Authoritarian populism has weakened democracy in Brazil - study
2024-10-01
The rise of authoritarian populism in Brazil weakened structures that stabilise democracy – mirroring trends in wider global society and potentially making it harder for the country to strengthen its democracy in future, a new study reveals.
The experiences of Brazilians in recent years under the administration of former President Jair Bolsonaro highlight the weakening of welfare systems and human rights protections critical in maintaining democratic stability.
This, in turn, contributed to the rise of militarism ...
Climate scientists express their views on possible future climate scenarios in a new study
2024-10-01
A new survey of climate experts reveals that a majority believes the Earth to be headed for a rise in global temperatures far higher than the 2015 Paris Agreement targets of 1.5 to well-below 2°C.
The study was published in the Nature journal Communications Earth & Environment. It also shows that two-thirds of respondents — all of them authors on the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) — believe we may succeed ...
Anu wins first place, $20,000 in SCORE’s 60th Anniversary Pitch Competition
2024-10-01
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — Anu™, a health and wellness brand developing innovative controlled-environment agriculture systems, won first place and $20,000 among 10 small businesses at the national SCORE 60th Anniversary Pitch Competition in Des Moines, Iowa. SCORE, or Service Corps of Retired Executives, is a resource partner of the U.S. Small Business Administration.
Purdue University alumni Scott Massey and Ivan Ball founded anu. The company has received financial support from the Purdue Research Foundation.
“This funding ...
NSF funds project to examine social, environmental impacts of AI
2024-10-01
As artificial intelligence continues to expand its footprint across society, some researchers are raising questions about the potential negative impact of this technological transformation.
Associate professor Mar Hicks and assistant professor Jess Reia of the University of Virginia’s School of Data Science are partnering with Tamara Kneese and the Data and Society Research Institute to examine this critical issue in a project that the National Science Foundation recently awarded a two-year, $300,000 grant.
Working with the Data ...
New study: neuroscientists spark shelter-seeking response by reactivating memory circuit
2024-10-01
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Using a sophisticated brain-imaging system, neuroscientists at Johns Hopkins Medicine say they have successfully reactivated a specific memory circuit in mice, causing them to seek out shelter when no shelter is actually present.
The researchers say the study, published Sept. 27 in Nature Neuroscience, advances understanding of how memories are structured in the mammalian brain. The findings could one day point to new ways of slowing down or preventing the memory loss that accompanies ...
Wendy Connors named Hertz Foundation President, succeeding Robbee Kosak
2024-10-01
The Fannie and John Hertz Foundation, a nonprofit organization that funds, supports, connects and catalyzes the nation’s top PhD students in science and technology, today announced that Wendy Connors, currently its chief development officer, will begin as president on Jan. 1, 2025. Connors will succeed current president Robbee Baker Kosak, who will retire after almost 10 years in the role.
Appointed by the Hertz Foundation board of directors, Connors is the sixth president of the foundation and second woman to hold the position since it was founded in 1957. She brings more than 25 years’ experience as an accomplished nonprofit executive ...
A tool to enhance the taste and texture of sourdough and study the complexity of microbiomes
2024-10-01
When millions of people went into lockdown during the pandemic, they went in search of new at-home hobbies to help cure their boredom. Among them was making sourdough bread. In addition to being sustainable for its use of natural ingredients and traditional methods which date back thousands of years to ancient Egypt, it also is valued for its nutritional benefits. For example, studies have shown that sourdough contains more vitamins, minerals and antioxidants compared to many other types of bread. For people with mild sensitivities to gluten, sourdough bread can be easier to digest since much of the gluten is broken down during ...
Structure of a eukaryotic CRISPR-Cas homolog, Fanzor2, shows its promise for gene editing
2024-10-01
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – October 1, 2024) A revolution in biomedicine is currently underway, driven by the application of genome engineering tools such as the prokaryotic CRISPR-Cas9. New genome editing systems continue to be identified in different organisms, adding to the potential toolbox for various therapeutic applications. Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital studied the evolutionary journey of Fanzors, eukaryotic genome-editing proteins. Using cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), the researchers provided insights into the structural divergence ...
St. Jude names M. Madan Babu, PhD, senior vice president and chief data scientist
2024-10-01
St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital today announced M. Madan Babu, PhD, FRS, as the institution’s first Chief Data Scientist, Senior Vice President for Data Science, and leader of the newly formed Office of Data Science. This $195 million research enterprise will have 115 new positions.
In his new role, Babu will bring new, advanced computing technologies and data science approaches to biomedical research. His team will also facilitate the integration of biological and biomedical ...
It all adds up: Study finds forever chemicals are more toxic as mixtures
2024-10-01
BUFFALO, N.Y. — A first-of-its-kind study has measured the toxicity of several types of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), better known as “forever chemicals,” when mixed together in the environment and in the human body.
The good news: Most of the tested chemicals’ individual cytotoxicity and neurotoxicity levels were relatively low.
The bad news: the chemicals acted together to make the entire mixture toxic.
“Though they are structurally similar, not all forever chemicals are ...
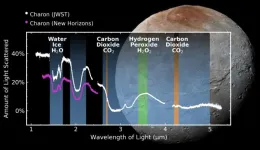
SwRI-led team discovers carbon dioxide and hydrogen peroxide on Pluto’s moon Charon
2024-10-01
SAN ANTONIO — October 1, 2024 — A Southwest Research Institute-led team has detected carbon dioxide and hydrogen peroxide for the first time on the frozen surface of Pluto’s largest moon, Charon, using observations from the James Webb Space Telescope. These discoveries add to Charon’s known chemical inventory, previously identified by ground- and space-based observations, that includes water ice, ammonia-bearing species and the organic materials responsible for Charon’s gray and red coloration.
“Charon is the only midsized Kuiper Belt object, in the range of 300 to 1,000 miles in diameter, that has been geologically mapped, thanks ...
More clarity on hereditary colorectal cancer
2024-10-01
The genetic confirmation of a suspected diagnosis of "hereditary colorectal cancer" is of great importance for the medical care of affected families. However, many of the variants identified in the known genes cannot yet be reliably classified in terms of their causal role in tumor formation. Under the leadership of the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and the University of Bonn, an international team of researchers has reassessed the medical relevance of a significant number of unclear variants and thus significantly ...
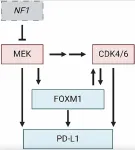
FOXM1 and PD-L1 in CDK4/6-MEK resistance in nerve tumors
2024-10-01
“We suggest that future therapeutic strategies targeting the oncogenic network of CDK4/6, MEK, PD-L1, and FOXM1 represent exciting future treatment options for MPNST patients.”
BUFFALO, NY- October 1, 2024 – A new mini review was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on September 30, 2024, entitled, “Linking FOXM1 and PD-L1 to CDK4/6-MEK targeted therapy resistance in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors.”
As highlighted in the abstract of this paper, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNSTs) are aggressive, Ras-driven sarcomas characterized ...
McMaster University researchers identify new therapeutic approach to preventing cancer from spreading to the brain
2024-10-01
Researchers at McMaster University have identified a new therapeutic approach to preventing cancer from spreading to the brain.
In a new study, published recently in the journal Cell Reports Medicine, researchers Sheila Singh and Jakob Magolan discovered a critical vulnerability in metastatic brain cancer, which they say can be exploited with new drugs to prevent spread.
Singh, a professor in McMaster’s Department of Surgery and director of the Centre for Discovery in Cancer Research, says brain metastases are becoming increasingly prevalent and are extremely fatal, with 90 per cent of patients dying within one ...
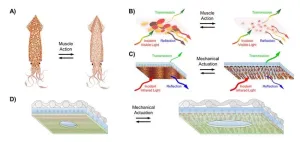
Squid-inspired fabric for temperature-controlled clothing
2024-10-01
WASHINGTON, October 1, 2024 – Too warm with a jacket on but too cold without it? Athletic apparel brands boast temperature-controlling fabrics that adapt to every climate with lightweight but warm products. Yet, consider a fabric that you can adjust to fit your specific temperature needs.
Inspired by the dynamic color-changing properties of squid skin, researchers from the University of California, Irvine developed a method to manufacture a heat-adjusting material that is breathable and washable and can be integrated into flexible fabric. They published their ...
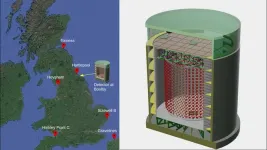
Using antimatter to detect nuclear radiation
2024-10-01
WASHINGTON, Oct. 1, 2024 – Nuclear fission reactors act as a key power source for many parts of the world and worldwide power capacity is expected to nearly double by 2050. One issue, however, is the difficulty of discerning whether a nuclear reactor is being used to also create material for nuclear weapons. Capturing and analyzing antimatter particles has shown promise for monitoring what specific reactor operations are occurring, even from hundreds of miles away.
In AIP Advances, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Sheffield and the University of Hawaii developed ...
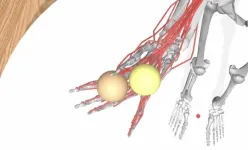
Modeling the minutia of motor manipulation with AI
2024-10-01
In neuroscience and biomedical engineering, accurately modeling the complex movements of the human hand has long been a significant challenge. Current models often struggle to capture the intricate interplay between the brain's motor commands and the physical actions of muscles and tendons. This gap not only hinders scientific progress but also limits the development of effective neuroprosthetics aimed at restoring hand function for those with limb loss or paralysis.
EPFL professor Alexander Mathis and his team have developed an AI-driven approach that ...
Survival gap eliminated for Black cord blood recipients with blood cancers, study finds
2024-10-01
Patients who receive umbilical cord blood transplants for blood cancers now live equally long regardless of their race, new research from UVA Cancer Center shows.
The findings, from UVA Health’s Karen Ballen, MD, and collaborators, suggests that a previously identified survival gap for Black recipients has closed and that overall survival for all recipients has increased.
The retrospective analysis looked at more than 2,600 adults and children with blood cancers who received cord blood between 2007 and 2017 ...
Nominate a stroke hero today: 2025 Stroke Hero Awards open for submissions
2024-10-01
DALLAS, Oct. 1, 2024 – Strokes can strike at any age, challenging survivors to overcome physical, emotional and cognitive changes. Nominations are open now for the 2025 Stroke Hero Awards from the American Stroke Association, a division of the American Heart Association, which is celebrating a century of lifesaving impact this year. The awards recognize stroke survivors, caregivers, advocates and experts making a difference in the stroke community.
Every 40 seconds someone in the U.S. has a stroke[1], according to the American Heart Association’s 2024 Heart Disease and Stroke Statistical Update. Nearly 1 in 4 stroke survivors face the ...
Seven years on, INSEAD study reveals #MeToo's unexpected impact
2024-10-01
Seven years after actor Alyssa Milano’s tweet launched the #MeToo movement into the global consciousness, attitudes towards sexual harassment and assault have shifted in many countries. A new study shows that the movement’s impact doesn’t stop there.
INSEAD professors Frédéric Godart and David Dubois, alongside Clément Bellet of Erasmus University Rotterdam, found that #MeToo triggered far-reaching changes in consumer behaviour. Sales of stereotypically feminine shoes like high heels dropped significantly weeks after the #MeToo movement swept the media ...
Addressing the geriatric healthcare workforce shortage
2024-10-01
INDIANAPOLIS – The pandemic has highlighted the acute shortage of nurses and nursing assistants needed to care for the growing number of older adults in long-term care facilities. Yet getting nursing students excited, engaged and feeling competent to take on the challenges of caring for nursing home patients has proved elusive.
To address this critical workforce gap, researchers from Regenstrief Institute and the Indiana University School of Medicine have developed and tested an innovative curriculum for nursing students, exposing ...
Age trumps gender, income and postcode for consumers' clothing habits
2024-10-01
The first-ever nationwide study into how Australians use and dispose of clothing has revealed people are buying too many clothes and are unsure how to discard them responsibly.
Conducted by RMIT University and commissioned by the Kmart Group and the Queensland Government, a study of 3,080 Australians explored how they acquired, used and disposed of their clothing.
Australians are among the world’s biggest clothing consumers, importing 1.4 billion units or over 383,000 tonnes annually.
But each year, more than 200,000 tonnes of clothing is sent to landfill.
The authors recommend establishing a national textile collection program for unwearable clothing that ...
Researchers develop method to obtain fine spatial and temporal resolution land surface temperature data
2024-10-01
Scientists need fine spatial and temporal resolution land surface temperature (LST) data for many types of research and applications. Spatio-temporal fusion, a technique that combines data from multiple sources to create high-resolution images with both spatial (space) and temporal (time) details, is an important solution for researchers needing fine spatio-temporal resolution LST data. A team of researchers propose a new spatio-temporal fusion method based on Restormer (RES-STF).
Their work is published in the Journal of Remote Sensing on August 21, 2024.
LST data, the measurement ...
Feet first: AI reveals how infants connect with their world
2024-10-01
Recent advances in computing and artificial intelligence, along with insights into infant learning, suggest that machine and deep learning techniques can help us study how infants transition from random exploratory movements to purposeful actions. Most research has focused on babies’ spontaneous movements, distinguishing between fidgety and non-fidgety behaviors.
While early movements may seem chaotic, they reveal meaningful patterns as infants interact with their environment. However, we still lack understanding of how infants intentionally engage with their surroundings and the principles guiding their ...
Addressing health equity in childhood asthma requires engaging affected communities
2024-10-01
NEW YORK, NY (Oct. 1, 2024) – Systemic racism remains a significant challenge in efforts to address health disparities in childhood asthma. A new American Thoracic Society report provides practical frameworks to begin the research necessary to make real progress in treating asthma in Black and Latino children, who are more likely than their white counterparts to report to emergency rooms in the U.S.
Stephanie Lovinsky-Desir, MD, and a diverse group of researchers, clinicians, social scientists and community health workers shared their findings in the report published online this week in ...
[1] ... [902]
[903]
[904]
[905]
[906]
[907]
[908]
[909]
910
[911]
[912]
[913]
[914]
[915]
[916]
[917]
[918]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.