U of A College of Nursing receives $1.6M grant to support Indigenous students
2024-08-28
Indigenous students pursuing nursing careers at the University of Arizona College of Nursing will benefit from additional financial support thanks to a $1.6 million grant from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services’ Indian Health Service.
The grant will fund the successful Indians in Nursing: Career Advancement and Transition Scholars, or INCATS, program for another five years. The program provides Indigenous students at the U of A College of Nursing with financial support for tuition, fees and a living stipend.
Additionally, the grant provides resources for dedicated time and personnel to partner with tribal ...
Moths may use disco gene to regulate day/night cycles
2024-08-28
How does one species become two? If you’re a biologist, that’s a loaded question. The consensus is that, in most cases, the process of speciation occurs when individuals from a single population become geographically isolated. If they remain separate long enough, they lose the ability to interbreed.
A new study published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences demonstrates what happens when a less common form of speciation occurs. Rather than being separated by a physical barrier, such as a mountain range or an ocean, members of a species can become ...
Henna secures $30,000 from PSU’s University Venture Development Fund to enhance AI fairness & safety
2024-08-28
UVDF Funding, Henna
Henna Secures $30,000 from PSU’s University Venture Development Fund to Enhance AI Fairness & Safety
Portland, OR – August 13, 2024 – Henna, a startup with deep ties to Portland State University (PSU), has successfully secured $30,000 in funding from the University Venture Development Fund (UVDF). This grant will support Henna's mission to make AI adoption fairer and safer.
Henna was founded earlier this year by Arsh Haque (they/them), Chair of the Diversity, Equity, & Inclusion ...
Heriot-Watt University breaks ground on new £2.5M Optical Ground Station
2024-08-28
Work has started on a new Quantum Communications Hub Optical Ground Station (HOGS), a state-of-the-art telescope which is being built on Heriot-Watt University’s Research Park.
The new facility will demonstrate and test satellite quantum secure communications, maintaining and growing the UK’s strength in the field of quantum technologies. It is scheduled to be fully operational by late Autumn [2024].
As well as helping to tackle future cyberattacks by researching methods to send secure transmissions via satellites, it will unlock new research on space environmentalism alongside innovative R&D activities for future laser communication ...
SUNY Board of Trustees and Chancellor King announce presidential appointment at SUNY College of Optometry
2024-08-28
New York, NY – The State University of New York Board of Trustees today appointed Dr. David Troilo as president of SUNY College of Optometry. He is the 4th president to serve the state’s only college of optometry, following the retirement of Dr. David A. Heath after 17 years of dedicated service to the campus. Dr. Troilo’s appointment is effective immediately.
The SUNY Board of Trustees said, “SUNY College of Optometry is a center of research and academic excellence, and Dr. Troilo is a collaborative and thoughtful leader who is ready to move the campus forward growing ...
Cold math, hot topic: Sea ice thermal conductivity
2024-08-28
A new applied mathematical theory could enhance our understanding of how sea ice affects global climate, potentially improving the accuracy of climate predictions.
The authors of a new paper published in the Proceedings of the Royal Society A on 28 August, offer new insights into how heat travels through sea ice, a crucial factor in regulating Earth's polar climate.
Dr Noa Kraitzman, Senior Lecturer in Applied Mathematics at Macquarie University and lead author of the study, says the research addresses a key gap in current climate modelling.
“Sea ice covers about 15 per cent of the ocean’s surface during ...
Individuals with type 2 diabetes who are at higher risk of certain cancers could be identified by a simple blood test, Danish study suggests
2024-08-28
Individuals with type 2 diabetes who are at higher risk of certain cancers could be identified by a simple blood test, this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) (Madrid, 9-13 September) will hear.
People with type 2 diabetes are known to be at higher risk of developing cancers associated with obesity (OR cancers), including breast, kidney, womb, thyroid and ovarian cancer, as well as gastrointestinal cancers, including colorectal and pancreatic ...
New UT School of Public Health San Antonio welcomes inaugural class, launches degree program designed for South Texas
2024-08-27
The University of Texas School of Public Health San Antonio (UT School of Public Health San Antonio), a collaboration between The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) and The University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA), proudly welcomes its inaugural class and the official launch of the region’s first Master of Public Health (MPH) graduate degree program.
Beginning Monday, Aug. 26, the first cohort of 40 students will attended classes at the new UT School of Public Health San Antonio, located on the Greehey Campus at UT Health San Antonio. Many of the students in the program ...
Mizzou researchers explore solutions to help reduce nurse burnout
2024-08-27
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- Even before the coronavirus pandemic, high rates of burnout and staffing shortages plagued the nursing industry, primarily because of the stressful demands of the job. The COVID-19 pandemic only amplified these challenges, and with nearly a third of all Missouri nurses nearing retirement, improving nurse retention is key to avoiding an impending nursing workforce crisis in our state.
Despite dozens of studies proving burnout is an issue, few provide interventions to help nurses — and their patients — overcome its challenges.
A recent study by the University of Missouri has found that ...
Algorithm raises new questions about Cascadia earthquake record
2024-08-27
The Cascadia subduction zone in the Pacific Northwest has a history of producing powerful and destructive earthquakes that have sunk forests and spawned tsunamis that reached all the way to the shores of Japan.
The most recent great earthquake was in 1700. But it probably won’t be the last. And the area that stands to be affected is now bustling metropolises that are home to millions of people.
Figuring out the frequency of earthquakes – and when the next “big one” will happen – is an active scientific question that involves looking for signs of past earthquakes in the geologic record in the form of shaken up rocks, ...
Defining chronic pain for high-performance athletes with disabilities
2024-08-27
With the Paris 2024 Paralympic Games just around the corner, the extensive training and the sacrifices athletes make to compete at the games take centre stage.
For Paralympians and high-performance athletes with spinal cord injuries (SCI), assessing chronic pain plays a key role in their training and readiness to compete. However, the source of chronic pain is often misattributed to acute trauma or overuse injuries. While the International Olympic Committee acknowledges pain management data among Paralympians and athletes with disabilities is limited, few studies have been launched investigating this dilemma.
Now, new research from UBC Okanagan highlights the need for more comprehensive ...
Illinois researchers develop near-infrared spectroscopy models to analyze corn kernels, biomass
2024-08-27
URBANA, Ill. – In the agricultural and food industry, determining the chemical composition of raw materials is important for production efficiency, application, and price. Traditional laboratory testing is time-consuming, complicated, and expensive. New research from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign demonstrates that near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy and machine learning can provide quick, accurate, and cost-effective product analysis.
In two studies, the researchers explore the use of NIR spectroscopy for analyzing characteristics of corn kernels and sorghum biomass.
“NIR spectroscopy has many advantages over traditional methods. ...
It’s the most common STI you’ve never heard of. Will this newly developed drug provide the cure?
2024-08-27
Researchers at Tulane University are leading a groundbreaking study to seek a more effective treatment for trichomoniasis, an infection that, despite being the most common curable sexually transmitted infection (STI) worldwide, continues to fly under the radar.
The five-year, multi-center study is funded by a $9.2 million National Institutes of Health grant and will compare the effectiveness of a recently approved medication, secnidazole, against the current standard treatment, metronidazole, using ...
Texas A&M researchers find that aoudad, bighorn sheep share respiratory pathogens
2024-08-27
By Courtney Price, Texas A&M College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences
A team of researchers at the Texas A&M College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences (VMBS) has discovered that aoudad — an animal in the sheep and goat family — can catch and spread many of the same respiratory pathogens that can impact desert bighorn sheep, a native species in Texas that often shares its habitat with aoudad.
The new research, recently published in the journal PLOS ONE, will help wildlife conservationists better understand the complex relationship between ...
CRF announces TCT 2024 late-breaking clinical trials and science
2024-08-27
NEW YORK – August 27, 2024 – The Cardiovascular Research Foundation® (CRF®) is pleased to announce the late-breaking clinical trials and science to be featured at TCT® 2024. As the annual scientific symposium of CRF® and the world’s premier educational meeting specializing in interventional cardiovascular medicine, TCT® 2024 will be held October 27-30 in Washington, D.C. at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center.
For over three decades, TCT® has been at the forefront of innovation, education, and collaboration in interventional ...
Not sure how to stand out as a leader on Zoom calls? It starts with how you communicate, new study shows
2024-08-27
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- More companies are embracing remote work, and with that comes a need for more frequent communication. Teamwork through a screen isn’t always the same as having a group in the same room, so how are companies cultivating leaders in these virtual settings?
New research involving a collaboration between Binghamton University, State University of New York schools and research centers shows how, in virtual teams where nonverbal cues are limited, a person’s engagement and influence in conversations can significantly shape whether they’re perceived as a leader.
But taking charge of the conversation isn’t enough, the study found; for leadership ...
Prenatal smoking risks academic achievement of unborn babies
2024-08-27
Smoking harms almost every part of your body. But if you smoke when pregnant, the toxic chemicals in tobacco will also harm your unborn baby, with new research showing that it could lead to reduced academic outcomes at school.
In a systematic review of 19 studies and 1.25 million participants, researchers at the University of South Australia along with a team at Curtin University, SAHMRI, Harvard University and others* found that 79% of studies reported reduced academic achievement in children exposed to maternal prenatal smoking.
An additional meta-analysis of eight primary studies with 723,877 participants ...
The importance of brand strength when designing group and individual sales incentives in brand-managed retail sales settings
2024-08-27
Researchers from Wake Forest University and University of California-Riverside published a new Journal of Marketing article that examines the dynamic BMR retail context and investigates the sales incentives there.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Group or Individual Sales Incentives? What is Best for Brand-Managed Retail Sales Operations?” and is authored by Wenshu Zhang, Jia Li, and Subramanian Balachander.
Should a brand adopt group or individual sales incentives for its retail sales force? Could differences in brand strength or brand equity affect how brands incentivize their sales ...
Discovery gives answers to parents of children with rare disease
2024-08-27
Shortly after Kelly Cervantes’ daughter Adelaide was born, she started having terrible seizures. Doctors were unable to give her a solution, or even a cause.
“We never had an overarching diagnosis for her, which was extraordinarily frustrating and isolating,” she says. “If we did, we could join groups or talk to people who had various symptoms in common. We also had no idea what her prognosis looked like, or if we could have other children.”
Over time her condition worsened and sadly she died five days before her fourth birthday.
“She ...
UT Health San Antonio School of Dentistry names director of Center for Pain Therapeutics and Addiction Research
2024-08-27
SAN ANTONIO, Aug. 27, 2024 – Kenneth M. Hargreaves, DDS, PhD, professor of endodontics at the School of Dentistry of The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio), has been named inaugural director of the school’s Center for Pain Therapeutics and Addiction Research.
Hargreaves, who chaired the Department of Endodontics at the school for 26 years, is a world-renowned expert in pain research and has served as principal or co-principal investigator on numerous National Institutes of Health, Department of Defense and foundation-funded projects totaling more than $139 million.
Just recently, his research proposal, ...
Researchers develop affordable, rapid blood test for brain cancer
2024-08-27
Researchers at the University of Notre Dame have developed a novel, automated device capable of diagnosing glioblastoma, a fast-growing and incurable brain cancer, in less than an hour. The average glioblastoma patient survives 12-18 months after diagnosis.
The crux of the diagnostic is a biochip that uses electrokinetic technology to detect biomarkers, or active Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors (EGFRs), which are overexpressed in certain cancers such as glioblastoma and found in extracellular vesicles.
“Extracellular vesicles or exosomes are unique ...
NREL advances method for recyclable wind turbine blades
2024-08-27
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) see a realistic path forward to the manufacture of bio-derivable wind blades that can be chemically recycled and the components reused, ending the practice of old blades winding up in landfills at the end of their useful life.
The findings are published in the new issue of the journal Science. The new resin, which is made of materials produced using bio-derivable resources, performs on par with the current industry standard of blades made from a thermoset resin and outperforms certain thermoplastic resins intended to be recyclable.
The researchers built a prototype 9-meter blade to ...
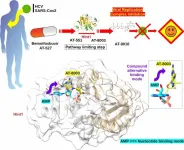
Atomic resolution of the broad-spectrum antiviral drug cascade to facilitate the design of antiviral drugs
2024-08-27
Atomic resolution of the broad-spectrum antiviral drug cascade to facilitate the design of antiviral drugs
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002743
Article Title: The activation cascade of the broad-spectrum antiviral bemnifosbuvir characterized at atomic resolution
Author Countries: France, United States, Germany
Funding: see manuscript END ...
This new technique for studying cell receptors could have sweeping implications for drug development
2024-08-27
One in every three FDA-approved drugs targets a single superfamily of receptors dotting the surfaces of human cells. From beta blockers to antihistamines, these essential, life-saving medications trigger winding biochemical pathways, via these receptors, to ultimately prevent a heart attack, or stop an allergic reaction in its tracks.
But scientists have learned that their story is much more complicated than initially believed—a number of these drugs are in fact targeting a complex composed of one receptor and one associated protein. Now, a ...
Bringing environmental justice to disadvantaged communities
2024-08-27
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Not all communities in the United States face the same risks for environmental problems such as air pollution, noise and wastewater. But how can federal agencies fairly identify which areas deserve the most help?
A new consensus study report from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine (NASEM) offer recommendations for developing tools that can help answer that question.
“Our job was to create methods to identify disadvantaged communities that most need federal resources to address environmental justice issues,” said Harvey Miller, ...
[1] ... [967]
[968]
[969]
[970]
[971]
[972]
[973]
[974]
975
[976]
[977]
[978]
[979]
[980]
[981]
[982]
[983]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.