Keep devices out of bed for better sleep – Otago study
2024-09-03
Despite what we’ve been led to believe, the timing of evening screen use, rather than the activity itself, negatively impacts youth sleep, a University of Otago study has found.
Current sleep guidelines recommend no screen use in the hour or two before bed. However, the researchers found screen time in the two hours before bed had little impact on youth sleep, it was screen time once in bed that caused problems.
Lead author Dr Bradley Brosnan, of the Edgar Diabetes and Obesity Research Centre, says screen time is a mainstay in adolescents’ bedtime routines, and sleep guidelines need to be revaluated to better reflect modern life.
Published in JAMA Pediatrics, ...
Dr. Torabi to study vulnerabilities in electric vehicle charging management systems
2024-09-03
Dr. Sadegh Torabi, Assistant Professor, Information Sciences and Technology, College of Engineering and Computing (CEC), and Research Fellow at the Center for Secure Information Systems (CSIS), is set to receive funding for the project: “Collaborative Research: CISE MSI: RPEP: OAC: Macroscopic and Microscopic Inference and Analysis of Vulnerabilities within EV Charging-Management Systems.”
Via this project, Dr. Torabi and his partners will establish a collaborative ecosystem among academia, industry, and the public sector to bolster the resilience of the EV Charging Infrastructure (CI). The critical nature of EV CI has made them targets for malicious attacks, often state-sponsored, ...
Think simpler, flow faster
2024-09-03
Analyzing and simulating fluid flow is a challenging mathematical problem that impacts various scenarios, including video game engines, ocean current modeling and hurricane forecasting. The core of this challenge lies in solving the Navier–Stokes equations, a set of classical equations that describe fluid dynamics. Recently, deep learning has emerged as a powerful tool to accelerate equation solving. Using this technique, a team designed a novel approach that can provide accurate solutions 1,000 times faster than traditional equation solvers. The team’s study was published June 26 in Intelligent ...
Eating fish but not omega-3 supplements during pregnancy associated with lower likelihood of autism diagnosis, NIH-funded study finds
2024-09-03
Eating any amount of fish during pregnancy was associated with about a 20% lower likelihood of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) diagnosis, particularly in females, and a slight reduction in autism-related traits in offspring, according to a new study funded by the Environmental influences on Child Health Outcomes (ECHO) Program at the National Institutes of Health.
However, researchers did not find the same association with supplements containing omega-3 fatty acids.
Fish is an important source of omega-3 fatty acids, an essential nutrient during pregnancy for supporting maternal health and child neurodevelopment. A recent analysis of ECHO Cohort data revealed that about ...
Study: racial and ethnic designation inaccuracies in children’s medical records may impede equity efforts
2024-09-03
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – Leaders at three Michigan hospitals aiming to address equity issues for pediatric patients wanted to start with inspecting data key to identifying potential inequities.
What they learned: much of those data are inaccurate.
A study from the Michigan Child Health Equity Collaborative, or Mi-CHEC, found substantial errors across the three health systems in racial and ethnic designations in their electronic medical records. Accuracy of these designations are important to clinical care improvement ...
Penn study finds taking semaglutide for weight management does not increase risk of depression or suicidal behavior in people without known major psychopathology
2024-09-03
PHILADELPHIA— Taking the weight loss medication semaglutide did not increase the risk of depressive symptoms, suicidal thoughts, or suicidal behavior in persons without known major mental health disorders, according to a new study led by researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania published this week in JAMA Internal Medicine. Both the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency are actively monitoring the psychiatric safety of semaglutide and similar medications after post marketing surveillance reports of depression, suicidal thoughts (ideation), ...
GLP-1 receptor agonist use and risk of suicide death
2024-09-03
About The Study: This cohort study, including mostly patients with type 2 diabetes, does not show an association between use of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists and an increased risk of suicide death, self-harm, or incident depression and anxiety-related disorders.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Peter Ueda, MD, PhD, email peter.ueda@ki.se.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2024.4369)
Editor’s ...
Psychiatric safety of semaglutide for weight management in people without known major psychopathology
2024-09-03
About The Study: The results of this post hoc analysis suggest that treatment with semaglutide, 2.4 mg, did not increase the risk of developing symptoms of depression or suicidal ideation/behavior vs placebo and was associated with a small but statistically significant reduction in depressive symptoms (not considered clinically meaningful). People with obesity should be monitored for mental health concerns so they can receive appropriate support and care.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Thomas A. Wadden, PhD, email wadden@pennmedicine.upenn.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2024.4346)
Editor’s ...
One minute to save lives: Teaming up with pediatricians to secure firearms
2024-09-03
Large study included 47,307 well-child visits at 30 clinics in Michigan and Colorado
Almost 50% of clinicians receiving a prompt plus added support delivered a secure firearm storage program during well visits versus just 22% of doctors receiving prompt only
Firearm-related injuries are the leading cause of death for young people in the U.S.
‘We can save lives’ with a brief program to support parents in secure storage
CHICAGO --- If it takes a pediatrician less than one minute per visit to talk to parents about how to securely store their firearms and offer a free cable lock, why do only 2% of doctors report routinely doing so?
Turns out, they ...
No link found between popular diabetes medication and suicide
2024-09-03
There has been concern that common diabetes drugs could increase the risk of suicide and self-harm. In a new study, led by researchers at Karolinska Institutet and published in Jama Internal Medicine, no such risk increase was observed.
Drugs of the type GLP-1 analogues lower blood sugar levels and are used by millions of people worldwide. They are mainly used to treat diabetes, but drugs such as Ozempic have also been shown to be effective against obesity, which has increased their popularity.
At the same time, both American and European drug authorities have warned that there may be risks associated with ...
Thousands of jellyfish clones are multiplying in B.C. lakes
2024-09-03
An invasive, freshwater jellyfish is popping up in B.C. waters in the thousands and future sightings could increase rapidly, according to UBC research.
The peach blossom jellyfish clones have been spotted in 34 places in B.C., its furthest northern range in North America, and a recent paper predicts sightings and the number of locations will increase by the end of the decade as climate change extends this range.
Dr. Florian Lüskow, who completed the research during his postdoctoral fellowship ...
Infertility challenges amongst endangered wild songbird population revealed in new study
2024-09-03
A new study using 10 years of data has provided the most comprehensive estimate of infertility rates to date in a threatened wild animal population
Researchers from the University of Sheffield found infertility accounts for 17 per cent of hatching failure in an endangered songbird, the hihi, with the majority of hatching failure being caused by embryo death
This is the first study to find a link between small population size, sex ratio bias, and reduced fertilisation rates in wild animals
By considering the impacts of population size and sex ratio on fertility, conservationists can better manage the numbers and composition of animals in populations ...
Representatives from NASA, ESA, JAXA, ASI, KASA meet during COSPAR 2024 to reinforce cooperation and coordination for future missions to the asteroid Apophis
2024-09-03
Each agency representative presented the status of their current involvement in current and future planning for missions to Apophis (including extended mission for OSIRIS-REx, renamed OSIRIS-APEX, for NASA and the RAMSES mission for ESA) as well as the existing partnerships and mutual involvement in other agency’s missions, e.g. the infrared camera provided by JAXA in ESA’s mission Hera. Concepts to fly to Apophis, as well as reuse of existing payloads, spare parts and hardware, coordination of arrival time at Apophis of the different spacecraft, techniques to be demonstrated, ...
Vision-based ChatGPT shows deficits interpreting radiologic images
2024-09-03
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Researchers evaluating the performance of ChatGPT-4 Vision found that the model performed well on text-based radiology exam questions but struggled to answer image-related questions accurately. The study’s results were published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Chat GPT-4 Vision is the first version of the large language model that can interpret both text and images.
“ChatGPT-4 has shown promise for assisting radiologists in tasks such as simplifying patient-facing radiology reports and identifying ...
Minimal ADHD risk from prenatal cannabis use new study reveals
2024-09-03
A new study reveals nuanced findings on the neuropsychiatric risks of prenatal cannabis exposure. The research found a slight increase in the risk of ADHD and a heightened vulnerability to cannabis use in offspring. These results highlight the need for continued caution and further investigation into the long-term effects of cannabis use during pregnancy.
A new study led by Prof. Ilan Matok and Hely Bassalov PharmD from the Department of Clinical Pharmacy at the School of Pharmacy in the Faculty of Medicine at Hebrew University in collaboration ...
Study suggests gun-free zones do not attract mass shootings
2024-09-03
Gun-free zones have often been blamed for making schools, malls and other public areas more attractive to shooters; however, there have been no quantitative studies examining those claims. Now, in a first of its kind study published in The Lancet Regional Health Americas, researchers at UC Davis Health and other institutions have shown that gun-free zones may, in fact, reduce the risk of mass shootings.
"Our most significant finding is that gun-free zones don't attract active shooters,” said the study’s first author, Paul Reeping, ...
Mathematicians model a puzzling breakdown in cooperative behaviour
2024-09-03
Darwin was puzzled by cooperation in nature—it ran directly against natural selection and the notion of survival of the fittest. But over the past decades, evolutionary mathematicians have used game theory to better understand why mutual cooperation persists when evolution should favour self-serving cheaters.
At a basic level, cooperation flourishes when the costs to cooperation are low or the benefits large. When cooperation becomes too costly, it disappears—at least in the realm of pure mathematics. ...
Kessler Foundation scientists publish protocol for combining aerobic exercise and cognitive rehabilitation in multiple sclerosis
2024-09-03
East Hanover, NJ – September 3, 2024 – Researchers at Kessler Foundation have published a new clinical protocol examining the combination of aerobic exercise and cognitive rehabilitation to improve learning and memory in individuals with multiple sclerosis (MS) who have mobility disability. The article, “Rationale and methodology for examining the combination of aerobic exercise and cognitive rehabilitation on new learning and memory in persons with multiple sclerosis and mobility disability: Protocol for a randomized controlled trial,” was published online and will appear in print in Contemporary Clinical Trials, ...
New hope for progressive supranuclear palsy with innovative trial
2024-09-03
$75 million NIH grant could lead to the first effective drugs for a condition with few treatment options
A clinical trial that will test three drugs concurrently, and could include more, represents new hope for patients with progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), an incurable neurodegenerative disorder that usually kills within seven years after symptoms start.
Researchers hope the trial, which will be led by UC San Francisco and conducted at up to 50 sites nationwide, will lead to the development of new therapies. There are currently no drugs to stall the disease’s deadly progression.
The ...
Mass General Brigham Gene and Cell Therapy Institute launches RNA Therapeutics Core
2024-09-03
The Mass General Brigham Gene and Cell Therapy Institute (GCTI) today announced it has launched the RNA Therapeutics Core, a first-of-its-kind, state-of-the-art facility and resource to advance the use of RNA technologies within and beyond the Mass General Brigham research ecosystem. This new Core is dedicated to accelerating the exploration of novel therapeutic targets to effectively translate RNA-based medicines into clinical practice by leveraging advanced RNA vectors and delivery systems.
Until now, a Core of this kind has not existed within an academic setting. With this launch, the RNA Therapeutics Core enables ...
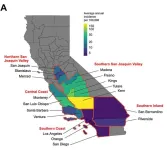
Dangerous airborne fungus boosted by California droughts
2024-09-03
Valley fever is an emerging fungal disease in the western United States that most often causes flu-like symptoms, but can also cause dangerous or even deadly complications. By analyzing data on reported cases of Valley fever in California, which have increased dramatically over the last two decades, researchers from University of California San Diego and University of California, Berkeley, have identified seasonal patterns that could help individuals and public health officials better prepare for future surges in Valley fever cases. The findings also have important implications for how the changing climate can exacerbate the threat of infectious diseases. The findings are published in The ...
$1.8 million NIH grant to FAU engineering fuels quest to decode human evolution
2024-09-03
Natural selection is an important evolutionary force that enables humans to adapt to new environments and fight disease-causing pathogens. However, the unique footprints of natural selection in our genome can be buried beneath those left by other evolutionary forces. Thus, by leveraging information about multiple evolutionary forces, researchers can identify signatures of natural selection in the human genome, and ultimately determine its role in human adaptation and disease.
Low-cost DNA sequencing has ...
Communication helps parent relationships with new college students but has limits
2024-09-03
PULLMAN, Wash. -- When young adults first go off to college, more communication with parents generally leads to better relationships, but parents should avoid always initiating it, according to a study led by Washington State University researchers.
In a paper published in the journal Emerging Adulthood, WSU Assistant Professor Jennifer Duckworth and co-authors found that phone, text, video or in-person communication made first-year students feel better about the relationship with their parents. Students also felt better about the relationship when parents offered support or advice, and when they discussed important topics, such as studying and friendships. However, researchers found ...
Natural selection may create inter-species exploitation
2024-09-03
A modeling study suggests that one-sided interspecies cooperation can spontaneously emerge and persist over time, despite only one species benefitting. Evolutionary game theory, and the prisoner’s dilemma in particular, are often used to model the evolution of cooperation within a single species. In the prisoner’s dilemma, both parties benefit by cooperating, but the greatest benefit is earned by a defector who plays with a cooperator. The temptation to cheat tends to push players towards defection, ...
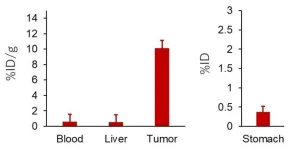
Targeted cancer therapies: Getting radioactive atoms to accumulate in tumors
2024-09-03
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men worldwide, following lung cancer. In the United States alone, nearly 300,000 new cases are diagnosed annually. While reducing testosterone and other male hormones can be an effective treatment for prostate cancer, this approach becomes ineffective once the disease progresses to metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). At this stage, the cancer advances quickly and becomes resistant to conventional hormonal therapies and chemotherapy.
A clever strategy for fighting mCRPC is to exploit the ...
[1] ... [956]
[957]
[958]
[959]
[960]
[961]
[962]
[963]
964
[965]
[966]
[967]
[968]
[969]
[970]
[971]
[972]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.