Light-based microcapillary monitoring sparks innovation in manufacturing and biotechnology
2024-10-01
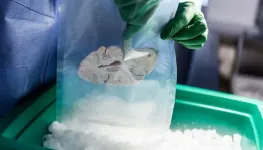
Dr. Jaeyeon Pyo of the Smart 3D Printing Research Team at the Korea Electrotechnology Research Institute (KERI) has developed a breakthrough technology that uses light to visualize nanoscale glass microcapillary tips, enabling precise and delicate contact with other objects.
A “‘Microcapillary” is a precision tool with a very small aperture (0.1 mm to 0.000010 mm in diameter) fabricated from a glass tube. It is utilized as a vital tool in various fields, from biotechnology to manipulate cells, to micro electroplating and nano 3D printing. Specifically, it is used in biotechnology faor tasks such as injecting sperm into an egg during in vitro fertilization (IVF) ...
Global effort to map the human brain releases first data
2024-10-01
Seattle, WA – October 1, 2024 – The BRAIN Initiative® Cell Atlas Network (BICAN) has launched its first major data release, marking a significant milestone in the ambitious effort to map the whole human brain.
The data, accessible through the BICAN Rapid Release Inventory, includes single-cell and single-nucleus transcriptomic and epigenomic profiles from humans, mice, and 10 other mammalian species. Sourced from multiple grants and labs within the consortium, including the Allen Institute, these data are from projects that aim to identify and define brain cell types based on molecular profiles.
“The ...
Scientists discover planet orbiting closest single star to our Sun
2024-10-01
Using the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope (ESO’s VLT), astronomers have discovered an exoplanet orbiting Barnard’s star, the closest single star to our Sun. On this newly discovered exoplanet, which has at least half the mass of Venus, a year lasts just over three Earth days. The team’s observations also hint at the existence of three more exoplanet candidates, in various orbits around the star.
Located just six light-years away, Barnard’s star is the second-closest stellar system — after Alpha Centauri’s three-star group — and the closest individual star to us. Owing to its proximity, it is a primary target in ...
New ACS report: Breast cancer mortality continues three decade decline overall, but steeper increases in incidence for women
2024-10-01
The American Cancer Society (ACS) today released Breast Cancer Statistics, 2024, the organization’s biennial update on breast cancer occurrence and trends in the United States. The new report finds breast cancer mortality rates overall have dropped by 44% since 1989, averting approximately 517,900 breast cancer deaths. However, not all women have benefited from this progress, notably American Indian and Alaska Native (AIAN) women, whose rates have remained unchanged over the past three decades. Also concerning ...
Immigrants to the United States still assimilate
2024-10-01
Children of immigrants to the United States typically incorporate themselves into US economic and cultural life, and this pattern of assimilation has not markedly changed in over a century. Today, one in seven US residents was born abroad, rates similar to those seen in the late nineteenth century. As immigrants’ countries of origin have shifted from Europe to Asia and the Americas, a narrative has developed that contemporary immigrants do not assimilate as thoroughly as older immigrants. But is this true? In a Perspective, Ran Abramitzky and Leah Boustan summarize their long-running research program matching individuals across historical US Censuses. The authors compare ...
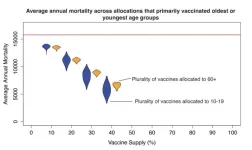
Vaccinating the young to save the old in the Tropics
2024-10-01
A model suggests that vaccinating children and teens against the flu can help protect the elderly in tropical countries. Influenza kills up to 650,000 people worldwide every year. In part due to the lack of strong seasonality and differences in vaccine supply, optimal vaccination strategies for the tropics may differ from those in temperate zones. Joseph Servadio and colleagues parameterized an age-structured mathematical model of influenza transmission to the asynchronous, non-annual epidemiology of tropical influenza in Vietnam, a country with low vaccine coverage. The model includes three subtypes of the flu virus. Vaccinating year-round was found to be ...
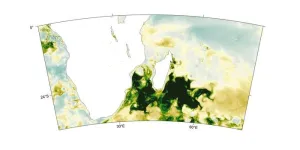
Climate change, drought, dust, and plankton blooms
2024-10-01
A study links an unusual plankton bloom off the coast of Madagascar to drought in Southern Africa. Climate warming has intensified droughts around the world. When vegetation dies from lack of water, the wind can pick up and carry unprotected soil particles for thousands of kilometers. These dust particles can then act as fertilizer when deposited in seawater. Dionysios Raitsos and colleagues show that dust from drought-stricken Southern Africa caused a bloom of marine phytoplankton off the southeast Madagascar coast from November 2019 through February 2020. The team used standardized anomalies of dust aerosol optical depth from the Copernicus ...
Nudges fail to reduce online hate
2024-10-01
Seven nudges aiming to reduce hateful speech online all failed—but the nudges unexpectedly succeeded in increasing engagement with harmless and wholesome content. Controlling hate speech is an ongoing challenge for online communities. In a pre-registered experiment, Tatiana Celadin and colleagues compared the effects of seven “nudges,” messages designed to promote prosocial behaviors: reminding posters of descriptive norms, injunctive norms, or personal norms; cooling down negative emotions; stimulating deliberation or empathy; and highlighting reputation. Over 4,000 Americans recruited through the online platform ...
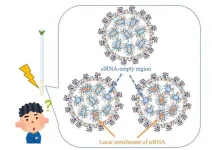
NMR-guided optimization of lipid nanoparticles for enhanced siRNA delivery
2024-10-01
Small interfering RNA (siRNA) molecules hold immense potential for treating diseases by silencing specific genes. Encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), siRNA can be delivered efficiently to target cells. However, the effectiveness of these therapies hinges on the internal structure of the LNPs, which can significantly impact their ability to deliver siRNA. Traditional methods often fall short in providing the detailed molecular insights needed to fine-tune LNP design for optimal therapeutic efficacy.
A study published in the Journal of Controlled Release on August 02, 2024, led by Assistant Professor Keisuke Ueda from ...
Mount Sinai leaders receive prestigious awards during the American College of Emergency Physicians 2024 Scientific Assembly (ACEP24)
2024-10-01
Mount Sinai Health System’s Chief Executive Officer (CEO) and the Emergency Department Chair at Mount Sinai Queens have been recognized with top honors for their outstanding achievements at the American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP) 2024 Scientific Assembly in Las Vegas during a special ceremony on Monday, September 30.
Brendan G. Carr, MD, MS, FACEP, CEO, Professor and Kenneth L. Davis, MD, Distinguished Chair of the Mount Sinai Health System, received the Colin C. Rorrie, Jr, PhD Award for Excellence in Health Policy.
This award is an extraordinary ...
Women more likely to choose wine with feminine labels
2024-10-01
PULLMAN, Wash. – To appeal to the majority of consumers, winemakers may want to pay as much attention to what’s on the bottle as what’s in it.
A three-part experimental study led by Washington State University researchers found that women were more inclined to purchase wine that had labels with feminine gender cues. The more strongly the participants identified with other women, a phenomenon called “in-group identification,” the greater this effect was. A feminine label also influenced their expectation that they would like the wine better.
With women representing 59% ...
Understanding regional climate change is essential for guiding effective climate adaptation policy, study finds
2024-10-01
The effects of climate change are not distant future scenarios or confined to remote parts of the world—they are unfolding now, right in our own backyards. In 2023, extreme weather events impacted communities across every inhabited continent, causing major flooding, droughts, and wildfires.
While worldwide changes, such as increases in global mean temperature, often dominate discussions of mitigation actions, a detailed understanding of the regional impacts of a warming world is crucial for protecting communities from escalating risks. A team of researchers writing in Frontiers in Science synthesized results ...
New AI model efficiently reaches clinical-expert-level accuracy in complex medical scans
2024-10-01
UCLA researchers have developed a deep-learning framework that teaches itself quickly to automatically analyze and diagnose MRIs and other 3D medical images – with accuracy matching that of medical specialists in a fraction of the time. An article describing the work and the system’s capabilities is published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
Unlike the few other models being developed to analyze 3D images, the new framework has wide adaptability across a variety of imaging modalities. The developers have studied it with 3D retinal scans (optical coherence tomography) for disease ...
Cool roofs could have saved lives during London’s hottest summer
2024-10-01
As many as 249 lives could have been saved in London during the 2018 record-setting hot summer had the city widely adopted cool roofs, estimates a new study by researchers at UCL and the University of Exeter.
The paper, published in Nature Cities, analysed the cooling effect that roofs painted white or other reflective colours would have on London’s ambient temperature between June and August 2018, the city’s hottest summer. From June through August, the average temperature around London was 19.2 degrees C, about ...
Solidarity drives online virality in a nation under attack, study of Ukrainian social media reveals
2024-10-01
While divisive social media posts get more traction in countries such as the US, a new study shows that celebrating national unity is the way to go viral in Ukraine.
“Ingroup solidarity” statements got far more likes and shares than hostile posts about Russians – a trend that only grew stronger in the wake of the invasion.
The first major study of social media behaviour during wartime has found that posts celebrating national and cultural unity in a country under attack receive significantly more online engagement than derogatory posts about the aggressors.
University of Cambridge psychologists analysed a total of 1.6 million ...
Research heralds new era for genetics
2024-10-01
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 10AM (UK TIME) ON TUESDAY 1 OCTOBER 2024.
Peer reviewed | Observational study | People
Research led by scientists at Queen Mary University of London is heralding in a new era for genetic sequencing and testing.
In the largest study of its kind to date, published today in Nature Medicine, an international group of researchers led by Queen Mary used new bioinformatics techniques to scan the genetic profiles of 80,000 people to understand the frequency of specific expansions of short repetitive DNA sequences in the general population.
These expansions are the most common cause of inherited neurological ...
Deep brain stimulation instantly improves arm and hand function post-brain injury
2024-10-01
Deep brain stimulation may provide immediate improvement in arm and hand strength and function weakened by traumatic brain injury or stroke, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine researchers report today in Nature Communications.
Encouraging results from extensive tests in monkeys and humans open a path for a new clinical application of an already widely used brain stimulation technology and offer insights into neural mechanisms underlying movement deficits caused by brain injury.
“Arm and hand paralysis significantly impacts the quality ...
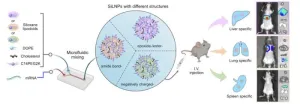
Siloxane nanoparticles unlock precise organ targeting for mRNA therapy
2024-10-01
Penn Engineers have discovered a novel means of directing lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), the revolutionary molecules that delivered the COVID-19 vaccines, to target specific tissues, presaging a new era in personalized medicine and gene therapy.
While past research — including at Penn Engineering — has screened “libraries” of LNPs to find specific variants that target organs like the lungs, this approach is akin to trial and error. “We’ve never understood how the structure of one key component of the LNP, ...
Building better solar cells: assembly of 2D molecular structures with triptycene scaffold
2024-10-01
Research in the field of material science and electronics relies on the innovative arrangement of molecules or atoms to develop materials with unique properties not found in conventional materials. Two-dimensional (2D) assemblies of π-electronic systems, arranged in thin layers, are becoming increasingly important in the fields of materials science and organic electronics. Their unique arrangement allows for specific electronic and physical properties, making them ideal for applications like solar cells, and flexible displays. However, creating such assemblies is challenging because it often requires special designs and techniques for each ...
Maybe we shouldn’t even call low-grade prostate cancer “cancer”
2024-10-01
A new paper in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, published by Oxford University Press, indicates that patients may benefit if doctors stop calling certain early-stage changes to the prostate “cancer” at all.
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death worldwide in men, but far more patients are diagnosed than die of the disease. In 2022, there were nearly 1.5 million cases of prostate cancer, but only 400,000 deaths. Low-grade prostate cancer, commonly known as GG1 among physicians, virtually never metastasizes or causes symptoms. Some medical researchers have wondered recently if it would be a benefit ...
‘Cheeky’ discovery allows scientists to estimate your risk of dying using cells found in the mouth
2024-10-01
We don’t all age at the same rate. But while some supercentenarians may age exceptionally slowly due to winning the genetics jackpot, a plethora of behavioral and lifestyle factors are known to speed up aging, including stress, poor sleep, poor nutrition, smoking, and alcohol. Since such environmental effects get imprinted on our genome in the form of epigenetic marks, it is possible to quantify molecular aging by characterizing the epigenome at prognostic genomic sites.
Over the past decade, scientists have developed several such ‘epigenetic clocks’, calibrated against chronological age and various lifestyle factors across large ...
ChatGPT shows human-level assessment of brain tumor MRI reports
2024-10-01
As artificial intelligence advances, its uses and capabilities in real-world applications continue to reach new heights that may even surpass human expertise. In the field of radiology, where a correct diagnosis is crucial to ensure proper patient care, large language models, such as ChatGPT, could improve accuracy or at least offer a good second opinion.
To test its potential, graduate student Yasuhito Mitsuyama and Associate Professor Daiju Ueda’s team at Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate ...
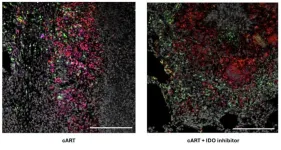
Promising TB therapy safe for patients with HIV
2024-10-01
SAN ANTONIO (October 1, 2024) – A therapy showing promise to help control tuberculosis (TB) does not interfere with combined antiretroviral therapy (cART), according to research by Texas Biomedical Research Institute (Texas Biomed).
“This is an important hurdle that this host-directed therapy had to clear in order to help patients battling both HIV and TB,” said Texas Biomed Professor Smriti Mehra, Ph.D., who led the study recently published in the peer-reviewed journal JCI Insight.
TB is responsible for more than 1.3 million deaths worldwide every year. Dr. Mehra ...
American Academy of Pediatrics examines the impact of school expulsion and recommends ways to create supportive learning environments for all students
2024-10-01
Media Contacts:
Alex Hulvalchick, 630-626-6282
Lisa Robinson, 630-626-6084, lrobinson@aap.org
American Academy of Pediatrics Examines the Impact of School Expulsion and Recommends Ways to Create Supportive Learning Environments for All Students
Updated policy statement on school suspension to be released during the AAP 2024 National Conference & Exhibition in Orlando.
ORLANDO, Fla.--Suspending or expelling a student is one of the most severe punishments a school can impose on a student – and it can have lifelong, devastating consequences. ...
Most pregnant people got vaccinated for COVID-19 in 2022
2024-10-01
A study of more than 28,000 pregnancies from 2022 has found that the majority of pregnant people received the COVID-19 vaccine during its initial release.
The study, co-led by McMaster University and the University of British Columbia, used data from ICES, an independent, not-for-profit research institute, to provide insight into vaccination rates among one of the groups most vulnerable to health complications caused by COVID-19.
The research, published in the Canadian Medical Association Journal (CMAJ) ...
[1] ... [903]
[904]
[905]
[906]
[907]
[908]
[909]
[910]
911
[912]
[913]
[914]
[915]
[916]
[917]
[918]
[919]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.