What’s in the microbiome of the foods we eat?
2024-08-29
Microbes are part of the food we eat and can influence our own microbiome, but we know very little about the microbes in our foods. Now, researchers have developed a database of the “food microbiome” by sequencing the metagenomes of 2,533 different foods. They identified 10,899 food-associated microbes, half of which were previously unknown species, and showed that food-associated microbes account for around 3% of the adult and 56% of the infant gut microbiome on average. The study published August 29 in the journal ...
Scientists discover how starfish get ‘legless’
2024-08-29
Researchers at Queen Mary University of London have made a groundbreaking discovery about how starfish manage to survive predatory attacks by shedding their own limbs. The team has identified a neurohormone responsible for triggering this remarkable feat of self-preservation.
Autotomy, the ability of an animal to detach a body part to evade predators, is a well-known survival strategy in the animal kingdom. While lizards shedding their tails are a familiar example, the mechanisms behind this process remain largely mysterious.
Now, scientists have unveiled a key piece of the puzzle. By studying the common European starfish, ...
Hormone therapy and biological aging in postmenopausal women
2024-08-29
About The Study: Postmenopausal women with historical hormone therapy (HT) use were biologically younger than those not receiving HT, with a more evident association observed in those with low socioeconomic status. The biological aging discrepancy mediated the association between HT and decreased mortality. Promoting HT in postmenopausal women could be important for healthy aging.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Chenglong Li, PhD, email chenglongli@bjmu.edu.cn.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.30839)
Editor’s ...
Persistent neighborhood poverty and breast cancer outcomes
2024-08-29
About The Study: The findings of this study of women ages 18 or older diagnosed with stage I to III breast cancer between 2010 and 2018 suggest that residing in persistently impoverished neighborhoods is associated with poor tumor characteristics and increased mortality.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Samilia Obeng-Gyasi, MD, MPH, email samilia.obeng-gyasi@osumc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.27755)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
Greenhouse gas emissions and costs of inhaler devices in the US
2024-08-29
About The Study: Inhaler prescriptions filled by Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services beneficiaries in 2022 resulted in an estimated 1.15 million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent emissions, equivalent to 226,960 homes’ yearly electricity use. Metered-dose inhalers were responsible for nearly all inhaler-related emissions, with the largest contribution arising from short-acting β-agonist medications. Although dry-powder and soft-mist inhalers had substantially lower emissions, they accounted for a disproportionate amount of spending, representing nearly two-thirds ...
Novel motion simulator reveals key role of air flow in rodent navigation
2024-08-29
How are rodents able to navigate pitch-black subway tunnels or other dark environments so adeptly, despite not being able to rely on vision?
With the assistance of a novel motion simulator, researchers at Bar-Ilan University in Israel have discovered that rats rely on airflow to navigate their surroundings. When they move, the flow of air relative to their bodies provides crucial information, complementary to their sense of balance, to perceive their own motion in space. This might explain their agility in the dark as they scurry through pipes and tunnels, ...
Combo immunotherapy produces distinct waves of cancer-fighting T cells with each dose
2024-08-29
PHILADELPHIA – A new tool for monitoring immune health patterns over time has revealed how a pair of checkpoint inhibitor therapies works together to recruit new cancer-fighting T cells with every infusion. Findings from the use of the new tool, developed by researchers at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine and Penn Medicine’s Abramson Cancer Center (ACC), were published today in Cancer Cell. The study challenges fundamental assumptions about how a common immunotherapy ...
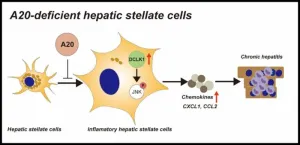
Finding new targets for blocking chronic hepatitis
2024-08-29
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) determine how a protein called A20 can regulate the inflammatory response to suppress chronic hepatitis
Tokyo, Japan – Many individuals worldwide suffer from chronic liver disease (CLD), which poses significant concerns for its tendency to lead to hepatocellular carcinoma or liver failure. CLD is characterized by inflammation and fibrosis. Certain liver cells, called hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), contribute to both these characteristics, but how they are specifically involved in the inflammatory response is not ...
New Microbiology Society Publish and Read consortium deal now available to science institutions and hospitals across Germany
2024-08-29
The Microbiology Society, one of the largest microbiology societies in Europe, is pleased to announce a new three year Publish and Read offering with German consortium ZB Med – Information Centre for Life Sciences, available to its 400 member institutions and 2,000 hospitals. This agreement was established in partnership with HARRASSOWITZ, the Society’s representative agency in Germany.
From 2025, member institutions can join this consortium-wide Publish and Read agreement to enjoy discounted pricing. For participating institutions, the ...
Atomic force microscopy upgrade captures 3D images of calcite dissolving
2024-08-29
Researchers at Nano Life Science Institute (WPI-NanoLSI), Kanazawa University, implement modifications to their high-speed atomic force microscopy that simultaneously improve resolution and speed, while enabling direct measurements of 3D structures to provide conclusive evidence of a contested hydration layer forming as calcite dissolves.
Understanding the dissolution processes of minerals can provide key insights into geochemical processes. Attempts to explain some of the observations during the dissolution of calcite (CaCO3) have led to the hypothesis that a hydration layer forms, although this has been contested. Hydration layers are also ...
New research unveils cellular pathways to Alzheimer’s and alternative brain aging
2024-08-29
A new study has found an answer for a long-lasting question in aging research - Is Alzheimer’s disease-dementia a form of accelerated aging or is there a different path that can lead us to healthier brain aging? In an international effort, the researchers mapped 1.65 million cells from 437 aging brains, and uncovered distinct paths of cellular change in the aging brains, with one leading to Alzheimer’s disease and the other to an alternative form brain aging. They also point to specific cell signatures predicted to advance disease once they appear in the aging ...
JMIR Medical Informatics is inviting submissions for a new theme issue titled: "Advancing Digital Health: Real-World Implementation and Strategic Insights from Industry-Driven Innovation"
2024-08-29
Toronto- August 27, 2024 - JMIR Publications invites submissions to a new theme issue titled “Advancing Digital Health: Real-World Implementation and Strategic Insights from Industry-Driven Innovation” in JMIR Medical Informatics, a leading peer-reviewed journal indexed in PubMed with a unique focus on clinical informatics and the digitization of care processes.
The health care landscape is transforming rapidly, driven by technological innovation and the pressing need for more efficient, accessible and patient-centric health care solutions.
Yet, the health IT industry grapples with ...
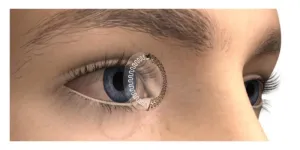
Terasaki Institute scientist awarded 2024 NARSAD Young Investigator Grant
2024-08-29
LOS ANGELES, August 29, 2024 — Yangzhi Zhu, Ph.D., Assistant Professor at the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI), has been awarded the prestigious 2024 NARSAD Young Investigator Grant for his groundbreaking work on a lab-on-a-contact lens (LoCL) system. This innovative technology is designed to monitor mental health by providing real-time, non-invasive tracking of panels of key biomarkers, from the wearer’s tears.
Mental health disorders, such as anxiety and depression, affect nearly a billion ...
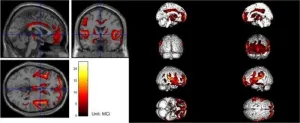
A breakthrough in diagnosing hydrocephalus: Multimodality approaches enhance accuracy and reduce costs
2024-08-29
A recent case report published in Cyborg Bionic Systems details the diagnosis of Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (iNPH) using multimodality diagnostic approaches, highlighting significant advancements in medical diagnostics and patient care. The study conducted by a team of researchers from Tianjin Medical University General Hospital, Tianjin, China, presents a comprehensive case study of a 68-year-old male patient diagnosed with iNPH, showcasing the effectiveness of these advanced diagnostic techniques.
iNPH is a condition characterized by the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) causing ventricular dilation, ...
This tiny backyard bug does the fastest backflips on earth
2024-08-29
Move over, Sonic. There’s a new spin-jumping champion in town – the globular springtail (Dicyrtomina minuta). This diminutive hexapod backflips into the air, spinning to over 60 times its body height in the blink of an eye, and a new study features the first in-depth look at its jumping prowess.
Globular springtails are tiny, usually only a couple millimeters in body length. They don’t fly, bite or sting. But they can jump. In fact, jumping is their go-to (and only) plan for avoiding predators. And they excel at it – to the naked eye it seems as though they vanish entirely when they take off.
“When globular springtails ...
Climate change increases foodborne illness risk from raw produce
2024-08-29
Highlights:
Salmonella enterica causes disease in 1.2 million people in the U.S. annually.
The most common way people get infected is by consuming contaminated fresh produce.
New research shows that bacterial leaf spot of lettuce and high humidity promote S. enterica growth in lettuce, and climate change is predicted to increase humid periods.
Washington, D.C.—Climate change will increase the risk of the foodborne illness from Salmonella enterica, according to a new study. The research was published today in Applied and Environmental Microbiology, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
S. enterica causes disease in 1.2 million people in the ...
NSF Grant empowers FAU to explore Caribbean climate crisis with ethnography
2024-08-29
Transformations in the global climate system are profoundly destabilizing ecosystems across the Caribbean, with South Florida and Puerto Rico experiencing notable impacts. To address this challenge, researchers from Florida Atlantic University and the University of Puerto Rico (UPR) in Cayey, are turning to ethnography – an in-depth, immersive research method that involves observing and interviewing people in their natural settings.
FAU’s Dorothy F. Schmidt College of Arts and Letters, in collaboration with UPR Cayey, has received a $650,000 grant from ...
A bacterial defense with potential application in genome editing
2024-08-29
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Scientists who have described in a new study the step-by-step details of a bacterial defense strategy see the mechanism as a promising platform for development of a new genome-editing method.
The system involves two proteins that team up to disable plasmids, small DNA molecules that exchange genetic information among different bacterial strains. While plasmids provide evolutionary benefits, they can also be seen by host bacteria as threats.
The research team determined that one protein uses a short piece of DNA – known as a DNA guide – to ...
Labor day crowds temporarily impact local streams, research shows
2024-08-29
Crowds flocking to rivers and streams over Labor Day weekend are doing more than cooling off and having fun. They’re temporarily introducing chemicals and microscopic organisms into their local waterways, according to new research from Johns Hopkins University.
The research, published today in ACS ES&T Water, is the first holistic assessment of how recreation impacts streams. Findings also provide insight into the compounds and chemicals people are splashing around in when their favorite swimming spots are packed.
“Residue from ...
Borderzone Breakthrough: A new source of cardiac inflammation
2024-08-29
Ischemic heart disease is the most common cause of death in the world. It begins with a “heart attack”, also known as a myocardial infarction (MI), which causes part of the heart to die due to inadequate coronary blood flow. This leads to vigorous inflammation, heart wall remodeling, and heart failure.
Anti-inflammatory drugs have been surprisingly ineffective at preventing heart failure. As a consequence, they are not a routine part of post-MI care. However, it is possible that the most potent molecular and cellular inflammation targets have yet to be discovered.
In the Aug. 28, ...
New study assesses the efficacy of suvorexant in reducing delirium in older adults
2024-08-29
Delirium is a sudden onset and temporary state of disturbed consciousness or cognition, occurring due to underlying medical issues like fever or alcohol withdrawal. It is most common among older hospitalized adults aged 75 years or above, leading to increased risk of falls, dementia, low life expectancy, and high healthcare expenses.
Non-pharmacological approaches to prevent or reduce delirium are time-consuming, hard to implement, and partially effective. So, pharmacological interventions offer hope. Insomnia, a significant risk factor for delirium, could be alleviated with sleep-promoting medications. However, not all ...
Gene therapy gets a turbo boost from University of Hawaii researchers
2024-08-29
For decades, scientists have dreamt of a future where genetic diseases, such as the blood clotting disorder hemophilia, could be a thing of the past. Gene therapy, the idea of fixing faulty genes with healthy ones, has held immense promise. But a major hurdle has been finding a safe and efficient way to deliver those genes.
Now, researchers at the University of Hawaiʻi’s John A. Burns School of Medicine (JABSOM) have made a significant breakthrough in gene editing technology that could revolutionize how we treat genetic diseases. Their new method offers a faster, safer, and more efficient way to deliver healthy ...
Global timber supply threatened as climate change pushes cropland northwards
2024-08-29
Climate change will move and reduce the land suitable for growing food and timber, putting the production of these two vital resources into direct competition, a new study has found.
The sight of vineyards in Britain is becoming more common as hotter summers create increasingly suitable conditions for growing grapes. But behind this success story is a sobering one: climate change is shifting the regions of the world suitable for growing crops.
Researchers at the University of Cambridge have uncovered a looming issue: as the ...
Researchers identify basic approaches for how people recognize words
2024-08-29
University of Iowa researchers have defined how people recognize words.
In a new study with people who use cochlear implants to hear, the researchers identified three main approaches that people with or without hearing impairment use to recognize words, an essential building block for understanding spoken language. Which approach depends on the person, regardless of hearing aptitude or ability: Some wait a bit before identifying a word, while others may tussle between two or more words before deciding which word has been heard.
When a person hears a word, the brain briefly considers hundreds, if not thousands, ...
Experts call for routine measurement of lipoprotein (a) levels
2024-08-29
London, UK: Heart experts say that everyone should have their levels of lipoprotein (a) (Lp(a) measured routinely at least once in life, following research from one of the most populous EU countries, Poland, that shows how common high levels of Lp(a) are in the general population.
The findings come from several studies presented at the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Congress taking place in London, UK, this week [1] and published in two journals: Progress in Cardiovascular Disease and Archives of Medical Sciences [2].
LP(a) is a parcel of fats (also known ...
[1] ... [962]
[963]
[964]
[965]
[966]
[967]
[968]
[969]
970
[971]
[972]
[973]
[974]
[975]
[976]
[977]
[978]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.