A new and unique fusion reactor comes together with PPPL's contributions
2024-09-30
Like atoms coming together to release their power, fusion researchers worldwide are joining forces to solve the world’s energy crisis. Harnessing the power of fusing plasma as a reliable energy source for the power grid is no easy task, requiring global contributions.
The Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) — a U.S. national laboratory funded by the Department of Energy (DOE) — is leading several efforts on this front, including collaborating on the design and development of a new fusion device at the University of Seville in Spain. The SMall Aspect Ratio Tokamak (SMART) strongly ...
Reduced risk of serious cardiovascular disease after COVID vaccination
2024-09-30
People who have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19 have a significantly lower risk of developing more severe cardiovascular conditions linked to COVID-19 infection, according to a nationwide study at the University of Gothenburg. At the same time, some cardiovascular effects are seen after individual doses of the vaccine.
The COVID-19 vaccine aims to reduce complications and overall mortality from the disease. At the same time, some cardiovascular effects have been seen after individual doses of the vaccine. A rare acute side effect is inflammation of the cardiac muscle or the pericardium in young men following mRNA vaccination. In terms of other cardiovascular ...
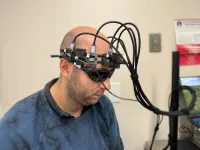
New laser-based headset can measure blood flow, assess risk of stroke
2024-09-30
When physicians want to know more about a patient’s risk of cardiovascular disease, they can order a cardiac stress test. But when it comes to risk of stroke, there is no equivalent scalable and cost-effective test of the brain’s function to help physicians counsel patients on their potential risk. A questionnaire that asks patients about contributing risk factors is currently the best tool for estimating such risk.
Now a team of engineers and scientists from Caltech and the Keck School ...
Researchers close in on understanding possible cause of Alzheimer’s disease
2024-09-30
CLEVELAND—With a four-year, $3.3 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), researchers from Case Western Reserve University will study whether certain brain proteins may play a role in the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
Alzheimer’s disease is a brain disorder that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills. According to the Alzheimer’s Association, nearly 7 million Americans 65 and older are living with the disease and there are more deaths from Alzheimer’s than breast and prostate cancer combined.
Previous research has ...
New synthesis strategy could speed up PFAS decontamination
2024-09-30
HOUSTON – (Sept. 30, 2024) – Rice University engineers have developed an innovative way to make covalent organic frameworks (COFs), special materials that can be used to trap gases, filter water and speed up chemical reactions. COFs have the potential to address significant environmental challenges, including energy storage and pollution control. An example of that is their potential use in the decontamination of “forever chemicals” or per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS).
Rice chemical engineer Rafael Verduzco and his team have described a new way to synthesize high-quality ...
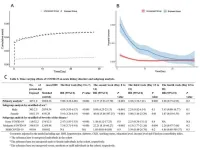
COVID-19 linked to increased risk of acute kidney disorders: New study reveals time-varying effects
2024-09-30
Researchers from West China Hospital, Sichuan University, have conducted a study revealing a significant association between COVID-19 and acute kidney disorders (AKD), including acute kidney injury (AKI), that varies over time. The study, led by Dr. Li Chunyang and Dr. Zeng Xiaoxi from the West China Biomedical Big Data Center, was recently published in the journal Health Data Science.
COVID-19, known for its impact on the respiratory system, also affects other organs, including the kidneys. The study aimed to investigate the time-dependent effects of COVID-19 on acute kidney disorders. Using data from the ...
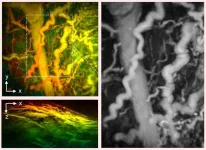
Medical imaging breakthrough could transform cancer and arthritis diagnosis
2024-09-30
A new hand-held scanner developed by UCL researchers can generate highly detailed 3D photoacoustic images in just seconds, paving the way for their use in a clinical setting for the first time and offering the potential for earlier disease diagnosis.
In the study, published in Nature Biomedical Engineering, the team show their technology can deliver photoacoustic tomography (PAT) imaging scans to doctors in real time, providing them with accurate and intricate images of blood vessels, helping inform patient care.
Photoacoustic ...
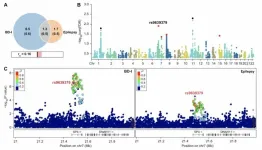
Genetic link between bipolar disorder and epilepsy unveiled in groundbreaking study
2024-09-30
Kunming, China - A team of researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences has uncovered compelling evidence of a genetic link between bipolar disorder type I (BD-I) and epilepsy, potentially revolutionizing our understanding of these complex neuropsychiatric conditions. The study, published in Genomic Psychiatry on September 30, 2024, reveals shared genetic variants and a causal relationship between the two disorders, opening new avenues for research and treatment.
Led by Dr. Ming Li from the Kunming ...
Social networks help people resolve welfare problems - but only sometimes, new research finds
2024-09-30
Lead researcher Dr Sarah Nason, from Bangor University’s School of History, Law and Social Sciences explained: “Debt, benefits, special educational needs, healthcare issues, these are everyday problems that many of us face, and it’s only natural to turn to people you know and trust for help and advice. However, we found that having to talk to more people or support services was an indicator that the problem was more complex and difficult to resolve.”
The team studied four distinct areas across England and Wales: Bryngwran, a village on Anglesey in North Wales; Deeplish, a district of Rochdale in Greater ...
Honey, I shrunk the city: What should declining Japanese cities do?
2024-09-30
Aging societies and population decline have been on the rise globally, but in Japan, the situation has exasperated tenfold. A staggering 36.21 million people, or 28.9% of the populace, are 65 and over. Further, 74.6% of Japan’s 1,747 cities are categorized as shrinking, with urban policies struggling to keep up with the decline. However, the factors that correlate with population changes in cities of varying sizes have not been clarified.
Dr. Haruka Kato, a junior associate professor at Osaka Metropolitan University, ...
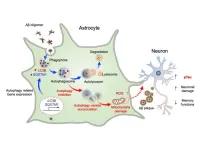
New brain cell cleaner: astrocytes raise possibility of Alzheimer’s disease treatment
2024-09-30
A research team led by Dr. Hoon Ryu from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, President Sang-Rok Oh) Brain Disease Research Group, in collaboration with Director Justin C. Lee of the Institute for Basic Science (IBS, President Do-Young Noh) and Professor Junghee Lee from Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, has uncovered a new mechanism involving astrocytes for treating Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and proposed a novel therapeutic target. In this study, the researchers revealed that autophagy pathway ...
American Academy of Pediatrics announces its first clinical practice guideline for opioid prescriptions
2024-09-30
Media contacts:
Lisa Robinson, lrobinson@aap.org
Alex Hulvalchick, ahulvalchick@aap.org
American Academy of Pediatrics Announces its First Clinical Practice Guideline for Opioid Prescriptions
Pediatricians should prescribe opioids for pain when necessary, with recommended precautions in place to increase safety, according to a clinical practice guideline released during the AAP 2024 National Conference & Exhibition
ORLANDO, Fla.--The American Academy of Pediatrics has published its first clinical ...
Drivers of electric vehicles are more likely to be at fault in road traffic crashes than drivers of petrol and diesel cars
2024-09-30
Drivers of electric vehicles (EVs) are more likely to be involved in at-fault road traffic accidents than drivers of petrol and diesel cars, research by Lero, the Research Ireland Centre for Software, at University of Limerick and Universitat de Barcelona, reveals.
In the analysis of insurance claims and data from onboard sensors, due to be published in the November issue of the journal Accident Analysis & Prevention, the Lero researchers reveal a number of key findings:
Electric and hybrid drivers exhibit different behaviours ...
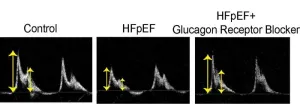
Duke-NUS study proposes new heart failure treatment targeting abnormal hormone activity
2024-09-30
Duke-NUS scientists and their collaborators have discovered a potential new treatment for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), a type of heart disease that is notoriously difficult to treat. The team discovered that the diseased heart cells had high levels of glucagon activity, a pancreatic hormone that raises blood sugar (glucose) levels. Armed with this novel insight, the scientists demonstrated that a drug that blocks the hormone’s activity, can significantly improve heart ...
People who experience side effects from cranial radiation therapy may recover full neurocognitive function within months
2024-09-29
WASHINGTON, September 29, 2024 — A substantial number of patients with brain metastases who experience cognitive side effects following radiation therapy may fully regain cognitive function, according to a pooled analysis of three large, phase III clinical trials. Recovery was more likely for people treated with conformal, or highly targeted, radiation techniques, compared to standard whole-brain treatment. The findings will be presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) ...
Radiopharmaceutical therapy offers promise for people with tough-to-treat meningioma brain tumors
2024-09-29
WASHINGTON, September 29, 2024 — A radiopharmaceutical therapy that has successfully extended progression-free survival for patients with neuroendocrine tumors shows early promise for delivering similar benefits to patients with difficult-to-treat meningioma, a type of brain tumor. Findings of the nonrandomized phase II study will be presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) Annual Meeting.
“We’ve found a therapy with a meaningful signal for effectiveness and safety for people with refractory meningioma, a condition with no ...
American Academy of Pediatrics promotes shared reading starting in infancy as a positive parenting practice with lifelong benefits
2024-09-29
ORLANDO, Fla.--The American Academy of Pediatrics encourages parents and caregivers to read aloud with their newborns and young children as an opportunity to foster loving, nurturing relationships during a critical time of brain development, and recommends that pediatricians support families with guidance and books at well-child visits, according to an updated policy statement.
The policy statement, “Literacy Promotion: An Essential Component of Primary Care Pediatric Practice,” marks the first update in AAP recommendations since 2014. Given the extraordinary amount of research in this area, an accompanying ...
Unexpected human behaviour revealed in prisoner's dilemma study: Choosing cooperation even after defection
2024-09-28
The study also examined the impact of different game structures, such as simultaneous versus alternating decision-making, and the option of voluntary participation. The results showed that these variations significantly influence participants' cooperation rate.
The research reveals that people tend to cooperate even after being defected, which contradicts many traditional game theory models. "This finding is particularly fascinating because it suggests that humans are more forgiving and cooperative than previously thought," said Dr. Hitoshi Yamamoto, the study's lead researcher.
The ...
Distant relatedness in biobanks harnessed to identify undiagnosed genetic disease
2024-09-27
An innovative analysis of shared segments within the genome — an indication of distant “relatedness” — has identified undiagnosed cases of Long QT syndrome, a rare disorder that can lead to abnormal heart rhythms, fainting and sudden cardiac death.
The findings, reported in the journal Nature Communications, illustrate the feasibility of the new approach developed by researchers at Vanderbilt University Medical Center to detect undiagnosed carriers of rare ...
UCLA at ASTRO: Predicting response to chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer, 2-year outcomes of MRI-guided radiotherapy for prostate cancer, impact of symptom self-reporting during chemoradiation and mor
2024-09-27
UCLA Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center researchers and physicians who specialize in treating patients with radiation therapies will present data on the latest radiation oncology research and clinical trial results at the 66th annual American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) meeting in Washington D.C., Sept. 29 to Oct. 2.
The annual meeting, which is the leading meeting in radiation oncology, will feature 23 abstracts from UCLA investigators that highlight key areas of radiation oncology, including new research in subspecialties ranging from survivorship, lung cancer/thoracic malignancies, physics, sarcoma, gastrointestinal cancer, genitourinary cancer, gynecological ...
Estimated long-term benefits of finerenone in heart failure
2024-09-27
About The Study: In this prespecified secondary analysis of the FINEARTS-HF randomized clinical trial, long-term treatment with the nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist finerenone was estimated to extend event-free survival by up to 3 years among people with heart failure with mildly reduced or preserved ejection fraction.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Scott D. Solomon, M.D., email ssolomon@rics.bwh.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at ...
MD Anderson launches first-ever academic journal: Advances in Cancer Education & Quality Improvement
2024-09-27
The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center today announced its first-ever academic journal, Advances in Cancer Education & Quality Improvement (ACE-QI). The journal will publish research, training program summaries and quality improvement interventions for the oncology provider community.
The open-access, peer-reviewed journal will feature research and professional perspectives focused on training health care providers to meet myriad challenges around prevention, diagnosis, treatment and survivorship in cancer care.
“We envision this journal as a catalyst for critical conversations across the cancer care continuum," said Joshua Kuban, M.D., associate ...
Penn Medicine at the 2024 ASTRO Annual Meeting
2024-09-27
PHILADELPHIA – Leading experts in radiation therapy from Penn Medicine’s Abramson Cancer Center and the Perelman School of Medicine will present new results from clinical trials and research studies at the American Society for Radiation Oncology's (ASTRO) 66th Annual Meeting, which will be held at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center in Washington, D.C., Sept. 29 through Oct. 2, 2024.
At the meeting, Neha Vapiwala, MD, FACR, FASTRO, FASCO, the Eli Glatstein Professor in Radiation Oncology, will take office as president-elect of ASTRO as the first Penn faculty member to lead the premier society ...
Head and neck, meningioma research highlights of University of Cincinnati ASTRO abstracts
2024-09-27
University of Cincinnati Cancer Center experts will present research at the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) Annual Meeting Sept. 29 through Oct. 2.
Osteoradionecrosis more common in patients with head and neck cancer that requires partial jaw removal
Following radiation treatment for head and neck cancer, some patients can experience osteoradionecrosis (ORN) when an area of exposed bone fails to heal after a three-month period.
“ORN of the mandible and maxilla (jaw bones) can be very debilitating, as it often causes severe pain, fistula formation, infection and susceptibility to fractures,” ...
Center for BrainHealth receives $2 million match gift from Adm. William McRaven (ret.), recipient of Courage & Civility Award
2024-09-27
Center for BrainHealth® at The University of Texas at Dallas has received a major match gift commitment from retired U.S. Navy four-star admiral and former University of Texas System chancellor William McRaven and his wife Georgeann. Adm. McRaven recently received the 2024 Bezos Courage & Civility Award presented by Amazon founder Jeff Bezos and Lauren Sánchez.
The $2 million challenge grant will support Optimal BrainHealth for Warfighters – including active-duty military, spouses and veterans. This program will help those with traumatic brain injury (TBI), post-traumatic stress (PTS) and similar issues, as well ...
[1] ... [906]
[907]
[908]
[909]
[910]
[911]
[912]
[913]
914
[915]
[916]
[917]
[918]
[919]
[920]
[921]
[922]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.