Attivare licenses Wyss Institute’s immune-modulating biomaterial technology to advance immunotherapies
2024-10-02
Attivare licenses Wyss Institute’s immune-modulating biomaterial technology to advance immunotherapies
The company is developing the biomaterial-based technology to develop novel therapies able to program anti-cancer immunity and prevent infectious diseases
By Benjamin Boettner
(BOSTON) — Today, the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University and Attivare Therapeutics Inc. announced that Attivare has licensed a portfolio of immune-modulating biomaterial technologies from Harvard University that was created at the ...
Regenstrief, Fairbanks researcher among 25 fellows to be inducted into American College of Medical Informatics
2024-10-02
The American College of Medical Informatics (ACMI) has announced that Chris Harle, PhD, of the Indiana University Richard M. Fairbanks School of Public Health and the Regenstrief Institute will be inducted as one of 25 new fellows on November 10 in San Francisco, CA, at ceremonies during the American Medical Informatics Association (AMIA) 2024 Annual Symposium.
ACMI is a college of elected fellows who have made significant and sustained contributions to the field of biomedical informatics. Individuals who have achieved national recognition in the field and are committed to advancing ...
Ontario Institute for Cancer Research funding aims to speed the development of new drugs for some of the most common cancers
2024-10-02
October 2, 2024, TORONTO – The Ontario Institute for Cancer Research (OICR) continues to support Ontario drug discovery research by funding high-quality investigations of new therapies for some of the most prevalent pediatric and adult cancers. These projects are tackling substantial challenges in cancer by increasing the effectiveness and availability of immunotherapies, making cancer more vulnerable to chemotherapy and developing a new drug for one of the deadliest forms of childhood brain cancer.
OICR’s Cancer Therapeutics Innovation Pipeline (CTIP) initiative is supporting three research teams ...
Trust in US Supreme Court continues to sink
2024-10-02
PHILADELPHIA – Driven by political partisanship, public trust in the U.S. Supreme Court has continued a downward slide since the court’s 2022 Dobbs decision overturning the Roe v. Wade ruling that established a constitutional right to abortion, according to a new survey by the Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC) of the University of Pennsylvania.
More than half of Americans (56%) now disapprove of the Supreme Court, saying they trust it either “a little” or “not at all” to act in the best interest ...
Rice’s Biotech Launch Pad to lead commercialization of bioelectrical implant treatment for obesity, type 2 diabetes
2024-10-02
Rice University is part of a multiuniversity research team that has secured an award of up to $34.9 million from the Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H) to accelerate the development of a bioelectronic implant designed to improve adherence for obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D) treatment while reducing development and manufacturing costs.
Rice University’s Biotech Launch Pad will lead the commercialization effort for “Rx On-site Generation Using Electronics” (ROGUE), a self-contained, durable implantable device that houses cells engineered ...
Carnegie Mellon to lead development of implantable cell-based bioelectronic devices for patient-specific treatment and disease monitoring
2024-10-02
PITTSBURGH – A Carnegie Mellon University-led team has secured an award of up to $42 million from the Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H) to accelerate the development of implantable, cell-based bioelectronic devices that deliver patient-specific therapy and monitor disease status, for conditions like hypo- and hyperthyroidism, in real time. This award is part of the ARPA-H REACT program, which supports the advancement of implantable bioelectronic devices to improve patient management of chronic diseases.
Burak ...
Case Western Reserve, Vanderbilt universities to develop incisionless prostate surgery using MRI and robotics
2024-10-02
CLEVELAND—Researchers at Case Western Reserve University and Vanderbilt University are pioneering a new approach to prostate cancer surgery by combining advanced robotics and “low-field” MRI technology.
The research aims to allow highly accurate, patient-tailored prostate cancer surgeries without the need for traditional incisions. This innovative research marks a major step in developing minimally invasive treatments for prostate cancer, with the potential to improve both safety and efficiency for patients.
The project is being funded by a new five-year, $3.7 million grant from the National Cancer Institute, part of the ...
Carnegie Mellon University secures ARPA-H award to improve adherence, lower cost of treatment for obesity and Type 2 diabetes patients
2024-10-02
PITTSBURGH – A Carnegie Mellon University-led team of researchers has secured an award of up to $34.9 million from the Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H). The funds will fast track a bioelectronic implant that could radically improve treatment options and significantly reduce the cost of care for patients with obesity and Type 2 diabetes.
The award will drive the accelerated development and testing of “Rx On-site Generation Using Electronics (ROGUE),” a bioelectrical device that hosts a “living pharmacy,” consisting of engineered cells that produce biological therapy to treat Type 2 diabetes and obesity. The device will offer continuous, ...
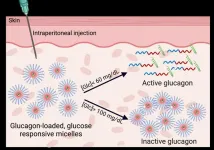
A new injectable to prevent and treat hypoglycemia
2024-10-02
People with diabetes take insulin to lower high blood sugar. However, if glucose levels plunge too low — from taking too much insulin or not eating enough sugar — people can experience hypoglycemia, which can lead to dizziness, cognitive impairment, seizures or comas. To prevent and treat this condition, researchers in ACS Central Science report encapsulating the hormone glucagon. In mouse trials, the nanocapsules activated when blood sugar levels dropped dangerously low and quickly restored glucose levels.
Glucagon is a hormone that signals the liver to ...
Turning plants into workout supplement bio-factories
2024-10-02
It’s important to eat your veggies, but some essential vitamins and nutrients can only be found in animals, including certain amino acids and peptides. But, in a proof-of-concept study published in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, researchers developed a method to produce creatine, carnosine and taurine — all animal-based nutrients and common workout supplements — right inside a plant. The system allows for different synthetic modules to be easily stacked together to boost production.
Plants can be surprisingly receptive when asked to produce compounds ...
Pablo Manavella appointed next Editor-In-Chief of The Plant Cell
2024-10-02
The American Society of Plant Biologists (ASPB) is excited to announce Pablo Manavella will serve as the next Editor-in-Chief of The Plant Cell. The Plant Cell is a leading international society journal that publishes novel research of special significance in plant biology, especially in the areas of cellular biology, molecular biology, biochemistry, genetics, development, and evolution.
Manavella is currently a Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC) researcher at the Institute for Mediterranean and Subtropical Horticulture (IHSM) in Málaga, Spain. He is the Principal Investigator in a lab focusing on the intricate mechanisms regulating ...
Unveiling genetic insights: how PAI-1 polymorphisms influence COVID-19 outcomes
2024-10-02
Despite global vaccination efforts, COVID-19 continues to pose significant risks, leading to severe complications and fatalities. These risks are driven by disrupted coagulation, impaired fibrinolysis, which is the process of breaking blood clots, and heightened inflammatory responses. The fibrinolytic system, crucial for maintaining balance within the coagulation cascade, relies on plasmin-mediated fibrin degradation. Plasminogen activators convert plasminogen into plasmin, an enzyme that breaks down ...
Redefining Publishing: PLOS receives multi-million-dollar grant funding for new research initiative
2024-10-02
SAN FRANCISCO —PLOS today announced that it has received a $1.5 million grant from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and a $1 million grant from the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation to support our mission to drive Open Science forward with meaningful change in scholarly publishing. The funds enable PLOS to embark on an ambitious 18-month research and design project to explore how to tackle two barriers that exclude many researchers from meaningfully participating in Open Science: affordability ...
Planning a drug’s route in the body with synthetic chemistry
2024-10-02
Researchers at the RIKEN Cluster for Pioneering Research (CPR) have developed technology that can alter, within the body, the recognized identity of proteins. The innovation, published in Nature Communications on October 2, allowed researchers to target mouse tumors with a protein and then transport that protein out of the body. This means that cancer-killing drugs could be sent directly to tumors and then excreted from the body after dropping off their payload. The technology also has the potential to allow multi-purpose drugs that can travel from organ to organ, performing ...
Smoke from megafires puts orchard trees at risk
2024-10-02
Smoke From Megafires Puts Orchard Trees at Risk
Effects Last Months, Reducing Nut Crop Yields
By Amy Quinton | October 2, 2023
Long-term smoke exposure from massive wildfires lowers the energy reserves of orchard trees and can cut their nut production by half, researchers at the University of California, Davis, found. The smoke can affect trees for months after a megafire, depressing their bloom and the next season’s harvest. This finding reveals a new danger from wildfires that could affect plant health in both agricultural and natural environments.
Nature Plants published ...
Health Data Research UK and National Research Foundation Singapore formalize landmark partnership in health data science
2024-10-02
Health Data Research UK (HDR UK) and the National Research Foundation Singapore (NRF) are pleased to have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) today, that formalises a collaborative partnership in healthcare and data science. The partnership will leverage cutting-edge data science and research, with a focus on trustworthy data use to power improvements in healthcare, research and innovation, strengthening existing links between the UK and Singapore.
The MoU was signed by Permanent Secretary for National Research and ...
CNIO researchers propose a new treatment for brain metastasis based on immunotherapy
2024-10-02
CNIO researchers have discovered that cancer perverts certain brain cells, the astrocytes, and causes them to produce a protein that works in favour of the tumour.
A drug, silibinin, inhibits this protein, and could be used to help treat brain metastasis with immunotherapy. A clinical trial is underway.
The work is published in the American Association for Cancer Research's journal Cancer Discovery.
Researchers at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) propose a new treatment for brain metastases that respond poorly, or not at all, to immunotherapy, and provide a biomarker to predict ...
Discovery of promising electrolyte for all-solid-state batteries
2024-10-02
Often overlooked, rechargeable batteries play an important part in contemporary life, powering small devices like smartphones to larger ones like electric vehicles. The keys to creating sustainable rechargeable batteries include having them hold their charge longer, giving them a longer life with more charging cycles, and making them safer. Which is why there is so much promise in all-solid-state batteries.
The problem so far is discovering which solid electrolytes offer such potential advantages.
In a step toward that goal, an Osaka Metropolitan University research group led by Assistant Professor Kota Motohashi, Associate Professor Atsushi Sakuda, ...
One-minute phone breaks could help keep students more focused in class and better in tests
2024-10-02
Phones can be useful tools in classrooms to remind students of deadlines or encourage more exchange between students and teachers. At the same time, they can be distracting: Students report using their phones for non-academic purposes as often as 10 times a day. Thus, in many classrooms, phones are not allowed.
Now, researchers in the US have investigated if letting students use their phones for very brief amounts of time – dubbed phone or technology breaks – can enhance classroom performance and reduce phone use.
“We show that technology breaks may be helpful for reducing cell phone use in the college classroom,” said Prof Ryan Redner, a ...
New study identifies gaps in menopause care in primary care settings
2024-10-02
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Oct 2, 2024)—Timely identification and treatment of bothersome hot flashes have the potential to improve the lives of many women and save employers countless days of related absenteeism and lost work productivity. Yet, a new study finds that such symptoms are often not documented in electronic health records (EHRs) or not adequately addressed during primary care visits. The study is published online today in Menopause, the journal of The Menopause Society.
Approximately 75% of women experience hot flashes as they go through the menopause transition. Despite the common occurrence of these bothersome ...
Do coyotes have puppy dog eyes? New study reveals wild canines share dog's famous expression
2024-10-02
New research from Baylor University reveals that coyotes, like domestic dogs, have the ability to produce the famous "puppy dog eyes" expression. The study – "Coyotes can do 'puppy dog eyes' too: Comparing interspecific variation in Canis facial expression muscles," published in the Royal Society Open Science – challenges the hypothesis that this facial feature evolved exclusively in dogs as a result of domestication.
The research team, led by Patrick Cunningham, a Ph.D. research student in the Department ...
Scientists use tiny ‘backpacks’ on turtle hatchlings to observe their movements
2024-10-02
New research suggests that green turtle hatchlings ‘swim' to the surface of the sand, rather than ‘dig’, in the period between hatching and emergence. The findings have important implications for conserving a declining turtle population globally.
Published today in Proceedings B, scientists from UNSW’s School of Biological, Earth and Environmental Sciences, used a small device, known as an accelerometer, to uncover novel findings into the behaviours of hatchlings as they emerge from their nests.
Sea turtle eggs are buried in nests 30 – 80cm deep. Once hatched, the newborn turtles make their way to the surface ...
Snakes in the city: Ten years of wildlife rescues reveal insights into human-reptile interactions
2024-10-02
A new analysis of a decade-long collection of wildlife rescue records in NSW has delivered new insights into how humans and reptiles interact in urban environments.
Researchers from Macquarie University worked with scientists from Charles Darwin University, and the NSW Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water to analyse over 37,000 records of snake and lizard rescues in the Greater Sydney region between 2011 and 2021.
Their study, Interactions between reptiles and people: a perspective from wildlife rehabilitation records is published in the journal Royal Society Open Science on Wednesday 2 October.
Lead author Teagan Pyne, ...
Costs of fatal falls among US older adults trump those attributed to firearm deaths
2024-10-01
The cost of fatal falls among older people (45-85+) trump those of firearm deaths in the US, finds research published in the open access journal Trauma Surgery & Acute Care Open.
The stark economics and shifting age demographics in the US underscore the urgency of preventive measures, conclude the researchers.
Falls account for around 1 in 5 of all injury-related hospital admissions, and the World Health Organization reports that falls are the second leading cause of unintentional injury deaths worldwide, with the over 65s especially vulnerable, highlight the researchers.
Like falls, firearms related injuries ...
Harmful diagnostic errors may occur in 1 in every 14 general medical hospital patients
2024-10-01
Harmful diagnostic errors may be occurring in as many as 1 in every 14 (7%) hospital patients—at least those receiving general medical care—suggest the findings of a single centre study in the US, published online in the journal BMJ Quality & Safety.
Most (85%) of these errors are likely preventable and underscore the need for new approaches to improving surveillance to avoid these mistakes from happening in the first place, say the researchers.
Previously published reports suggest that current trigger tools for ...
[1] ... [900]
[901]
[902]
[903]
[904]
[905]
[906]
[907]
908
[909]
[910]
[911]
[912]
[913]
[914]
[915]
[916]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.