Circadian disruption, gut microbiome changes linked to colorectal cancer progression
2024-09-27
Irvine, Calif., Sept. 27, 2024 — Research from the University of California, Irvine has revealed how disruption of the circadian clock, the body’s internal, 24-hour biological pacemaker, may accelerate the progression of colorectal cancer by affecting the gut microbiome and intestinal barrier function. This discovery offers new avenues for prevention and treatment strategies.
The study, published online today in the journal Science Advances, offers a more comprehensive understanding of how important changes occur in the function and composition of the gut microbiome when the circadian clock is disturbed in the presence ...
Grant helps UT develop support tool for extreme weather events
2024-09-27
The University of Tennessee and the UT Institute of Agriculture have received a $434,038 Seeding Solutions grant from the Foundation for Food & Agriculture Research (FFAR) to develop and test a decision support tool for farmers to better manage crop production from risks of extreme weather events across the Tennessee River Basin and surrounding southeast US regions.
UT is providing matching funds for a total investment of $966,119 over the three-year project.
The U.S. Department of Agriculture estimates that extreme weather is responsible for 90% of crop losses. These estimates are generally based on annual climate conditions. ...
Autonomous vehicles can be imperfect — As long as they’re resilient
2024-09-27
Researchers from three of Virginia’s premier universities, including the University of Virginia’s Homa Alemzadeh, aim to take the risk out of self-driving vehicles by overcoming inevitable computer failures with good engineering.
The trio will share a $926,737 National Science Foundation award to identify when and where autonomous vehicle systems are most vulnerable to safety-critical failures. They plan to use this knowledge to design ways to efficiently mitigate potential safety hazards and enhance the overall system resilience.
Alemzadeh, an associate professor of electrical and computer engineering in UVA’s School of Engineering and Applied ...
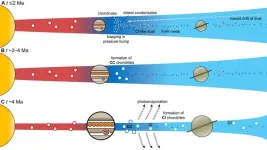
Asteroid Ceres is a former ocean world that slowly formed into a giant, murky icy orb
2024-09-27
Since the first sighting of the first-discovered and largest asteroid in our solar system was made in 1801 by Giuseppe Piazzi, astronomers and planetary scientists have pondered the make-up of this asteroid/dwarf planet. Its heavily battered and dimpled surface is covered in impact craters. Scientists have long argued that visible craters on the surface meant that Ceres could not be very icy.
Researchers at Purdue University and the NASA's Jet Propulsion Lab (JPL) now believe Ceres is a very icy ...
McMaster researchers discover what hinders DNA repair in patients with Huntington’s Disease
2024-09-27
Researchers with McMaster University have discovered that the protein mutated in patients with Huntington’s Disease doesn't repair DNA as intended, impacting the ability of brain cells to heal themselves.
The research, published in PNAS on Sept. 27, 2024, found that the huntingtin protein helps create special molecules that are important for fixing DNA damage. These molecules, known as Poly [ADP-ribose] (PAR), gather around damaged DNA and, like a net, pull in all the factors needed for the repair process.
In people with Huntington’s Disease, however, the research found that the mutated version of this protein doesn’t function properly ...
Estrogens play a hidden role in cancers, inhibiting a key immune cell
2024-09-27
DURHAM, N.C. – Estrogens are known to drive tumor growth in breast cancer cells that carry its receptors, but a new study by Duke Cancer Institute researchers unexpectedly finds that estrogens play a role in fueling the growth of breast cancers without the receptors, as well as numerous other cancers.
Appearing Sept. 27 in the journal Science Advances, the researchers describe how estrogens not only decrease the ability of the immune system to attack tumors, but also reduce the effectiveness of immunotherapies that are used to treat many cancers, notably triple-negative breast cancers. Triple-negative ...
A new birthplace for asteroid Ryugu
2024-09-27
In December 2020 the space probe Hayabusa 2 brought samples of asteroid Ryugu back to Earth. Since then, the few grams of material have been through quite a lot. After initial examinations in Japan, some of the tiny, jet-black grains traveled to research facilities around the world. There they were measured, weighed, chemically analyzed and exposed to infrared, X-ray and synchroton radiation, among other things. At the MPS, researchers examine the ratios of certain metal isotopes in the samples, as in the current study. Scientists refer to isotopes as variants of the same element that differ only in the number of neutrons in the nucleus. Investigations ...
How are pronouns processed in the memory-region of our brain?
2024-09-27
A new study shows how individual brain cells in the hippocampus respond to pronouns. “This may help us unravel how we remember what we read.”
Read the following sentence: “Donald Trump and Kamala Harris walked into the bar, she sat down at a table.” We all immediately know that it was Kamala who sat at the table, not Donald. Pronouns like “she” help us to understand language, but pronouns can have multiple meanings. Depending on the context, we understand who the pronoun is referring to. But ...
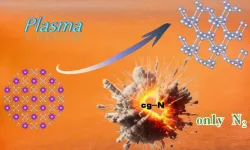
Researchers synthesize high-energy-density cubic gauche nitrogen at atmospheric pressure
2024-09-27
Recently, a research group led by Prof. WANG Xianlong from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, successfully synthesized high-energy-density materials cubic gauche nitrogen (cg-N) at atmospheric pressure by treating potassium azide (KN3) using the plasma-enhanced chemical vapour deposition technique (PECVD).
The research results were published in Science Advances.
Cg-N is a pure nitrogen material consisting of nitrogen atoms bonded by N-N single bonds, resembling the structure of diamond. It has attracted attention because it has a high-energy-density and produces only nitrogen gas when it decomposes. ...
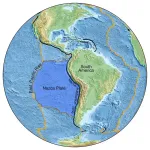
Ancient sunken seafloor reveals earth’s deep secrets
2024-09-27
University of Maryland scientists uncovered evidence of an ancient seafloor that sank deep into Earth during the age of dinosaurs, challenging existing theories about Earth’s interior structure. Located in the East Pacific Rise (a tectonic plate boundary on the floor of the southeastern Pacific Ocean), this previously unstudied patch of seafloor sheds new light on the inner workings of our planet and how its surface has changed over millions of years. The team’s findings were published in the journal Science Advances on September 27, 2024.
Led by geology postdoctoral researcher Jingchuan Wang, the team used innovative seismic imaging techniques to ...
Automatic speech recognition learned to understand people with Parkinson’s disease — by listening to them
2024-09-27
As Mark Hasegawa-Johnson combed through data from his latest project, he was pleasantly surprised to uncover a recipe for Eggs Florentine. Sifting through hundreds of hours of recorded speech will unearth a treasure or two, he said.
Hasegawa-Johnson leads the Speech Accessibility Project, an initiative at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign to make voice recognition devices more useful for people with speech disabilities.
In the project’s first published study, researchers asked an automatic ...
Addressing global water security challenges: New study reveals investment opportunities and readiness levels
2024-09-27
NEW YORK, September 27, 2024 – Water scarcity, pollution, and the burden of waterborne diseases are urgent issues threatening global health and security. A recently published study in the journal Global Environmental Change highlights the pressing need for innovative economic strategies to bolster water security investments, focusing on the “enabling environment” that influences regional readiness for new business solutions.
Initiated and led by researchers at the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC), ...
Commonly used drug could transform treatment of rare muscle disorder
2024-09-27
The study, published in Lancet Neurology, detailed the “head-to-head” trial implemented by the researchers to test two drugs, mexiletine and lamotrigine, on people with the condition.
The trial, which was conducted at the UCL Queen Square Multidisciplinary Centre for Neuromuscular Diseases and the National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, UCLH, involved 60 adults with confirmed non-dystrophic myotonia.
Patients were randomly assigned to receive either mexiletine for eight weeks followed by lamotrigine for eight weeks, or the reverse order, with a seven-day ...
Michael Frumovitz, M.D., posthumously honored with Julie and Ben Rogers Award for Excellence
2024-09-27
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center has posthumously awarded Michael Frumovitz, M.D., with the Julie and Ben Rogers Award for Excellence in Patient Care. The annual award recognizes employees who consistently demonstrate excellence in their work and dedication to MD Anderson’s mission to end cancer. The award’s focus rotates among the areas of patient care, research, education, prevention and administration, with this year’s award focusing on patient care.
Frumovitz dedicated more than 20 years of service to MD Anderson, most recently as chief patient experience officer and professor in Gynecologic ...
NIH grant supports research to discover better treatments for heart failure
2024-09-27
A University of Arizona College of Medicine – Phoenix researcher was recently awarded a $1.9 million National Institutes of Health grant to study the molecular mechanisms of how dilated cardiomyopathy progresses to heart failure, which could eventually lead to better preventive and treatment options for heart failure.
Heart failure is inextricably linked with dilated cardiomyopathy, or DCM, a disease characterized by the progressive enlargement of the heart and reduced contractility reflected by reduced ejection fraction. ...
Clinical cancer research in the US is increasingly dominated by pharmaceutical industry sponsors, study finds
2024-09-27
Clinical cancer research in the U.S. is increasingly dominated by pharmaceutical industry sponsors, study finds
Study underscores need for increased investment in federally funded cancer clinical trials
SEATTLE – September 27, 2024 – Researchers at Fred Hutch Cancer Center identified a substantial increase over the past decade in the proportion of patients with cancer in the U.S. who participate in pharmaceutical industry sponsored clinical trials compared to those conducted with federal government support. Published in The Journal of Clinical Oncology and presented at the ASCO Quality Care Symposium, these findings reveal trends of underinvestment in federally ...
Discovery of 3,775-year-old preserved log supports ‘wood vaulting’ as a climate solution
2024-09-27
A new study published in the journal Science suggests that an ordinary old log could help refine strategies to tackle climate change.
A team of researchers led by University of Maryland Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Professor Ning Zeng analyzed a 3,775-year-old log and the soil it was excavated from. Their analysis, published on September 27, 2024, revealed that the log had lost less than 5% carbon dioxide from its original state thanks to the low-permeability clay soil that covered it.
“The wood is nice and solid—you could probably make a piece of furniture out of it,” Zeng noted.
Understanding the ...
Preterm births are on the rise, with ongoing racial and economic gaps
2024-09-27
Preterm births have increased by more than 10 percent over the past decade, with racial and socioeconomic disparities persisting over time, according to a new study analyzing more than five million births.
The study, published in the journal JAMA Network Open, also found that some factors that increase the risk for preterm birth—such as diabetes, sexually transmitted infections, and mental health conditions—became much more common over the past decade, while other factors that protect against preterm birth declined.
“Our findings not only show that preterm births are on the rise, but provide clues as ...
Menopausal hormone therapy use among postmenopausal women
2024-09-27
About The Study: The results of this cross-sectional study show that over the past 2 decades, menopausal hormone therapy use declined among U.S. postmenopausal women of all age and racial and ethnic groups. Women of racial and ethnic minority groups had lower prevalence of menopausal hormone therapy use compared to non-Hispanic white women.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Lin Yang, PhD, (lin.yang@ahs.ca) and Adetunji T. Toriola, MD, PhD, MPH, (a.toriola@wustl.edu).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2024.3128)
Editor’s ...
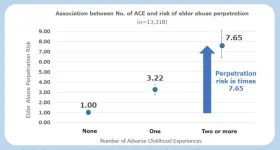
Breaking the chain of intergenerational violence
2024-09-27
New research shows the connection between adverse childhood experiences (ACEs), such as physical or emotional abuse, and an increased risk of people growing up to be abusive against older generations. While generational trauma is known to be passed down from parent to child, the study showed that it can also reverberate upwards from parent to older generations. A survey of over 13,000 people in Japan found that about half had one or more ACEs. Of these, 8.5% self-reported committing some form of physical or verbal abuse against people aged over 65. An important contributing factor was the person’s mental and physical health, both of which are known to be affected by ...
Unraveling the role of macrophages in regulating inflammatory lipids during acute kidney injury
2024-09-27
Tsukuba, Japan—Acute kidney injury (AKI) is associated with a poor prognosis, and no effective treatment has been established to date. Understanding the mechanisms that prevent the progression of AKI is crucial. In AKI, immune cells known as macrophages produce lipid mediators (LMs), which are lipids with significant physiological activity and play a pivotal role in promoting and suppressing inflammation. Thus, elucidating their function is of paramount importance.
In this study, researchers focused ...
Deep underground flooding beneath arima hot springs: A potential trigger for the 1995 Kobe (Hyogo-Ken Nanbu) earthquake
2024-09-27
Tsukuba, Japan—Hot springs frequently contain water that originates from rocks within the Earth's crust. This can be confirmed through isotopic analysis. Arima Hot Springs, located in Kobe, Hyogo Prefecture, Japan, exhibit unique characteristics, including salinity that is more than twice that of seawater, indicating that their water likely originates from the Philippine Sea Plate. However, a direct evidence supporting this connection is lacking.
In this study, researchers confirmed that the isotopic ratios of plate-derived water beneath Arima Hot Springs, as predicted by a numerical model, agreed with those of nonmeteoric water components found ...
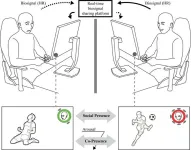
Sharing biosignals with online gaming partners to enhance a mutual sense of social presence between complete strangers
2024-09-27
Tsukuba, Japan—Online communication tools are intended to bring people closer together. However, they often fail to sufficiently meet the human need for fulfilling social interactions. What is missing is a sense of social presence, that is, a "sense of being present with another person." This sense of social presence can be felt during mediated interactions, such as when using web conferencing tools or playing video games.
Researchers at the University of Tsukuba have identified a method for augmenting the sense of social presence in online interactions through the sharing of biosignals. Biosignals such as heart rate can ...
ABM releases position statement on breastfeeding in emergency situations
2024-09-27
The Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine (ABM) has released a pioneering position statement that provides comprehensive, global recommendations on protecting, promoting, and supporting breastfeeding in emergency situations. The recommendations are the first of their kind specifically tailored for physicians to support breastfed and non-breastfed infants in emergencies and to serve as an invaluable resource for all emergency relief personnel involved in supporting families with infants during disasters. Click here to read the full position statement, published with Breastfeeding Medicine.
“Breastfeeding ...
Elucidating the mechanism underlying de novo membrane formation during gametogenesis
2024-09-27
Tsukuba, Japan—Sexual reproduction, a common mode of reproduction among numerous species, involves gametogenesis in which offspring are produced through fertilization, conjugation, or mating. In plants and animals, eggs and sperm differentiate from germ cells to form gametes. However, in budding yeast, spores are produced within diploid cells. During this process, de novo membrane structures form within the cytosol, encapsulating the meiotic haploid nuclei to produce spores. Despite this knowledge, the precise mechanism underlying the formation of these nascent membrane structures remains poorly understood.
To ...
[1] ... [907]
[908]
[909]
[910]
[911]
[912]
[913]
[914]
915
[916]
[917]
[918]
[919]
[920]
[921]
[922]
[923]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.