Knowing you have a brain aneurysm may raise anxiety risk, other mental health conditions
2024-08-26
Research Highlights:
People diagnosed with unruptured cerebral aneurysms (weakened areas in brain blood vessels) who are being monitored without treatment have a higher risk of developing mental illness compared to those who have not been diagnosed with a cerebral aneurysm. The largest impact was among adults younger than age 40.
The study conducted in South Korea found that the psychological burden caused by the diagnosis of an unruptured aneurysm may contribute to the development of mental health conditions, such as anxiety, stress, depression, eating ...
Non-cognitive skills: the hidden key to academic success
2024-08-26
A new Nature Human Behaviour study, jointly led by Dr Margherita Malanchini at Queen Mary University of London and Dr Andrea Allegrini at University College London, has revealed that non-cognitive skills, such as motivation and self-regulation, are as important as intelligence in determining academic success. These skills become increasingly influential throughout a child's education, with genetic factors playing a significant role. The research, conducted in collaboration with an international team of experts, suggests that fostering non-cognitive skills alongside cognitive abilities could significantly improve educational ...
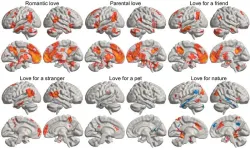
Finding love: Study reveals where love lives in the brain
2024-08-26
We use the word ‘love’ in a bewildering range of contexts — from sexual adoration to parental love or the love of nature. Now, more comprehensive imaging of the brain may shed light on why we use the same word for such a diverse collection of human experiences.
‘You see your newborn child for the first time. The baby is soft, healthy and hearty — your life’s greatest wonder. You feel love for the little one.’
The above statement was one of many simple scenarios presented to fifty-five parents, self-described as being in a loving relationship. Researchers from Aalto University utilised ...
Researchers develop high-entropy non-covalent cyclic peptide glass
2024-08-26
Researchers from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed a sustainable, biodegradable, biorecyclable material: high-entropy non-covalent cyclic peptide (HECP) glass. This innovative glass features enhanced crystallization-resistance, improved mechanical properties, and increased enzyme tolerance, laying the foundation for its application in pharmaceutical formulations and smart functional materials. This study was published in Nature Nanotechnology on ...
Mapping the sex life of Malaria parasites at single cell resolution, reveals the genetics underlying Malaria transmission
2024-08-26
Malaria is caused by a eukaryotic microbe of the Plasmodium genus, and is responsible for more deaths than all other parasitic diseases combined. In order to transmit from the human host to the mosquito vector, the parasite has to differentiate to its sexual stage, referred to as the gametocyte stage. Unlike primary sex determination in mammals, which occurs at the chromosome level, it is not known what causes this unicellular parasite to form males and females. New research at Stockholm University has implemented high-resolution genomic tools to map the global repertoire of genes ...
Communicating consensus strengthens beliefs about climate change
2024-08-26
Climate scientists have long agreed that humans are largely responsible for climate change. However, people often do not realize how many scientists share this view. A new 27-country study published in the journal Nature Human Behaviour finds that communicating the consensus among scientists can clear up misperceptions and strengthen beliefs about climate change.
The study is co-led by Bojana Većkalov at the University of Amsterdam and Sandra Geiger of the University of Vienna. Kai Ruggeri, professor of health policy and management at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, is the corresponding author.
Scientific consensus identifying humans as primarily ...
Almost half of FDA-approved AI medical devices are not trained on real patient data
2024-08-26
Artificial intelligence (AI) has practically limitless applications in healthcare, ranging from auto-drafting patient messages in MyChart to optimizing organ transplantation and improving tumor removal accuracy. Despite their potential benefit to doctors and patients alike, these tools have been met with skepticism because of patient privacy concerns, the possibility of bias, and device accuracy.
In response to the rapidly evolving use and approval of AI medical devices in healthcare, a multi-institutional team of researchers at the UNC School of Medicine, Duke University, Ally Bank, Oxford University, Colombia University, and University of Miami have been on a mission to build ...
Does the extent of structural racism in a neighborhood affect residents’ risk of cancer from traffic-related air pollution?
2024-08-26
High levels of traffic-related air pollutants have been linked with elevated risks of developing cancer and other diseases. New research indicates that multiple aspects of structural racism—the ways in which societal laws, policies, and practices systematically disadvantage certain racial or ethnic groups—may contribute to increased exposure to carcinogenic traffic-related air pollution. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Most studies suggesting that structural racism, which encompasses factors such as residential segregation and differences in economic status and homeownership, may influence ...
2 in 3 parents want help preventing their child from developing hereditary health conditions
2024-08-26
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – Among things many families don’t wish to pass down to their children and grandchildren: medical issues.
One in five parents say their child has been diagnosed with a hereditary condition, while nearly half expressed concerns about their child potentially developing such a condition, a new national poll suggests.
And two thirds of parents want their healthcare provider to suggest ways to prevent their child from developing a health problem that runs in the family, according to the University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National ...
Could psychedelic-assisted therapy change addiction treatment?
2024-08-26
by Amy Norton
PISCATAWAY, NJ – After years of being seen as dangerous “party drugs,” psychedelic substances are receiving renewed attention as therapies for addiction -- but far more research is needed, according to a new special series of articles in the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, published at Rutgers University.
Psychedelics are substances that essentially alter users’ perceptions and thoughts about their surroundings and themselves. For millennia, indigenous cultures have used plants with psychedelic properties in traditional medicine and spiritual rituals. And for a time in the mid-20th ...
Sustaining oyster farming with sturdier rafts
2024-08-26
Amid the rising human population and pressure on food supplies, the world can’t be everyone’s oyster. But perhaps there might be more oysters to eat if an Osaka Metropolitan University-led research team’s findings mean sturdy plastic rafts will be used in their farming.
Conventional oyster farming uses bamboo rafts with additional flotation devices such as Styrofoam. Though relatively affordable, these rafts can be damaged in typhoons. The OMU-led researchers propose a polyethylene raft that keeps costs manageable but is about five times more durable than a bamboo raft.
OMU Graduate School of Engineering Associate ...
People of lower socioeconomic status less likely to receive cataract surgery in private clinics
2024-08-26
Despite increased funding for cataract surgeries to private, for-profit clinics, access to surgery fell 9% for lower-income people, according to new research published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.240414.
“Unexpectedly, despite new public funding for operations provided in private for-profit surgical centres, which was intended to fully cover all overhead costs and remove the need to charge patients, this disparity did not decrease, but instead grew ...
Tick-borne Powassan virus in a child
2024-08-26
With tick-borne viruses such as Powassan virus increasing in Canada, clinicians should consider these infections in patients with encephalitis, as a case study shows in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.240227.
Although rare, Powassan virus is serious, with a death rate of 10%–15% in people with encephalitis, and it can cause lingering health effects after infection. The virus can transmit within 15 minutes of tick attachment, and symptoms can develop 1–5 weeks later.
In this case study, a 9-year-old child with up-to-date vaccinations ...
Survey finds more than 3 in 4 Americans don’t feel they could help someone suffering an opioid overdose
2024-08-26
EMBARGOED UNTIL 12:01 A.M. AUGUST 26, 2024
NOTE TO EDITOR: (To download broadcast-quality video and other multimedia elements: https://bit.ly/3M2ljhX (password: naloxone)
COLUMBUS, Ohio – International Overdose Awareness Day is a worldwide campaign held each Aug. 31 that acknowledges the grief of family and friends left behind from those who have died from a drug overdose. This year’s campaign theme “Together we can” highlights the power of the community standing together to help end overdose.
However, a new survey of 1,000 Americans from The Ohio State University Wexner Medical ...
How to control your screentime use and make technology work for you
2024-08-26
Many of us feel that we, or our children, spend too much time staring at a screen. From gaming to social media use or ‘doomscrolling,’ it can sometimes feel that we are mindlessly spending hours going down a rabbit hole of technology.
However, according to Catherine Knibbs, a psychotherapist who specializes in cybertrauma and online harms, there are tangible steps we can all take to wrestle back control from the hands of the technology corporations.
In her new book, Managing Your Gaming and Social ...
Matching dinosaur footprints found on opposite sides of the Atlantic Ocean
2024-08-25
DALLAS (SMU) – An international team of researchers led by SMU paleontologist Louis L. Jacobs has found matching sets of Early Cretaceous dinosaur footprints on what are now two different continents.
More than 260 footprints were discovered in Brazil and in Cameroon, showing where land-dwelling dinosaurs were last able to freely cross between South America and Africa millions of years ago before the two continents split apart.
“We determined that in terms of age, these footprints were similar,” Jacobs said. “In their geological and plate ...
Turning bacteria into bioplastic factories
2024-08-23
In a world overrun by petroleum-based plastics, scientists are searching for alternatives that are more sustainable, more biodegradable and far less toxic to the environment.
Two new studies by biologists at Washington University in St. Louis highlight one potential source of game-changing materials: purple bacteria that, with a little encouragement, can act like microscopic factories for bioplastics.
A study led by graduate student Eric Conners found that two relatively obscure species of purple bacteria have the ability to produce polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), natural ...
Researcher finds sound progress in babies’ speech development
2024-08-23
The sounds babies make in their first year of life may be less random than previously believed, according to a language development researcher from The University of Texas at Dallas.
Dr. Pumpki Lei Su, an assistant professor of speech, language, and hearing in the School of Behavioral and Brain Sciences, is co-lead author on two recent articles in which researchers examined the sounds babies make. The results suggest that children in their first year are more active than previously thought in their acquisition of speech.
“We observed in these studies that infant vocalizations are not produced randomly; they form a pattern, producing three categories of sounds in clusters,” ...
Two epicenters led to Japan’s violent Noto earthquake on New Year's Day
2024-08-23
Key takeaways
The 7.5- magnitude earthquake beneath Japan’s Noto Peninsula on Jan. 1, 2024, occurred when a “dual-initiation mechanism” applied enough energy from two different locations to break through a fault barrier – an area that locks two sides of a fault in place and absorbs the energy of fault movement, slowing it down or stopping it altogether.
An international team of researchers led by UCLA graduate student Liuwei Xu, professor Lingsen Meng and UC Santa Barbara’s Chen Ji analyzed a preceding seismic swarm and identified a previously unknown barrier in the region of the swarm.
The team’s data collection methods could ...
A leaky sink: Carbon emissions from forest soil will likely grow with rising temperatures
2024-08-23
Photos
The soils of northern forests are key reservoirs that help keep the carbon dioxide that trees inhale and use for photosynthesis from making it back into the atmosphere.
But a unique experiment led by Peter Reich of the University of Michigan is showing that, on a warming planet, more carbon is escaping the soil than is being added by plants.
"This is not good news because it suggests that, as the world warms, soils are going to give back some of their carbon to the atmosphere," said Reich, director of the Institute for Global Change ...
Rice bioengineers develop lotus leaf-inspired system to advance study of cancer cell clusters
2024-08-23
HOUSTON – (Aug. 23, 2024) – The lotus leaf is a pioneer of self-cleaning, water-repellant engineering. Water droplets all but hover on its surface, whose unique texture traps air in its nanosized ridges and folds.
Rice University bioengineers report harnessing the lotus effect to develop a system for culturing cancer cell clusters that can shed light on hard-to-study tumor properties. The new zinc oxide-based culturing surface mimics the lotus leaf surface structure, providing a highly tunable platform for the high-throughput generation of three-dimensional nanoscale tumor models.
The superhydrophobic array device (SHArD) designed by Rice bioengineer Michael King and ...
To mask or not to mask: That is still the question
2024-08-23
CHICAGO --- Despite the association between mask mandates/mask wearing and reduced death rates during the pandemic, masking remains controversial and highly politicized, with many people still asking, “do masks work, and should they be recommended?”
In an editorial about the use of surgical face masks in public, published today, Aug. 23, in The BMJ, Northwestern Medicine internal medicine experts Drs. Jeffrey Linder and Rachel Amdur make the case for masking but acknowledge it’s not a cut-and-dried topic.
The ...
A switch for immune memory and anti-tumor immunity
2024-08-23
AUGUST 23, 2024, NEW YORK – A Ludwig Cancer Research study has identified a metabolic switch in the immune system’s T cells that is essential to the generation of memory T cells—which confer lasting immunity to previously encountered pathogens—and a T cell subtype found in tumors that drives anti-tumor responses during immunotherapy.
Led by Ludwig Lausanne’s Ping-Chih Ho and Alessio Bevilacqua and published in the current issue of Science Immunology, the study identifies PPARβ/δ, a master regulator of gene expression, as that essential molecular switch. Ho, Bevilacqua and their colleagues also show that the switch’s dysfunction compromises ...
Study finds nearly half of U.S. counties have at least one ‘pharmacy desert’
2024-08-23
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Nearly half of counties in the United States have at least one ‘pharmacy desert’ where there is no retail pharmacy within 10 miles, according to a new study published by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC – James).
“As pharmacies close, more and more Americans are left without easy access to medications, with disproportionate consequences on certain communities. We found that patients in counties with higher social vulnerabilities and fewer primary care providers were up to 40% more likely to reside in a region ...
MSU study finds placebos reduce stress, anxiety, depression — even when people know they are placebos
2024-08-23
MSU has a satellite uplink/LTN TV studio and Comrex line for radio interviews upon request.
EAST LANSING, Mich. – A study out of Michigan State University found that nondeceptive placebos, or placebos given with people fully knowing they are placebos, effectively manage stress — even when the placebos are administered remotely.
Researchers recruited participants experiencing prolonged stress from the COVID-19 pandemic for a two-week randomized controlled trial. Half of the ...
[1] ... [972]
[973]
[974]
[975]
[976]
[977]
[978]
[979]
980
[981]
[982]
[983]
[984]
[985]
[986]
[987]
[988]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.