systematic look at the available evidence. They concluded that drinking enough water can help with weight loss and prevent kidney stones, as well as migraines, urinary tract infections and low blood pressure.
“For such a ubiquitous and simple intervention, the evidence hasn’t been clear and the benefits were not well-established, so we wanted to take a closer look,” said senior and corresponding author Benjamin Breyer, MD, MAS, the Taube ...
Men at high risk of cardiovascular disease face brain health decline 10 years earlier than women
2024-11-27
Men with cardiovascular disease risk factors, including obesity, face brain health decline a decade earlier—from their mid 50s to mid 70s—than similarly affected women who are most susceptible from their mid 60s to mid 70s, suggest the findings of a long term study, published online in the Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery & Psychiatry.
The most vulnerable regions of the brain are those involved in processing auditory information, aspects of visual perception, emotional processing and memory, with ...
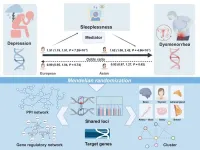
Irregular sleep-wake cycle linked to heightened risk of major cardiovascular events
2024-11-27
An irregular sleep-wake cycle is associated with a heightened risk of major cardiovascular events, such as heart attack and stroke, even for those who clock up the recommended nightly hours of shut-eye, finds research published online in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health.
Most studies looking at the impact of sleep on health have focused on sleep length and less is known about the impact of sleep patterns, in particular the impact of irregular sleep—defined as variations in the time a person goes to sleep and wakes up.
To explore this further, the researchers drew on 72,269 people aged 40 to 79, taking part in the UK ...
Depression can cause period pain, new study suggests
2024-11-27
Women are twice as likely as men to suffer from depression and often experience more severe physical symptoms. This gender difference is particularly evident during reproductive years and dramatically impacts the lives of hundreds of millions of people worldwide. However, although links between mental health and reproductive health have been found, the associations have remained underexplored.
In a new study published in Briefings in Bioinformatics, researchers from China and the UK have found that depression can increase the chances of a person experiencing menstrual pain (dysmenorrhea).
Shuhe Liu, lead author of the study and a PhD ...
Wistar Institute scientists identify important factor in neural development
2024-11-26
PHILADELPHIA — (Nov. 26, 2024) — The Wistar Institute’s Alessandro Gardini, Ph.D., and lab have shed new light on how certain biological processes determine the development of neural cells. Their findings on a molecular “bridge” complex demonstrate a new level of detail in the understanding of early neural development — which is fundamental for the further understanding of neurodevelopmental syndromes. The new paper, “The enhancer module of integrator controls cell identity and early neural fate commitment” was published in the journal, Nature Cell Biology.
“By achieving a better understanding of how the nervous system develops ...
New imaging platform developed by Rice researchers revolutionizes 3D visualization of cellular structures
2024-11-26
A team of researchers led by Anna-Karin Gustavsson at Rice University has developed an innovative imaging platform that promises to improve our understanding of cellular structures at the nanoscale. This platform, called soTILT3D for single-objective tilted light sheet with 3D point spread functions (PSFs), offers significant advancements in super-resolution microscopy, enabling fast and precise 3D imaging of multiple cellular structures while the extracellular environment can be controlled and flexibly adjusted. The research was recently published in Nature Communications.
Studying ...
To catch financial rats, a better mousetrap
2024-11-26
Enron. Lehman Brothers. More recently, General Electric and Supermicro. During the past quarter century, a variety of high-profile companies have been caught cooking their books.
But they’re often not caught before they’ve cost investors billions of dollars. That’s why analysts have long tried to sniff out businesses that may be using questionable or flat-out illegal accounting tricks to hide poor performance.
New research from Urooj Khan, accounting professor and the Deloitte & Touche Centennial Faculty Fellow at Texas McCombs, proposes a new and more effective way to gauge companies’ “earnings quality.”
In analyses of corporate ...
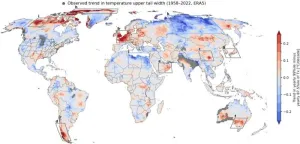
Mapping the world's climate danger zones
2024-11-26
With 2024 on track to be declared the hottest on record, scientists from IIASA and Columbia University have noticed that specific regions are consistently more affected by extreme temperatures. A new study provides the first worldwide map of these regional climate danger zones.
Amid the continued upward march in average temperatures over the past decades, a recent surge of record shattering extreme heat waves raise questions about the degree to which climate models can provide adequate estimates of relations between global mean temperature changes and regional climate risks. The study just published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) provides the ...
Emory heart team implants new blood-pumping device for first time in U.S.
2024-11-26
On Nov. 18, the heart failure and transplantation team at Emory University Hospital (EUH) made history, performing the first-ever surgical implantation in the United States of a brand-new type of ventricular assist device (VAD), which provides crucial care to patients with failing hearts.
An expert team led by veteran cardiothoracic surgeon Mani Daneshmand, MD, successfully implanted a novel magnetically levitated pump, a VAD that has been specifically designed for patient ease and long-term health. The BrioVAD System, made by BrioHealth Solutions Inc., was authorized by the FDA to begin clinical trials ...
Congenital heart defects caused by problems with placenta
2024-11-26
Congenital heart defects are the most common form of human birth defect, but we still don’t fully understand what causes them. Previous research had suggested that some heart defects could be triggered by problems with the placenta, the organ that provides oxygen and nutrients to the developing embryo. Now, researchers at Nanjing University, China have confirmed this link by focusing on a protein whose levels are reduced in many patients with congenital heart defects, called SLC25A1. SLC25A1 plays a key role in transporting ...
Schlechter named Cancer Moonshot Scholar
2024-11-26
Chelsey Schlechter, MPH, PhD, Huntsman Cancer Institute investigator and assistant professor in the Department of Population Health Sciences at the University of Utah (the U), has been selected as a Cancer Moonshot Scholar.
Schlechter is one of only eleven researchers in the U.S. chosen for the prestigious program this year, which aims to both advance impactful cancer research and broaden the research workforce.
For the project, Schlechter and her team partnered with the Association for Utah Community Health and Utah Community Health Centers—organizations which ...
[1] ... [795]
[796]
[797]
[798]
[799]
[800]
[801]
[802]
803
[804]
[805]
[806]
[807]
[808]
[809]
[810]
[811]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.