New NSF Center for Pandemic Insights
2024-08-22
Preventing the next pandemic begins before diseases emerge. This “pre-emergence” phase is the focus of a new center funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation and led by the University of California, Davis.
Supported with $18 million over seven years, the U.S. National Science Foundation Center for Pandemic Insights (NSF CPI) includes partnering institutions from across the United States. It aims to harness new technologies and develop sensing to detect, investigate, and ultimately prevent ...
FAMU-FSU College of Engineering research shows how insulin, zinc and pH can block harmful protein clumps linked to Type 2 diabetes
2024-08-22
An estimated 462 million people around the world suffer from Type 2 diabetes, a chronic disease in which the body has problems using sugar as a fuel, leading to a buildup of sugar in the blood and chronic health issues.
New research led by Ayyalusamy Ramamoorthy, a professor at the FAMU-FSU College of Engineering and the Florida State University-headquartered National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, shows how zinc, pH levels and insulin work together to inhibit the buildup of protein clumps that contribute to this disease. The work, which points toward promising avenues for innovative treatments, ...
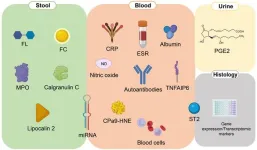
Fecal, blood, and urinary biomarkers in inflammatory bowel diseases
2024-08-22
The global burden of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), primarily Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), continues to rise. Recent data show incidence rates of up to 17.8 cases per 100,000 person-years for CD and even higher for UC, reaching 28.4 per 100,000 person-years. These diseases primarily affect older populations and vary geographically, with higher prevalence rates in highly developed countries. Currently, endoscopic assessment through ileo-colonoscopy is the gold standard for diagnosing and monitoring IBD. However, this approach is invasive and often has limited availability, leading to long ...
ARDD 2024 | What can we do before the "cliff" of aging arrives?
2024-08-22
When exactly does the aging process start? With the aging mechanisms unclear, no consensus has been reached about aging “cliffs”, where our body functions and biological processes just change dramatically, as if overnight.
In 2019, a study published in the authoritative peer-reviewed journal Nature Medicine, based on plasma proteomics data, identified 34, 60, and 78 years old as key time points of aging. In August 2024, Nature Aging, a Nature portfolio journal focusing on aging mechanisms, published the latest findings incorporating comprehensive data including transcriptomics and metabolomics, pinpointing the aging cliffs to the 40s and 60s.
In the biomedical field, multi-omics ...
Hydrogels can play Pong by “remembering” previous patterns of electrical simulation
2024-08-22
Non-living hydrogels can play the video game Pong and improve their gameplay with more experience, researchers report August 23 in the Cell Press journal Cell Reports Physical Science. The researchers hooked hydrogels up to a virtual game environment and then applied a feedback loop between the hydrogel’s paddle—encoded by the distribution of charged particles within the hydrogel—and the ball’s position—encoded by electrical stimulation. With practice, the hydrogel’s accuracy improved by up to 10%, resulting in longer rallies. The researchers say that this demonstrates ...
Precision drug olaparib may be effective without hormone therapy for some men with biochemically recurrent prostate cancer
2024-08-22
The anti-cancer drug olaparib may be effective in treating biochemically recurrent prostate cancer without accompanying hormone therapy for men who have mutations in genes such as BRCA2, according to results of a phase II clinical trial of 51 patients conducted at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and three other sites.
The study was done of men experiencing signs of cancer recurrence after surgical removal of the prostate, as measured by a high level of the protein prostate-specific antigen (PSA). Following treatment with olaparib, 13 participants, including all 11 who had BRCA2 mutations, had a decrease in PSA of at least 50% ...
Americans face disparities in exposure to tobacco on streaming platforms
2024-08-22
Tens of millions of Americans are being exposed to tobacco content on streaming services, according to new research from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. The researchers found that the odds of encountering tobacco products being advertised, marketed or promoted on these platforms increased based on race, ethnicity, socioeconomic status and smoking habits.
The nationally representative study, published today in JAMA Network, revealed an estimated 12.4% of American adults were exposed to tobacco promotion on streaming services. Exposure was highest among those with a high school education or less (16.4%), Black/African American respondents (19.4%), ...
Elinzanetant for the treatment of vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause
2024-08-22
About The Study: In two pivotal phase 3 clinical trials, elinzanetant, a selective neurokinin-1,3 receptor antagonist, demonstrated statistically significant reductions in vasomotor symptoms (VMS) frequency and severity vs placebo in postmenopausal individuals with moderate to severe VMS. Elinzanetant also significantly improved sleep disturbances and menopause-related quality of life vs placebo; the safety profile was favorable.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, JoAnn V. Pinkerton, ...
Trends in children’s exposure to food and beverage advertising on television
2024-08-22
About The Study: In this repeated cross-sectional study of children’s exposure to food-related television advertisements, exposure via children’s programming decreased substantially. However, most advertisements seen were still for unhealthy products, and exposure from all programming remained substantial. Findings of more than 90% of advertising exposure not from children’s programming and more than 1,000 food-related advertisements seen per year suggest the need for government regulations based on time of day rather than programming.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Lisa M. Powell, PhD, email powelll@uic.edu.
To ...
Disparities in exposure to tobacco on television or streaming platforms
2024-08-22
About The Study: In this study of the prevalence of exposure to tobacco advertisements on TV or streaming platforms among U.S. adults, disparities in exposure by race or ethnicity, education level, and smoking status were identified. These findings underscore the need for targeted public health interventions and regulation to address these disparities and reduce the impact of tobacco advertisements on vulnerable populations.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Sanjay Shete, PhD, email sshete@mdanderson.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.27781)
Editor’s ...
How thyroid hormone fuels the drive to explore
2024-08-22
Thyroid hormone plays a key role in regulating a range of physiologic functions, including metabolism, temperature, heart rate, and growth. It accomplishes this impressive array of activities by interacting with almost every organ system in the body. Yet despite a long history of research on how thyroid hormone influences different organs, its effects on arguably the most crucial organ — the brain — have remained shrouded in mystery.
Now, scientists at Harvard Medical School have gained ...
Higher thiazide doses shown to reduce kidney stone events
2024-08-22
Higher thiazide doses are associated with greater reductions in urine calcium, which in turn correlate with fewer symptomatic kidney stone events, according to a Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) study published in JAMA Network Open.
Thiazide diuretics, commonly prescribed to prevent kidney stone recurrence, are drugs that act directly on the kidneys to promote diuresis (urine flow) by inhibiting the sodium/chloride cotransporter located in the distal convoluted tubule of a nephron ...
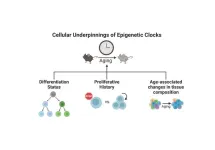
Reading your biological age in your blood or saliva? It’s not as simple as that
2024-08-22
How old are you, really? Your chronological age is the number of years you have been alive. Your biological age is how old your cells are which scientists believe may better assess one’s age-related health and disease risk. People biologically age at different rates, depending on genetic and environmental factors, so that a person’s chronological age does not necessarily match their biological age. In recent years, direct-to-consumer biological age tests have become increasingly accessible and popular as interest has increased ...
Pong prodigy: Hydrogel material shows unexpected learning abilities
2024-08-22
In a study published today (22 August) in Cell Reports Physical Science, a team led by Dr Yoshikatsu Hayashi demonstrated that a simple hydrogel - a type of soft, flexible material - can learn to play the simple 1970s computer game ‘Pong’. The hydrogel, interfaced with a computer simulation of the classic game via a custom-built multi-electrode array, showed improved performance over time.
Dr Hayashi, a biomedical engineer at the University of Reading’s School of Biological Sciences, said: "Our research shows that even very simple materials can exhibit complex, adaptive behaviours typically associated with living systems or sophisticated AI.
"This ...
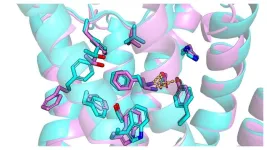
AI can speed up drug development
2024-08-22
Artificial intelligence (AI) can help identify molecules that could serve as new drugs for mental health disorders. AI can be used to predict the three-dimensional structures of important receptors and thereby speed up the development of potential drugs. This is the result of a new study from Uppsala University published in Science Advances.
In drug development, experimental methods are often used to determine the three-dimensional structures of target proteins and to understand how molecules bind to them. This information is needed to design drug molecules efficiently. However, the process to determine structures can be demanding, meaning this ...
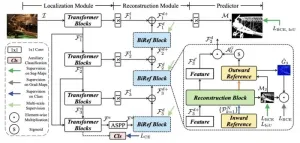
Bilateral reference framework for high-resolution dichotomous image segmentation
2024-08-22
A research team has developed a computer vision technique that can perform dichotomous image segmentation, high-resolution salient object detection, and concealed object detection in the same framework. Their novel bilateral reference framework (BiRefNet) is able to capture tiny-pixel features and holds potential for a wide range of practical computer vision applications.
The work is published in the journal CAAI Artificial Intelligence Research on August 22.
In computer vision research, ...
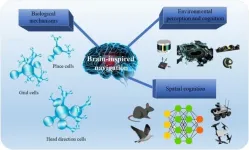
The future of robotics: Brain-inspired technologies paving the way
2024-08-22
In the ever-evolving field of robotics, a groundbreaking approach has emerged, revolutionizing how robots perceive, navigate, and interact with their environments. This new frontier, known as brain-inspired navigation technology, integrates insights from neuroscience into robotics, offering enhanced capabilities and efficiency.
Brain-inspired navigation technologies are not just a mere improvement over traditional methods; they represent a paradigm shift. By mimicking the neural mechanisms of animals, these technologies provide robots with the ability to navigate through complex and unknown terrains with unprecedented accuracy ...
IHME’s 2024 Roux Prize awarded to Community Health Impact Coalition CEO – recognized for contributions to improve population health
2024-08-22
On behalf of the Community Health Impact Coalition (CHIC), Dr. Madeleine Ballard, global health leader and CEO of CHIC, is the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation’s 2024 Roux Prize winner. The award recognizes Dr. Ballard’s work alongside thousands of community health workers (CHWs) to secure quality care for all, through evidence-based health systems benefiting millions of people across the world.
Half of the world's population lacks access to essential health services. Around the globe, CHWs have stepped up to address this critical gap and deliver care in a way that improves access, increases equity, and saves lives. Despite their ...
New detectable gravitational wave source from collapsing stars predicted from simulations
2024-08-22
The death of a massive, rapidly spinning star can shake the universe. And the resulting ripples — known as gravitational waves — could be felt by instruments on Earth, according to new research published August 22 in The Astrophysical Journal Letters. These new sources of gravitational waves just await discovery, the scientists behind the research predict.
The gravitational waves emerge following the violent deaths of rapidly rotating stars 15 to 20 times the mass of the sun. Upon running ...
New study examines use of opioids for chronic cough
2024-08-22
INDIANAPOLIS – Chronic cough, with symptoms lasting more than eight weeks, affects approximately one in 10 adults. Cough is among the most common reasons for seeking medical care in the United States, yet chronic cough is difficult to treat. One of the largest studies of chronic cough and one of the first to explore the use of opioids, which are known to suppress cough, to treat these patients, has found that 20 percent of patients with chronic cough received a prescription for a cough suppressant containing an opioid.
With the goals of estimating opioid prescription in the chronic cough population and of informing alternative treatment ...
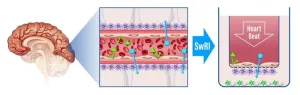
SwRI develops novel methodology for measuring blood-brain barrier permeability
2024-08-22
SAN ANTONIO — August 22, 2024 —Scientists at Southwest Research Institute have developed a new screening method to identify drug formulations that can penetrate the blood-brain barrier (BBB), to facilitate treatment of brain diseases and conditions.
“The BBB protects the brain and central nervous system from potentially harmful substances in the bloodstream, regulating the transport of essential nutrients and ions while maintaining the stability of the central nervous system,” said Research Engineer Nicholas McMahon, from SwRI’s Bioengineering group. “However, the very characteristics that make the BBB such an ...
Role of bitter polyphenols in the regulation of blood sugar
2024-08-22
Bioactive compounds like polyphenols and their health benefits have long captured public attention and interest. Commonly present in plant-based food like fruits, vegetables, seeds, coffee, and tea, the polyphenols have a strong bitter taste and, in the normal course, is excreted by our body due to poor absorption.
The polyphenols interact with human bitter taste receptors also known as Type 2 taste receptors (T2R) expressed within and outside the oral cavity. Notably, the activation of T2R expressed along the ...
Promising treatment for rectal cancer confirmed in major study
2024-08-22
A new treatment for locally advanced rectal cancer shows favourable results in that surgery can sometimes be avoided completely. It also reduces the risk of recurrence. The method has been confirmed as effective in a comprehensive study conducted at Uppsala University and published in eClinicalMedicine.
“The tumour disappears completely more often, thereby increasing the chance of avoiding surgery and retaining normal rectum and rectal function. Moreover, there are fewer metastases,” says Bengt Glimelius, Professor of Oncology ...
Chronic cough may be hereditary
2024-08-22
Chronic cough is among the most common reasons for seeking medical care, with middle-aged women the group most affected. New studies at Uppsala University also show that this condition appears to be a hereditary phenomenon. The studies have been published in ERJ Open Research and PLOS ONE.
“More than 10% of the population has a chronic cough, which has been shown to entail several negative consequences: reduced quality of life, reduced ability to work and voice problems. At present, we have insufficient knowledge about ...
Universal flu vaccine candidate protects against infection in mice
2024-08-22
Highlights:
Flu vaccine efficacy varies year to year.
A universal flu vaccine would protect people against all influenza strains that infect humans and last more than a season.
A new vaccine candidate incorporates proteins from 8 strains of influenza.
Recent tests of the candidate show efficacy in animal models, and the researchers hope to move to clinical trials soon.
Washington, D.C.—Annual flu vaccines protect against severe infection, but they vary in efficacy and may not match the most virulent strains ...
[1] ... [976]
[977]
[978]
[979]
[980]
[981]
[982]
[983]
984
[985]
[986]
[987]
[988]
[989]
[990]
[991]
[992]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.