First participant enrolled in NIH-Funded Access for All in ALS Consortium
2024-08-14
The Access for All in ALS Consortium (ALL ALS) announced the successful enrollment of the first participant.
Established in the autumn of 2023 with funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), ALL ALS is a multi-institutional effort, and aims to disrupt the ALS clinical research landscape using open science methods to build broadly accessible resources to advance ALS research. The consortium brings together research scientists from across the country, combining their efforts to collect clinical and biomarker data from people with ALS symptoms, asymptomatic individuals at risk of developing inherited forms of ALS, and control participants. The ALL ALS ...
Department of Energy Office of Science accepting applications, offering workshops for Office of Science Graduate Student Research (SCGSR) awards
2024-08-14
Washington, D.C. - Current U.S. Ph.D. students in qualified graduate programs at accredited U.S. academic institutions who are conducting their graduate thesis research in targeted areas of importance to the DOE Office of Science are invited to apply for the Office of Science Graduate Student Research (SCGSR) program.
Helpful application assistance workshops will be held on Thursday, September 12, 2024, 2:00 PM – 3:30 PM EDT and Thursday, October 10, 2024, 2:00 PM – 4:30 PM EDT.
Applications are due at 5:00 pm Eastern Daylight Time (EDT) on November 6, 2024.
The September 12, ...
Brian Peters part of multi-disciplinary team awarded $3.9 million to study mixed fungal-bacterial infections
2024-08-14
Brian Peters, PhD, First Tennessee Endowed Chair of Excellence in Clinical Pharmacy and professor in the Department of Clinical Pharmacy and Translational Science at the UT Health Science Center, was recently awarded $3.9 million from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases for a project aimed at unravelling intricate mysteries surrounding complex fungal-bacterial infections. James Cassat, MD, PhD, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, and Paul Fidel, PhD, LSU Health New Orleans, are also principal investigators.
Infections caused by both fungi ...
New study unveils the power of physical forces in enhancing T cell immune response
2024-08-14
Study Title: Parsing digital or analog TCR performance through piconewton forces
Publication: Science Advances
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute authors: Aoi Akitsu, Kristine N. Brazin, Robert J. Mallis, Jonathan S. Duke-Cohan, Matthew A. Booker, Vincenzo Cinella, Jonathan Lee, Michael Y. Tolstorukov and Ellis L. Reinherz, MD
Summary:
Researchers at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute investigate new features of T cell performance, delineating a class of digital cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) that are optimal in providing protection against virally infected or otherwise altered body cells, and by extension, most useful for immunotherapy. These digital ...
Researchers unveil mysteries of ancient Earth
2024-08-14
A team of researchers has made strides in understanding the formation of massif-type anorthosites, enigmatic rocks that only formed during the middle part of Earth’s history. These plagioclase-rich igneous rock formations, which can cover areas as large as 42,000 square kilometers and host titanium ore deposits, have puzzled scientists for decades due to conflicting theories about their origins.
A new study published in Science Advances on Aug. 14 highlights the intricate connections between Earth’s evolving ...
UNC-Chapel Hill launches the Institute for Risk Management and Insurance Innovation
2024-08-14
The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill is launching the Institute for Risk Management and Insurance Innovation, a new interdisciplinary research and innovation hub that will leverage the expertise of faculty and students from various disciplines across campus to address complex challenges in risk management and insurance.
“The institute will address the financial risks arising from a growing number of threats to our state and beyond, ranging from extreme weather to cybersecurity,” explains Vice Chancellor for Research Penny Gordon-Larsen. “UNC-Chapel Hill is a world leader in translating extreme environmental events into financial risk and now seeks to expand ...
Integrating positive psychology and autism: A roundtable
2024-08-14
A new Roundtable Discussion in the peer-reviewed journal Autism in Adulthood explores how the two fields of positive psychology and autism might integrate and benefit each other, and the autism community at large. Click here to read the Roundtable.
The Roundtable was co-moderated by Patricia Wright, PhD, MPH who is the Executive Director of Proof Positive: Autism Wellbeing Alliance, an organization committed to integrating autism services and the field of positive psychology and Rachel Moseley, ...
UC Irvine scientists create material that can take the temperature of nanoscale objects
2024-08-14
Irvine, Calif., Aug. 14, 2024 — University of California, Irvine scientists recently discovered a one-dimensional nanoscale material whose color changes as temperature changes. The team’s results appeared in Advanced Materials.
“We found that we can make really small and sensitive thermometers,” said Maxx Arguilla, UC Irvine professor of chemistry whose research group led the study. “It’s one of the most applied and translatable works to come out of our lab.”
Arguilla ...
Dark rituals: Understanding society's fascination with death and disaster
2024-08-14
Understanding why the popularity of organised events steeped in themes of death, disaster and suffering, such as the well-known Dia de los Muertos (Day of the Dead), Jack the Ripper Walking Tours and Remembrance Sunday, could be key to a deeper understanding of society, say researchers from the University of Surrey.
In a study published by Annals of Tourism Research, researchers introduce a comprehensive framework to analyse these events, drawing from fields as diverse as thanatology (the scientific study of death and the practices associated with it), dark tourism, and collective memory ...
Combining computational methods and experimental techniques to unlock floating offshore wind potential
2024-08-14
A collaboration between researchers from Johns Hopkins Whiting School of Engineering (WSE) and Portland State University (PSU) aims to help unlock the vast potential of floating offshore windfarms in the United States by improving understanding of wind-wave-turbine interactions, which if not accounted for properly, can greatly reduce the power output of a group of wind turbines.
The project combines developing a new computational method for enhancing the accuracy of Large Eddy Simulations (LES) – a mathematical computer model that depicts the wind field within floating offshore windfarms, with advanced experimental ...
Twelve Ochsner Health hospitals recognized for efforts to improve outcomes for Americans with heart disease and stroke
2024-08-14
NEW ORLEANS, La. – Twelve Ochsner Health owned and affiliated hospitals are among the more than 3,000 nationwide that participate in the American Heart Association’s Get With The Guidelines® (GWTG) and other programs to improve outcomes for Americans who experience heart disease or stroke.
Heart disease and stroke are the No. 1 and No. 5 causes of death in the United States, respectively. These health crises require swift and proven treatment to ensure the best outcomes for patients. The American Heart Association, celebrating 100 years of work to advance health and hope for everyone, everywhere, ...
Hydrometeorology and location affect hospitalizations for waterborne infectious diseases in the US
2024-08-14
An analysis of 12 years of data collected from over 500 hospitals in 25 different states shows that weather, geographic location, and urban or rural location all appear to influence hospitalizations for waterborne infectious diseases, according to a study published August 7, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS Water by Victoria Lynch and Jeffrey Shaman from Columbia University.
Waterborne infectious diseases caused by bacteria, parasites, and viruses still affect over 7,000,000 people annually in the United States. Lynch and Shaman analyzed potential links between weather and hospitalizations for waterborne ...
Alzheimer’s cognitive decline predicted by patient’s age, sex, and irregular heart rhythm
2024-08-14
Older age, female sex, irregular heart rhythms, and daily activity levels can help to predict how much Alzheimer’s Disease patients’ cognitive function will decline, and how much they will depend on their caregivers over the next two years. The results suggest new ways to predict cognitive decline in patients, and that caregivers need to be considered in treatment plans. 'Liane Kaufmann from the Ernst von Bergmann Clinic in Potsdam, Germany, Josef Marksteiner from the General Hospital in Hall, Austria, and colleagues present these findings in the open access journal PLOS ...
Gender-sensitive job titles may affect women’s interest in job ads
2024-08-14
A new study suggests that the use of gender-sensitive language in the title of job advertisements may influence the level of interest demonstrated by female potential applicants. Dominik Hetjens of Technische Universität Dresden, Germany, and Stefan Hartmann of Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf, Germany, present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on August 14, 2024.
German is one of many languages in which every noun is grammatically masculine, feminine, or neutral. For instance, ...
CNIO researchers discover a 'switch' for the desire to engage in physical activity: Two proteins that get activated in the muscle during exercise
2024-08-14
"We have discovered a muscle-brain pathway that controls the eagerness to train more when we exercise," explains Guadalupe Sabio, a researcher at the Spanish National Cancer Research Center (CNIO).
One of the proteins identified activates the area of the brain that controls movement. Obese patients have lower blood levels of this protein.
This result suggest it may be possible to develop drugs for people specially in need of the benefits that come from exercise, but are reluctant to do it.
The ...
A taste for carbon dioxide
2024-08-14
Nitrogenases are among the most geochemically important enzymes on Earth, providing all forms of life with bioavailable nitrogen in the form of ammonia (NH3). Some nitrogenases can also directly convert CO2 into hydrocarbon chains, making them an exciting target for the development of biotechnological processes. A team of researchers in Marburg, Germany, led by Max Planck scientist Johannes Rebelein, has now provided a comprehensive insight into the substrate specificity and preferences of nitrogenase. Their results challenge the current understanding of nitrogenases and highlight their potential for sustainable bioproduction.
Nitrogen is one of the main building blocks ...
US companies' global market reach linked to cloud computing use
2024-08-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — U.S. firms that use cloud computing services are more likely to export their products and services, according to a new study by researchers at Penn State and the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF). The team said the findings were stronger for firms located outside of large cities and demonstrate the need for expanded availability of the high-speed internet required for cloud computing to support economic development.
The study, which also found that cloud-using firms exported goods and services even more than exporting firms ...
Lake Erie walleye growth is driven by parents’ size, experience
2024-08-14
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Parent size and the conditions in which actively spawning adults lived are the most influential factors affecting growth of Lake Erie walleye, a new study has found.
The findings surprised the scientists, who expected recent temperatures and food availability to have the highest impact on walleye growth.
Cold winters and more sizable mothers were associated with faster growth in 3- to 5-year-old walleye offspring, the analysis showed, suggesting that warmer winters that come with ...
Texas Tech University joins US DOE’s $44 million carbon storage project
2024-08-14
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) Office of Fossil Energy and Carbon Management (FECM) has selected Texas Tech University as one of nine university and industry-led projects to split $44.5 million in federal funding to advance commercial-scale carbon capture, transport and storage across the U.S.
With an award just over $6.2 million, Texas Tech intends to implement and accelerate the equitable and environmentally responsible deployment of storage-based carbon management projects in the Permian Basin. The team will provide technical and engagement support for stakeholders to develop a framework ...
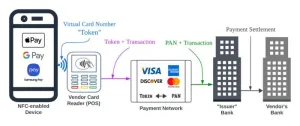
New study reveals loophole in digital wallet security—even if rightful cardholder doesn’t use a digital wallet
2024-08-14
Digital wallets — like Apple Pay, Google Pay and PayPal — are projected to be used by more than 5.3 billion people by 2026. While these wallets promote increased security over traditional payment methods, reliance on outdated authentication methods and prioritizing convenience over security leaves digital wallets vulnerable, according to new research led by computer engineers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst.
“What we have discovered is [that] these digital wallets are not secure,” says Taqi Raza, assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering and an author on the paper. “The main reason is that they have unconditional trust between ...
Researchers discover new way inflammation impacts cell communication
2024-08-14
INDIANAPOLIS – Indiana University School of Medicine researchers have made significant progress in understanding how cells communicate during inflammation. The study, recently published in PNAS, was conducted over a period of five years and focused on the molecules that enable cells to function during inflammation, particularly in the central nervous system where diseases like multiple sclerosis occur.
“Communication is key in any relationship, even at the level of cells that cause disease,” said Mark Kaplan, PhD, chair of the Department of Microbiology and Immunology at the IU ...
Purdue physicists throw world’s smallest disco party
2024-08-14
Physicists at Purdue are throwing the world’s smallest disco party. The disco ball itself is a fluorescent nanodiamond, which they have levitated and spun at incredibly high speeds. The fluorescent diamond emits and scatters multicolor lights in different directions as it rotates. The party continues as they study the effects of fast rotation on the spin qubits within their system and are able to observe the Berry phase. The team, led by Tongcang Li, professor of Physics and Astronomy and Electrical and Computer Engineering at Purdue University, published their results ...
Tropical Atlantic mixing rewrites climate pattern rules
2024-08-14
The churning of the upper ocean in the tropics of Atlantic Ocean plays a crucial role in shaping long-term climate patterns across the world, a new study has found.
Researchers have discovered that changes in the ocean's mixed layer - the topmost section where wind and waves blend warm surface waters with cooler depths - are the primary force behind a climate phenomenon known as Atlantic Multidecadal Variability (AMV) in the tropics.
The AMV has far-reaching effects on global climate. It influences weather patterns from North America to Europe and Africa, affecting everything from hurricane ...
New open access journal from APS and Sage expands publishing opportunity for psychological scientists
2024-08-14
The Association for Psychological Science (APS) and Sage announce the launch of Advances in Psychological Science Open, a fully open access journal that will publish high-quality empirical, technical, theoretical, and review articles, across the full range of areas and topics in psychological science. The journal will accept submissions in a variety of formats, including long-form articles and short reports, and APS is encouraging scientists to submit integrative and interdisciplinary research articles.
“APS is always working to identify new ways to catalyze advances in psychological science,” said APS CEO Robert Gropp. “We are excited to announce ...
iFAB Tech Hub grows net-zero industrial chemical partnerships, champions bioeconomy
2024-08-14
In the wake of the $51 million funding announcement from the Economic Development Administration, momentum is tangible for the Illinois Fermentation and Agriculture Biomanufacturing (iFAB) Tech Hub. Today marks the beginning of a new collaboration to replace fossil fuel-derived petrochemicals with zero-emission alternatives produced through precision fermentation.
Industrial Microbes (iMicrobes) is partnering with the iFAB Tech Hub’s Integrated Bioprocessing Research Laboratory at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign to harness microbes to produce acrylic acid, a versatile chemical ...
[1] ... [954]
[955]
[956]
[957]
[958]
[959]
[960]
[961]
962
[963]
[964]
[965]
[966]
[967]
[968]
[969]
[970]
... [8790]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.