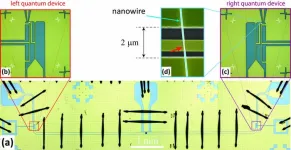
Strong coupling between Andreev qubits mediated by a microwave resonator
2024-10-03
Quantum communication and quantum computing operate based on quantum bits (qubits) as the smallest unit of information — related to bits in a classical computer. Of the many different approaches currently being investigated around the world, one promising option is to use Andreev pair qubits.
These qubits are formed at interfaces between a metal and a superconductor in a process known as Andreev reflection. Here, an electron from the metal enters the superconductor, where it becomes part of an electron pair (a Cooper pair) — while a hole, ...
UNF biological sciences professor receives NIH grant to study muscle atrophy
2024-10-03
Jacksonville, Fla. – A University of North Florida biology professor has been awarded a prestigious four-year National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant totaling over $720K to study the functional role of an enzyme called dual-specificity phosphatase 4 (Dusp4) in skeletal muscle atrophy.
Dr. David Waddell’s NIH-funded research project will help contribute to knowledge about skeletal muscle atrophy associated with neuromuscular disorders, neurodegenerative diseases and aging. Skeletal muscle atrophy is a decrease in muscle mass that occurs when protein degradation exceeds protein ...
Child Health Day 2024: influenza vaccine protects children from infection and hospitalization for the disease, Spanish study shows
2024-10-03
A study published on Eurosurveillance has demonstrated that Spain's influenza vaccination campaign for children aged 6-59 months during the 2023/24 season was effective in preventing acute respiratory infections (ARI) and hospitalisation, as vaccination was recommended for this age group at the national level for the first time.
In the context of Child Health Day 2024, this research emphasises that continued efforts should be made to increase vaccination coverage among children for future seasons.
Context and methods
Influenza A was dominant in the 2023/2024 season, ...
Announcing the 2024 Glenn Foundation Discovery Awards: Jeffrey Friedman, MD, Ph.D/ (the Rockefeller University) and Myriam Heiman, Ph.D. (MIT)
2024-10-03
Santa Barbara, CA and New York, NY -- The Glenn Foundation for Medical Research (GFMR) and the American Federation for Aging Research (AFAR) are pleased to announce the 2024 recipients of the Glenn Foundation Discovery Awards: Jeffrey Friedman, MD, PhD (Professor, The Rockefeller University and Investigator, Howard Hughes Medical Institute) and Myriam Heiman, PhD (Associate Professor of Neuroscience, Massachusetts Institute of Technology).
The Glenn Foundation Discovery Award supports research projects with strong potential to develop pioneering discoveries to understand ...
Stem cell transplants close macular holes in monkeys
2024-10-03
Human stem cell transplants successfully repaired macular holes in a monkey model, researchers report October 3rd in the journal Stem Cell Reports. After transplantation, the macular holes were closed by continuous filling of the space with retinal tissue.
“We confirmed for the first time in a non-human primate model that embryonic stem-derived retinal organoid sheet transplantation facilitates the closure of macular holes,” says senior study author Michiko Mandai of the Kobe City Eye Hospital. “Our results suggest that this method could become a practical, safe, and effective ...
Our brains divide the day into chapters. New psychology research offers details on how.
2024-10-03
The moment a person steps off the street and into a restaurant—to take just one example—the brain mentally starts a new “chapter” of the day, a change that causes a big shift in brain activity. Shifts like this happen all day long, as people encounter new environments, like going out for lunch, attending their kid’s soccer game, or settling in for a night of watching TV.
But what determines how the brain divides the day into individual events that we can understand and remember separately? That’s what a new paper in the journal Current Biology aimed to find ...
Fear of cancer recurrence in adult survivors of childhood cancer
2024-10-03
About The Study: Decades following treatment, one-third of childhood cancer survivors in this study reported elevated fear their cancer will recur or a subsequent malignant neoplasm will develop. Findings suggest that fear of cancer recurrence should be routinely screened, and clinically significant symptoms intervened upon as a part of survivorship care.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Nicole M. Alberts, PhD, email nicole.alberts@concordia.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.36144)
Editor’s ...
AI algorithm for subclinical breast cancer detection
2024-10-03
About The Study: In this retrospective cohort study of women undergoing screening mammography, mean absolute artificial intelligence (AI) scores were higher for breasts developing vs not developing cancer 4 to 6 years before their eventual detection. These findings suggest that commercial AI algorithms developed for breast cancer detection may identify women at high risk of a future breast cancer, offering a pathway for personalized screening approaches that can lead to earlier cancer diagnosis.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Solveig Hofvind, PhD, email sshh@kreftregisteret.no.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Study identifies potential novel drug to treat tuberculosis
2024-10-03
Highlights:
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which causes tuberculosis (TB), is a threat to public health.
A new study identified that a semi-synthetic compound can be derived from natural compounds and shows potent activity against M. tuberculosis, including multi-drug resistant strains.
This is a promising step toward new potent treatment for TB.
Washington, D.C.—A new study published in the American Society for Microbiology journal Microbiology Spectrum demonstrates that a novel semi-synthetic compound can be derived from ...
UTEP study: Zooplankton go “Eew!” to cleaning feces contaminated water
2024-10-03
EL PASO, Texas (Oct. 3, 2024) – Scientists at The University of Texas at El Paso and Stanford University were recently surprised to find that the natural community of zooplankton — tiny, aquatic animals known to graze on bacteria — present in freshwater and saltwater do not clean water that is contaminated with fecal microorganisms.
The research, published today in the biology journal mSphere, reveals important insights about the limitations of zooplankton in treating bodies of water that have been contaminated with fecal organisms, the team said. A 2017 U.S. water quality inventory ...
FAU awarded $10M to train people with disabilities for in-demand tech jobs
2024-10-03
The rising demand for tech jobs presents an outstanding opportunity for growth and inclusivity in the industry. Developing accessible training programs tailored for individuals with disabilities can foster a more diverse workforce. Florida Atlantic University’s College of Education and the College of Engineering and Computer Science have received a $9,961,460 grant from the United States Department of Education’s Office of Special Education and Rehabilitative Services to increase the capacity and participation of transition-age youths and working-age adults with disabilities in high demand technology jobs locally and nationally. ...
Plants have a backup plan
2024-10-03
Tending a garden is hard work. Imagine it from the plants’ perspective. Each relies on fine-tuned genetic processes to pass down accurate copies of chromosomes to future generations. These processes sometimes involve billions of moving parts. Even the tiniest disruption can have a cascading effect. So, for plants like Arabidopsis thaliana, it’s good to have a backup plan.
“Chromosomes have to be accurately partitioned every time a cell divides,” explains Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor and HHMI Investigator Rob Martienssen. “For that to happen, each chromosome has ...
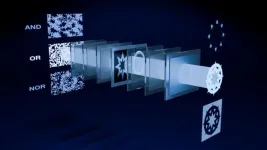
Logic with light
2024-10-03
Increasingly complex applications such as artificial intelligence require ever more powerful and power-hungry computers to run. Optical computing is a proposed solution to increase speed and power efficiency but has yet to be realized due to constraints and drawbacks. A new design architecture, called diffraction casting, seeks to address these shortcomings. It introduces some concepts to the field of optical computing that might make it more appealing for implementation in next-generation computing devices.
Whether ...
Wastewater bacteria can breakdown plastic for food
2024-10-03
Researchers have long observed that a common family of environmental bacteria, Comamonadacae, grow on plastics littered throughout urban rivers and wastewater systems. But what, exactly, these Comamonas bacteria are doing has remained a mystery.
Now, Northwestern University-led researchers have discovered how cells of a Comamonas bacterium are breaking down plastic for food. First, they chew the plastic into small pieces, called nanoplastics. Then, they secrete a specialized enzyme that breaks down the plastic even further. Finally, the bacteria use a ring of carbon atoms from the plastic as a ...
Researchers study 3D printing tungsten parts for extreme conditions in nuclear reactors
2024-10-03
10-2-24
Contacts:
Sougata Roy, Mechanical Engineering, 515-294-5001, sroy@iastate.edu
Mike Krapfl, News Service, 515-294-4917, mkrapfl@iastate.edu
Researchers study 3D printing tungsten parts for extreme conditions in nuclear reactors
AMES, Iowa – Sougata Roy, who doesn’t study electrons or grids or wind turbines, has found a way to contribute to a clean-energy future.
“This work in advanced manufacturing, particularly in using additive manufacturing, is about making a difference,” ...
Promising ‘first’ in Alzheimer’s drug development
2024-10-03
EMBARGOED: NOT FOR RELEASE UNTIL THURSDAY 3 OCTOBER AT 07:00 ET (12:00 UK TIME)
An international team of researchers have made a promising breakthrough in the development of drugs to treat Alzheimer’s Disease.
For the first time, scientists have developed a drug that works on both major aggregation-promoting ‘hotspots’ of the Tau protein - addressing a critical gap in current treatments.
The drug, a peptide inhibitor called RI-AG03, was effective at preventing the build-up of Tau proteins - a key driver of neurodegeneration - in both lab and fruit fly studies.
The ...
Quantum researchers come up with a recipe that could accelerate drug development
2024-10-03
University of Copenhagen mathematicians have developed a recipe for upgrading quantum computers to simulate complex quantum systems, such as molecules. Their discovery brings us closer to being able to predict how new drugs will behave within our bodies and has the potential to revolutionize pharmaceutical development.
Developing a new drug can take more than a decade and cost anywhere from hundreds of millions to billions of euro — with multiple failed attempts along the way. But what if we could predict how a drug worked ...
Experts publish the latest guide for systematic reviews of preclinical research
2024-10-03
A new publication in Nature Reviews Methods Primers provides essential guidance for conducting rigorous systematic reviews on studies with animals and cells. It also highlights the benefits of these reviews, such as improving reproducibility and reducing animal use, and addresses potential pitfalls and recent advancements like review automation.
Systematic reviews synthesize existing evidence in a scientific field to answer specific research questions in a structured and unbiased way. With over 100 million animals used in scientific ...
Oyster reefs once thrived along Europe’s coasts – now they’re gone
2024-10-03
Oysters once formed extensive reefs along much of Europe's coastline – but these complex ecosystems were destroyed over a century ago, new research shows.
Based on documents from the 18th and 19th Centuries, the study reveals that European flat oysters formed large reefs of both living and dead shells, providing a habitat supporting rich biodiversity.
Today these oysters are mostly found as scattered individuals – but the researchers found evidence of reefs almost everywhere, from Norway to the Mediterranean, covering at least 1.7 million hectares, an area larger than Northern Ireland.
The research was ...
Decades-long research reveals new understanding of how climate change may impact caches of Arctic soil carbon
2024-10-03
Utilizing one of the longest-running ecosystem experiments in the Arctic, a Colorado State University-led team of researchers have developed a better understanding of the interplay among plants, microbes and soil nutrients — findings that offer new insight into how critical carbon deposits may be released from thawing Arctic permafrost.
Estimates suggest that Arctic soils contain nearly twice the amount of carbon that is currently in the atmosphere. As climate change has caused portions of Earth’s northernmost polar regions to thaw, scientists have long been concerned about significant amounts of carbon being released in the ...
How Soviet legacy has influenced foreign policy in Georgia and Ukraine
2024-10-03
The legacy of the Soviet Union’s collapse plays a greater role in the foreign policies of Georgia and Ukraine than previous studies have suggested. Conducting foreign policy in former Soviet countries can be a major challenge as the Russian state does not accept the new order. These are the findings outlined in the thesis of political scientist Per Ekman from Uppsala University.
“To understand Russia’s war in Ukraine, for example, it is important to see the war as part of a longer historical event. Since their first day of independence, Georgia and Ukraine have had to deal with Russian ambitions to control the region. For many in the West, it took a ...
Robin Dunbar: Pioneering evolutionary psychologist redefines human social networks
2024-10-03
Oxford, UK – Genomic Press has released a captivating interview with Professor Robin Dunbar, the eminent evolutionary psychologist and anthropologist whose work has fundamentally altered our understanding of human social networks. Published in the Innovators and Ideas section of Genomic Psychiatry, this in-depth conversation offers unique insights into Professor Dunbar's scientific journey and the far-reaching implications of his research.
Professor Dunbar, best known for conceptualizing "Dunbar's number" - the cognitive limit to the number of stable social relationships ...
Balancing health: diabetes and obesity increase risk of liver cancer relapse
2024-10-03
Hepatocellular carcinoma, a type of liver cancer associated with hepatitis infections, is known to have a high recurrence rate after cancer removal. Recent advances in antiviral therapy have reduced the number of patients affected, but obesity and diabetes are factors in hepatocellular carcinoma prevalence. However, these factors’ effects on patient survival and cancer recurrence have been unclear.
To gain insights, Dr. Hiroji Shinkawa’s research team at Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Medicine analyzed the relationship between diabetes mellitus, obesity, and postoperative outcomes in 1,644 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma ...
Duke-NUS launches new pictograms to clarify medication instructions, enhancing patient care
2024-10-03
Duke-NUS introduces 35 innovative pictograms to make medication instructions clearer, especially for seniors.
These visual aids are designed to ensure patients take their medications correctly and safely, with the aim of improving overall health outcomes.
The team looks to collaborate with healthcare institutions and pharmacies to standardise pictograms portraying medication instructions across Singapore.
SINGAPORE, 3 OCTOBER 2024 – Transforming patient care through clarity and simplicity, Duke-NUS Medical School has introduced visual aids or pictograms designed to make medication instructions clearer. ...
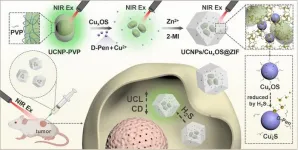
Chiral nanocomposite for highly selective dual-mode sensing and bioimaging of hydrogen sulfide
2024-10-03
With the continuous development of nanotechnology, more artificial chiral nanomaterials have been constructed. As one of the most representative optical properties of these chiral nanomaterials, CD is a powerful sensing technology. Compared with other analytical methods, CD signal has higher sensitivity, but it cannot achieve in-situ imaging in vivo. Scientists have managed to prepare chiral nanocomposites with more diverse biological functional properties to compensate for this shortcoming. However, some chiral nanocomposites assembled by electrostatic adsorption or other methods are easily dissociated and destroyed in complex physiological environments, resulting in performance ...
[1] ... [897]
[898]
[899]
[900]
[901]
[902]
[903]
[904]
905
[906]
[907]
[908]
[909]
[910]
[911]
[912]
[913]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.