Study uncovers mutations and DNA structures driving bladder cancer
2024-10-09
How bladder cancer originates and progresses has been illuminated as never before in a study led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and the New York Genome Center. The researchers found that antiviral enzymes that mutate the DNA of normal and cancer cells are key promoters of early bladder cancer development, and that standard chemotherapy is also a potent source of mutations. The researchers also discovered that overactive genes within abnormal circular DNA structures in tumor cells genes drive bladder cancer resistance to therapy. These findings are novel insights into bladder cancer biology and point to new therapeutic strategies for this ...
A matter of taste: Electronic tongue reveals AI inner thoughts
2024-10-09
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A recently developed electronic tongue is capable of identifying differences in similar liquids, such as milk with varying water content; diverse products, including soda types and coffee blends; signs of spoilage in fruit juices; and instances of food safety concerns. The team, led by researchers at Penn State, also found that results were even more accurate when artificial intelligence (AI) used its own assessment parameters to interpret the data generated by the electronic tongue.
The researchers published their results today (Oct. 9) in Nature.
According to the researchers, ...
Another step towards decoding smell
2024-10-09
We often only realize how important our sense of smell is when it is no longer there: food hardly tastes good, or we no longer react to dangers such as the smell of smoke. Researchers at the University Hospital Bonn (UKB), the University of Bonn and the University of Aachen have investigated the neuronal mechanisms of human odor perception for the first time. Individual nerve cells in the brain recognize odors and react specifically to the smell, the image and the written word of an object, for example a banana. The results of this study close a long-standing knowledge gap between animal and human odor research and have now been published in the renowned ...
Plant Science Research collaboration will explore key mosses critical to storing carbon
2024-10-09
ST. LOUIS, MO, October 9, 2024 - Plant scientists at the Donald Danforth Plant Science Center and the HudsonAlpha Institute for Biotechnology have been awarded a four-year National Science Foundation (NSF) Enabling Discovery through GEnomics (EDGE) grant to advance their understanding of sphagnum moss, a crucial component of peatlands and a vital player in global ecosystems. The collaborative research team will develop genetic and genomic resources to study sphagnum's life cycle, growth, and adaptation to various environmental conditions.
Sphagnum ...
Researchers examine the persistence of invisible plastic pollution
2024-10-09
Plastic pollution – tiny bits of plastic, smaller than a grain of sand – is everywhere, a fact of life that applies even to newborn rodents, according to a Rutgers Health study published in the journal Science of the Total Environment.
Researchers have long understood that micro- and nanoplastic particles (MNPs), which enter the environment through oxidation and natural degradation of consumer products, are easily deposited in the human body through inhalation, absorption and diet.
Experts also understand that these pollutants can cross the placental barrier and deposit ...
Coffee during pregnancy safe for baby’s brain development
2024-10-09
A University of Queensland-led study has failed to find any strong links between drinking coffee during pregnancy and neurodevelopmental difficulties in children, but researchers are advising expectant mothers to continue following medical guidelines on caffeine consumption.
Dr Gunn-Helen Moen and PhD student Shannon D’Urso from UQ’s Institute for Molecular Bioscience (IMB) led an in-depth genetic analysis of data from tens of thousands of families in Norway.
“Scandinavians are some of the biggest coffee consumers in the world, drinking at least 4 cups a day, with little stigma about drinking coffee during pregnancy,” ...
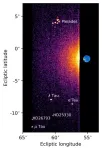
SwRI-led instrument aboard Jupiter-bound spacecraft nails in-flight test
2024-10-09
SAN ANTONIO — October 9, 2024 —As European Space Agency (ESA)’s Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (Juice) spacecraft hurtled past the Moon and Earth in mid-August to provide its first gravity assist maneuver to the Jovian system, the Southwest Research Institute-led Ultraviolet Spectrograph (UVS) instrument imaged the UV emissions radiating from the Earth and Moon.
It was a successful test of one of three science instrument projects comprising NASA’s contribution to ESA’s Juice mission. The UVS data collected were then analyzed and found to be consistent with expectations for the Moon and the Earth. This confirmation that the instrument works ...
New AI models of plasma heating lead to important corrections in computer code used for fusion research
2024-10-09
New artificial intelligence (AI) models for plasma heating can do more than was previously thought possible, not only increasing the prediction speed 10 million times while preserving accuracy, but also correctly predicting plasma heating in cases where the original numerical code failed. The models will be presented on October 11 at the 66th Annual Meeting of the American Physical Society Division of Plasma Physics in Atlanta.
“With our intelligence, we can train the AI to go even beyond the limitations ...
Study: Rise in English learner students in “new destination” states helps, does not hurt, academic outcomes for existing students
2024-10-09
Washington, October 9, 2024—English learner (EL) students represent the fastest growing student group in the United States over the past two decades, with numbers of EL students in public schools soaring in “new destination” states across the South and Midwest. Some commentators have expressed concerns about the possible adverse effect of immigrant students on current students if they require additional resources that are diverted from their peers.
However, a new study finds significant positive spillover effects ...
LANDFEED project kicks off: Transforming agro-food waste into bio-based fertilizers to support Europe’s circular economy
2024-10-09
The LANDFEED project, co-funded by the European Union, held its official kick-off meeting on 12-13 September in Bilbao, Spain. Coordinated by Miriam Pinto from NEIKER, LANDFEED brings together experts across Europe to implement sustainable, circular solutions to Europe’s waste challenges, helping to increase the continent's self-sufficiency in agricultural resources while reducing environmental impact.
LANDFEED will focus on converting under-utilised waste from the agri-food industry, forestry, urban centres, and the natural environment into ...
Mcity opens for remote testing of autonomous vehicle technologies, calls for federal standards
2024-10-09
Images/Videos
As Mcity begins welcoming researchers in autonomous and connected vehicle technologies from around the U.S. to be remote users of its physical and virtual testing environment, its leadership is calling for federal standards for safety testing, arguing that the lack of clear goalposts is hampering development.
The opening also coincides with a new industry partnership project announced at the NVIDIA AI Summit.
Following two years of upgrades, the University of Michigan's hub for autonomous testing has officially kicked ...
Adding vagus nerve stimulation to training sessions may boost how well sounds are perceived
2024-10-09
Just as a musician can train to more sharply distinguish subtle differences in pitch, mammals can improve their ability to interpret hearing, vision, and other senses with practice. This process, which is called perceptual learning, may be enhanced by activating a major nerve that connects the brain to nearly every organ in the body, a new study in mice shows.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health, the investigation centers on the vagus nerve, which carries signals between the brain and the heart, digestive system, and other organs. Experts have long explored targeting this nerve with ...
ACS president comments on award of 2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
2024-10-09
WASHINGTON, Oct. 9, 2024 — On behalf of the American Chemical Society (ACS), President Mary K. Carroll congratulates today’s winners of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry: David Baker, of the University of Washington; Demis Hassabis, of Google DeepMind; and John M. Jumper, of Google DeepMind. The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences awarded the prize with one half to Baker “for computational protein design” and the other half jointly to Hassabis and Jumper “for protein structure prediction.”
“This incredibly complex problem of predicting the 3D structures of proteins from the sequence of amino acids has been one of the biggest challenges ...
Effect of tele-ICU on clinical outcomes of critically ill patients
2024-10-09
About The Study: Daily multidisciplinary rounds conducted by a board-certified intensivist through telemedicine did not reduce intensive care unit (ICU) length of stay in critically ill adult patients.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Adriano J. Pereira, M.D., Ph.D., email adrianojop@einstein.br.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.20651)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
Restrictive vs liberal transfusion strategy in patients with acute brain injury
2024-10-09
About The Study: Patients with acute brain injury and anemia randomized to a liberal transfusion strategy were less likely to have an unfavorable neurological outcome than those randomized to a restrictive strategy.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Fabio Silvio Taccone, MD, PhD, email fabio.taccone@ulb.be.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.20424)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict ...
Extracorporeal blood purification and acute kidney injury in cardiac surgery
2024-10-09
About The Study: The use of a nonselective extracorporeal blood purification device connected to the cardiopulmonary bypass circuit in a nonemergent population of patients undergoing cardiac surgery was associated with a significant reduction of cardiac surgery–associated acute kidney injury in the first 7 days after surgery.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Xose L. Perez-Fernandez, PhD, MD, email xose74@gmail.com.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Frequency of screening and spontaneous breathing trial techniques
2024-10-09
About The Study: Among critically ill adults who received invasive mechanical ventilation for more than 24 hours, screening frequency (once-daily vs more frequent screening) and spontaneous breathing trial (SBT) technique (pressure-supported vs T-piece SBT) did not change the time to successful extubation. However, an unexpected and statistically significant interaction was identified; protocolized more frequent screening combined with pressure-supported SBTs increased the time to first successful ...
International collaboration addresses rising cancer rates in South America
2024-10-09
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [October 9, 2024] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers in the United States—announces a renewed collaboration with the Latin American Cooperative Oncology Group (LACOG) to improve cancer outcomes in South America. The international oncology organizations worked together to publish new NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Prostate Cancer: Brazil Edition.
The NCCN Guidelines® for Prostate Cancer: Brazil Edition are now available free-of-charge at NCCN.org/global. Additional Brazilian adaptations of NCCN Guidelines ...
The secret to slimming? Special ‘skinny genes’ double weight loss
2024-10-09
The secret to losing weight could all be down to a combination of 14 ‘skinny genes’, a new study has found.
University of Essex researchers discovered they helped people drop twice as much weight when they ran for half an hour three times a week.
The team - led by Dr Henry Chung, from the School of Sport, Rehabilitation and Exercise Sciences - found those with more of the genes slimmed the most across eight weeks.
People with the most markers lost up to 5kg during the study and people without ...
Study finds persistent infection could explain long COVID in some people
2024-10-09
EMBARGOED UNTIL OCTOBER 9, 2024 AT 6:30 AM ET
Brigham researchers found people with wide-ranging long COVID symptoms were twice as likely to have SARS-CoV-2 proteins in their blood, compared to those without long COVID symptoms
A persistent infection could explain why some people experience long COVID symptoms, according to a new study led by researchers at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system. The team found evidence of persistent infection in 43 percent of participants with cardiopulmonary, ...
COVID-19 infection appeared to increase risk of heart attack & stroke up to 3 years later
2024-10-09
Research Highlights:
An analysis of UK Biobank health data that included adults who had mild to severe COVID-19 before vaccines were available found an increased risk of heart attack, stroke and death among those adults during the nearly three-year follow-up period after COVID infection.
The elevated risk of heart attack, stroke and death linked to COVID-19 infection was found to be comparable to cardiovascular risk factors such as Type 2 diabetes, peripheral artery disease and cardiovascular disease.
The study found that having a non-O blood type (A, B, AB) was associated with an increased risk of heart attack and stroke among ...
History of COVID-19 doubles long-term risk of heart attack, stroke and death
2024-10-09
Wednesday, October 9, 2024, Cleveland: A history of COVID-19 can double the risk of heart attack, stroke or death according to new research led by Cleveland Clinic and the University of Southern California.
The study found that people with any type of COVID-19 infection were twice as likely to have a major cardiac event, such as heart attack, stroke or even death, for up to three years after diagnosis. The risk was significantly higher for patients hospitalized for COVID-19 and more of a determinant than a previous history of heart disease.
Further genetic analysis ...
Tiny antibodies to fight the dangerous effects of opioids
2024-10-09
Opioid drugs are highly effective at relieving pain but come with severe drawbacks. Their side effects range from dizziness to potentially fatal respiratory depression. Their illegal use contributes to nearly half a million deaths worldwide each year. Researchers from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) have discovered a molecule, called nanobody NbE, which binds tightly and durably to the cell receptors that usually bind to opioids, thereby blocking the drugs’ activity. Moreover, the scientists were able to create even smaller molecules that retain the same properties, which could prove far more effective than current treatments in ...
Researchers discover how plants produce a novel anti-stress molecule
2024-10-09
New research identifies for the first time the genes that help plants grow under stressful conditions - with implications for producing more sustainable food crops in the face of global climate change.
Led by the University of East Anglia (UEA), the study reveals the genes that enable plants to make a novel anti-stress molecule called dimethylsulfoniopropionate, or DMSP. It shows that most plants make DMSP, but that high-level DMSP production allows plants to grow at the coast, for example in salty conditions.
The research also shows that plants can be grown under other ...
You get your energy from your mom. A new study explains why
2024-10-09
It’s one of the basic tenets of biology: We get our DNA from our mom and our dad.
But one notable exception has perplexed scientists for decades: Most animals, including humans, inherit the DNA inside their mitochondria —the cell’s energy centers – from their mothers alone, with all traces of their father’s mitochondrial genome destroyed the moment sperm joins egg.
A new University of Colorado Boulder study published Oct. 4 in the journal Science Advances sheds new light on why this happens, showing that when the process fails, and paternal mitochondria slips into a developing embryo, it can lead to lasting neurological, behavioral and reproductive ...
[1] ... [892]
[893]
[894]
[895]
[896]
[897]
[898]
[899]
900
[901]
[902]
[903]
[904]
[905]
[906]
[907]
[908]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.