Lights, camera, action! Coronavirus spike proteins can be selectively detected in 5 minutes
2024-09-19
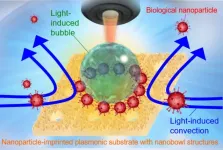
Like moths to a flame, microbes can also be moved by light. Using this knowledge, researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University’s Research Institute for Light-induced Acceleration System (RILACS) have demonstrated a method to detect the presence of viruses quickly and using only a small sample.
The research team led by OMU Professor Takuya Iida, the director of RILACS, and Associate Professor Shiho Tokonami, the deputy director, report in npj Biosensing on a light-induced immunoassay. Using ...
Your Zoom background could influence how tired you feel after a video call
2024-09-19
Part of many people’s pandemic experience included working from home. Even after lockdowns, videoconferencing remains a big part of life as people continue to work remotely, connect with families and friends online, and attend virtual events hosted on videoconferencing platforms.
Spending hours on video calls, however, can be exhausting and manifest as physical, emotional, or cognitive tiredness – a phenomenon known as videoconferencing fatigue (VF). Now, researchers in Singapore have asked if a relationship between virtual backgrounds and VF exists and ...
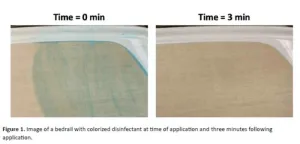
With the use of visual cues, hospital rooms get nearly 70% cleaner
2024-09-19
With the Use of Visual Cues, Hospital Rooms Get Nearly 70% Cleaner
New study shows that a simple color additive in disinfectant wipes dramatically improved room cleanliness and even reduced time needed for cleaning
Arlington, Va. — September 19, 2024 — A new study published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC) reports a comparison of hospital room cleanliness using standard disinfectant wipes versus wipes with a color additive that allows users to see which surfaces have been sanitized. With the color additive, rooms ...
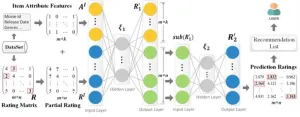
Serial-autoencoder for personalized recommendation
2024-09-19
In the last decade, auxiliary information has been widely used to address data sparsity. Due to the advantages of feature extraction and the no-label requirement, autoencoder-based methods addressing auxiliary information have become quite popular. However, most existing autoencoder-based methods discard the reconstruction of auxiliary information, which poses a huge challenge for better representation learning and model scalability.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Zhu YI published their new research on 15 August 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
The team proposed a novel representation ...
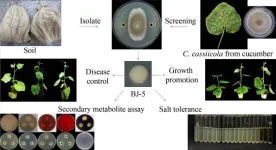
How do look for microbes in nature that are beneficial to plant?
2024-09-19
Cucumber is a common vegetable on people’s table because of its crisp and refreshing characteristics. In order to meet the market demand throughout the year, cucumber is now mainly planted in facility greenhouses. However, the loss of soil nutrients and the accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms are inevitable in successive years of cultivation. Cucumber corynespora leaf spot, also known as cucumber target spot disease, is a major foliar disease that causes cucumber yield reduction, and its pathogen is the Corynespora cassiicola. The pathogen harms cucumber leaves, causing irregular spots and affecting the photosynthesis ...
Exotic species invasions enhance biodiversity response to climate change
2024-09-19
Globally, more than 13,000 plant species, equivalent to the entire native flora of Europe, have been naturalized outside their native ranges. A recent study, jointly conducted by scientists from China and the USA, has provided new insights about biodiversity, exotic invasion, and their relationship to climate change.
Published in Nature Plants, the research uncovers the climatic niche mechanisms that shape both the vulnerability of native ecosystems and the invasiveness of exotic species in a warming world.
A long-standing debate exists over the impact of exotic species on native ecosystems and ...
Arctic warming may fuel ice formation in clouds
2024-09-19
The Arctic frequently experiences temperatures that support the formation of mixed-phase clouds that contain supercooled liquid droplets and ice crystals. The composition of such clouds plays a crucial role in the region's energy balance and climate system. Clouds with more liquid last longer and reflect more sunlight than those with more ice crystals.
With Arctic warming, meteorologists have been interested in determining the effect of rising temperatures on cloud composition and its broader effect on the region. Climate models generally predict that as the Arctic warms, clouds in the region will ...
Rugged Falklands landscape was once a lush rainforest
2024-09-19
A researcher from the University of Southampton (UK) has found evidence that the treeless, rugged, grassland landscape of the Falkland Islands was home to a lush, diverse rainforest up to 30 million years ago.
A study by Dr Zoë Thomas, leading an international team of scientists, reveals that the South Atlantic archipelago was once covered in cool, wet woodland – similar to the present day rainforests found in Tierra del Fuego, off the tip of South America.
The scientists conducted the research after clues to the whereabouts of buried remains of the ancient forest reached them via word-of-mouth in the tight knit community of Port Stanley, the Falklands’ ...
Dizziness in older adults is linked to higher risk of future falls
2024-09-19
IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON PRESS RELEASE
Peer reviewed/Systematic review and meta-analysis/People
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL Thursday 19th September at 00:01 UTC (01:01 BST)
Dizziness in older adults is linked to higher risk of future falls
Researchers say it’s not just a normal part of ageing
The first meta-analysis of its kind has shown a conclusive link between older adults experiencing spells of dizziness and a dramatically elevated risk of falling.
Dizziness is a term used to describe sensations such as vertigo, imbalance, light-headedness, and disorientation. It is common in older adults, affecting one in three of those aged 65 years and older. For the first time, dizziness ...
Triptans more effective than newer, more expensive migraine drugs
2024-09-18
Some triptans are a more effective treatment for acute migraines than newer, more expensive drugs, finds an analysis of the latest evidence published by The BMJ today.
Triptans work by narrowing blood vessels in the brain and preventing the release of chemicals that cause pain and inflammation.
The findings show that four triptans - eletriptan, rizatriptan, sumatriptan, and zolmitriptan - were better at relieving migraine pain than the recently marketed and more expensive drugs lasmiditan, rimegepant, and ubrogepant, which were comparable to paracetamol ...
Iron given through the vein corrects iron deficiency anaemia in pregnant women faster and better than iron taken by mouth
2024-09-18
Researchers found that a medicine called ferric carboxymaltose given in drip through the vein works faster and better than an iron tablet taken by mouth for the treatment of anaemia – and it is as safe as the tablet. The findings were published in Lancet Global Health.
Anaemia (low blood level) is a common cause of ill-health or death in mothers and their babies, especially in sub-Saharan Africa and South-East Asia where more than four out of ten pregnant women have the condition. A sizeable proportion of pregnant women in Nigeria proceed to giving birth while still anaemic ...
The Lancet Neurology: Air pollution, high temperatures, and metabolic risk factors driving global increases in stroke, with latest figures estimating 12 million cases and over 7 million deaths from st
2024-09-18
Between 1990 and 2021, the number of people who had a new stroke (up by 70%), died from a stroke (up by 44%), and stroke-related health loss (up by 32%), has risen substantially worldwide.
Stroke is highly preventable, with 84% of the stroke burden in 2021 attributable to 23 modifiable risk factors, including air pollution, excess body weight, high blood pressure, smoking, and physical inactivity—presenting a public health challenge and an opportunity for action.
Notably, the contribution of high temperatures to poor health and early death due to stroke has ...
Incidence of neuroleptic malignant syndrome during antipsychotic treatment in children and youth
2024-09-18
A new study in the peer-reviewed Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology estimated the incidence of neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS), a potentially fatal adverse effect of antipsychotic treatment, among individuals ages 5-24 years. Click here to read the article now.
Wayne Ray, PhD, from the Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, and coauthors, used national Medicaid data from 2004-2013 to identify patients beginning antipsychotic treatment and calculated the incidence of NMS during antipsychotic use. The investigators identified five ...
Levels of protection from different cycle helmets revealed by new ratings
2024-09-18
Cyclists choosing a new helmet can see how much protection different helmets offer, thanks to new safety testing and ratings from Imperial College London.
Researchers at Imperial College London have developed a simple new cycle helmet safety rating system with simple-to-understand scores from 0-5, designed to help buyers select which helmet to buy and assist manufacturers in future helmet design. The system is based on extensive new safety testing experiments on medium-sized helmets at Imperial.
Testing on the UK’s 30 most popular helmets, funded by The Road Safety Trust, revealed significant ...
Pupils with SEND continue to fall behind their peers
2024-09-18
Pupils with special educational needs and disabilities (SEND) are continuing to fall behind their peers with the gap widening despite the introduction of SEND legislation.
This is according to a new study by Durham University which analysed data on 2.5 million Year 6 pupils across four school years from 2014-2019.
The research suggests there is a need to re-evaluate the policies for SEND provision and how pupils with SEND are supported in schools.
It calls for more investment to support SEND pupils and for increased professional development for teachers and teaching assistants.
Using ...
Half of heavier drinkers say calorie labels on alcohol would lead to a change in their drinking habits
2024-09-18
Half of heavier drinkers say calorie labels on alcohol would lead to a change in their drinking habits
Just over half of heavier drinkers in England say they would make changes to their drinking if calorie labels for alcohol were introduced, according to a new study by UCL researchers.
The findings, the researchers said, suggested calorie labels could help some drinkers maintain a healthier weight.
The study, published in the journal BMJ Open, looked at survey responses from 4,683 adults in England to assess the impact that alcohol calorie labelling might have on people’s attitudes and drinking ...
Study first to link operating room design to shorter surgery
2024-09-18
LAWRENCE – Xiaobo Quan is proud that his study is the first of its kind to link operating room design to the length of knee- and hip-replacement surgeries.
Thus, the University of Kansas School of Architecture & Design associate professor believes its findings can be used to optimize spaces that will both produce better outcomes, via shorter surgeries, for patients and boost the hospital’s bottom line.
For the article “Can Operating Room Design Make Orthopedic Surgeries Shorter, Safer, and More Efficient?: A Quasi-Experimental Study,” ---------- link to: https://doi.org/10.1177/19375867241254529 --------- in the journal Health Environments Research & Design, ...
New study uncovers therapeutic inertia in the treatment of women with multiple sclerosis
2024-09-18
A study has revealed significant therapeutic inertia in the treatment of women with multiple sclerosis (MS), highlighting gender disparities that could impact long-term health outcomes for women of childbearing age.1
The findings, presented today at ECTRIMS 2024, suggest that concerns related to pregnancy may lead to delayed or reduced use of disease-modifying treatments (DMTs), even before pregnancy becomes a consideration.
In an extensive analysis of 22,657 patients with relapsing MS (74.2% women) who were on the French ...
Cancer Cooperative Group leaders propose a re-engineering of the nation’s correlative science program for cancer
2024-09-18
With publicly funded correlative science in the nation’s Cancer Cooperative Groups reduced to a trickle, Group leaders propose implementing a long-standing National Academy of Medicine recommendation to bring new money to this area of research through public-private partnerships. They also recommend major process changes to remove significant barriers for researchers to access the biological samples contributed by patients. The current Journal of Clinical Oncology issue features ‘Correlative Science in the Cooperative Group System—Re-Engineering for Success.’
This Position Paper represents consensus among Evanthia Galanis, MD, DSc for the Alliance for Clinical ...
Nawaz named ASME Fellow
2024-09-18
Kashif Nawaz, distinguished researcher and section head for Building Technologies Research at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, has been named a Fellow of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, or ASME. The Fellow grade recognizes outstanding engineering achievements for members with 10 or more years of active practice.
Nawaz joined ORNL in 2016 as a research scientist in buildings equipment. He specializes in the heating, cooling and dehumidification systems of buildings including the development of novel heat exchangers and enhanced phase-change material ...
U2opia signs license to commercialize anomaly-detection technology for cybersecurity
2024-09-18
U2opia Technology has licensed Situ and Heartbeat, a package of technologies from the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory that offers a new method for advanced cybersecurity monitoring in real time. Situ, which discovers and understands otherwise-undetectable events by analyzing security data, will go to the market through a commercial license. The company will continue to explore opportunities for Heartbeat, which detects cyber attacks by focusing on the physical behavior of a protected device, through a research and development license.
U2opia Technology, a woman- and minority- led company, is directed by Maurice Singleton III, chief executive officer, ...
Explaining dramatic planetwide changes after world’s last ‘Snowball Earth’ event
2024-09-18
Some of the most dramatic climatic events in our planet’s history are “Snowball Earth” events that happened hundreds of millions of years ago, when almost the entire planet was encased in ice up to 0.6 miles (1 kilometer) thick.
These “Snowball Earth” events have happened only a handful of times and do not occur on regular cycles. Each lasts for millions of years or tens of millions of years and is followed by dramatic warming, but the details of these transitions are poorly ...
Cleveland Clinic study is first to show success in treating rare blood disorder
2024-09-18
Wednesday, September 18, 2024, CLEVELAND: A clinical trial has demonstrated that the cancer drug pomalidomide is safe and effective in treating hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT), a rare bleeding disorder that impacts more than 1 in 5,000 people worldwide. The trial, led by Keith McCrae, M.D., of Cleveland Clinic and supported by the National Institutes of Health, was stopped early because of these successful findings, and has been published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The impetus for this trial was a single patient. About ...
Bone marrow cancer drug shows success in treatment of rare blood disorder
2024-09-18
A clinical trial supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) was stopped early after researchers found sufficient evidence that a drug used to treat bone marrow cancer and Kaposi sarcoma is safe and effective in treating hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT), a rare bleeding disorder that affects 1 in 5,000 people worldwide. The trial results, which are published in the New England Journal of Medicine, detail how patients with HHT given the drug, called pomalidomide, experienced a significant reduction in the severity of nosebleeds, needed fewer of the blood transfusions and iron infusions that HHT often demands, ...
Clinical trial successfully repurposes cancer drug for hereditary bleeding disorder
2024-09-18
A drug approved for treating the blood cancer multiple myeloma may offer a safe and effective way to reduce the risk of severe nosebleeds from a rare but devastating bleeding disorder. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT), the world's second-most-common inherited bleeding disorder, affects approximately 1-in-5,000 people and can have life-threatening complications, but there are currently no U.S. FDA-approved drugs to treat HHT. The PATH-HHT study, the first-ever randomized, placebo-controlled ...
[1] ... [886]
[887]
[888]
[889]
[890]
[891]
[892]
[893]
894
[895]
[896]
[897]
[898]
[899]
[900]
[901]
[902]
... [8790]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.