Astrophysicists use AI to precisely calculate universe’s ‘settings’
2024-08-26
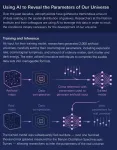
The standard model of the universe relies on just six numbers. Using a new approach powered by artificial intelligence, researchers at the Flatiron Institute and their colleagues extracted information hidden in the distribution of galaxies to estimate the values of five of these so-called cosmological parameters with incredible precision.
The results were a significant improvement over the values produced by previous methods. Compared to conventional techniques using the same galaxy data, the approach yielded less than half ...
SETI Institute starts first low frequency search for alien technology in distant galaxies
2024-08-26
August 26, 2024, Mountain View, CA -- The SETI Institute, the Berkeley SETI Research Center and the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research announced a groundbreaking study using the Murchison Widefield Array (MWA) in Western Australia. Led by Dr. Chenoa Tremblay of the SETI Institute and Prof. Steven Tingay of Curtin University, this research is the first to search for signs of alien technology in galaxies beyond our own, focusing on low radio frequencies (100 MHz). This innovative study used the MWA’s large field of view (FOV), allowing the team to cover about 2,800 galaxies in one observation, of which 1300 we know the distance to. Usually, the search for extraterrestrial ...
Bicycle rolling-stop laws don’t lead to unsafe behavior by riders or motorists, research shows
2024-08-26
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Laws that let bicyclists treat stop signs as yield signs lead neither riders nor motorists to act unsafely, according to a groundbreaking Oregon State University study.
The project by OSU College of Engineering researchers featured a novel experimental technique – linking separate bicycle and motor vehicle simulators – and the findings are important as more and more states consider bicycle rolling-stop legislation, said David Hurwitz, the study’s leader.
“It required fully connecting two independent simulators, running subjects in pairs simultaneously and having each subject interacting with an avatar of the other in a shared virtual ...
How a retracted paper affected the course of Alzheimer’s research (video)
2024-08-26
WASHINGTON, Aug. 26, 2024 — In June 2024, a landmark Alzheimer's research paper was retracted due to fraud allegations. Did we waste billions of dollars and thousands of hours of scientists’ time? Maybe not. There are now two potentially helpful drugs on the market targeting the subject of the paper: amyloid beta. This video breaks down the amyloid-beta hypothesis, the fraud itself and where we go from here.
Reactions is a video series produced by the American Chemical Society and PBS Digital Studios. Subscribe to Reactions and follow us on X, formerly Twitter @ACSReactions.
The American Chemical ...
Genotype Matters: Tailored screening for germline CHEK2 variants
2024-08-26
“In our study, we postulated that these differences were driven by three common low-risk (LR) missense variants: p.I157T, p.S428F, and p.T476M, all of which have a BC odds ratio of <1.4.”
BUFFALO, NY- August 26, 2024 – A new editorial was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on July 10, 2024, entitled, “Genotype matters: Personalized screening recommendations for germline CHEK2 variants.”
Recognized as a moderate-risk gene, CHEK2—responsible for encoding the CHK2 protein, ...
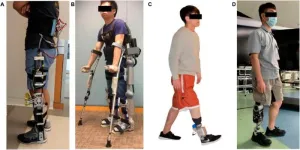
Interlimb and intralimb synergy modeling for lower limb assistive devices: Modeling methods and feature selection
2024-08-26
A research paper by scientists at Hainan University proposed FSS-eq2Seq as a 2-stage strategy for gait synergy modeling in lower limb assistive devices to achieve synergic and user-adaptive trajectories that improve human-machine interactions.
The new research paper, published on Jul. 03 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, indicatedSeq2Seq outperforms LSTM, RNN, and GRU in both interlimb and intralimb synergy modeling. Further, FS significantly improves Seq2Seq’s modeling performance.
The concept of gait synergy provides novel human-machine interfaces and has been applied ...
Darwin’s fear was unjustified: Writing evolutionary history by bridging the gaps
2024-08-26
Fossils are used to reconstruct evolutionary history, but not all animals and plants become fossils and many fossils are destroyed before we can find them (e.g., the rocks that contain the fossils are destroyed by erosion). As a result, the fossil record has gaps and is incomplete, and we’re missing data that we need to reconstruct evolutionary history. Now, a team of sedimentologists and stratigraphers from the Netherlands and the UK examined how this incompleteness influences the reconstruction of evolutionary history. To their surprise, they found that the incompleteness itself is actually not such a big issue. “It’s ...
Trends of heat-related deaths in the US, 1999-2023
2024-08-26
About The Study: This study found that heat-related mortality rates in the U.S. increased between 1999 and 2023, especially during the last 7 years. Although a study using data through 2018 found a downward trend in heat-related mortality in the U.S., this study is the first to our knowledge to demonstrate a reversal of this trend from 2016 to 2023. These results align with site-specific data analyzed in a global study that suggest increases in heat-related mortality. As temperatures continue to rise because of climate change, the recent increasing trend is likely to continue. Local authorities in high-risk areas should consider investing in the expansion of access to hydration centers ...
Transgender students more likely than cisgender peers to seek support from school staff, UW–Madison and NYU study finds
2024-08-26
MADISON – Transgender students are more likely to seek support from school staff and less likely to seek support from their parents when compared to their cisgender peers, according to a new study from researchers at the University of Wisconsin–Madison and New York University.
The study, published in JAMA Pediatrics, found among students who felt depressed or anxious, transgender students were 74% less likely than their cisgender peers to seek help from parents than from adults in schools. It also found transgender students were 25% less likely than cisgender students to seek support from ...
Longitudinal changes in youth mental health from before to during the COVID-19 pandemic
2024-08-26
About The Study: In this longitudinal cohort study of economically and racially diverse U.S. youth, there was evidence of differential susceptibility and resilience for mental health problems during the pandemic that was associated with prepandemic mental health and sociodemographic characteristics. These differences are critical to understand for recovery and may yield novel insights into causes of youth mental health problems.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Courtney ...
Repetitive head impacts and perivascular space volume in former football players
2024-08-26
About The Study: In this cross-sectional cohort study of 170 former football players and 54 unexposed controls, larger perivascular space (PVS) volume was associated with greater exposure to repetitive head impacts (RHI). Additionally, PVS volume was associated with worse performance on cognitive tests. These findings suggest that PVS volume may contribute to the association between exposure to RHI, cognitive impairment, and the development of RHI-associated neurodegeneration.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding ...
Sharing expands caring – UMD study finds solution to a major source of doctor burnout
2024-08-26
COLLEGE PARK, Md. – Who hasn’t sat in a medical office, listening to computer keys clacking while their provider rapidly types up notes, wondering what they are spending so much time writing about? For doctors, who have always written clinical care notes but increasingly must spend time cataloging billing details, this additional documentation is a major source of job dissatisfaction and burnout. A new study out today by University of Maryland’s School of Public Health illuminates a solution that can meaningfully reduce the amount of time doctors spend writing notes, without losing vital information.
“Providers are already stretched thin and under intense pressure to ...
Human stem cell models point to glia as key players in multiple sclerosis
2024-08-26
NEW YORK, NY (AUGUST 26, 2024) — A team of scientists from The New York Stem Cell Foundation (NYSCF) Research Institute and Case Western Reserve University has created the largest reported collection of stem cell models from multiple sclerosis (MS) patients and used them to identify unique ways in which glia – integral support cells in the brain – contribute to the disease.
The study, published today in Cell Stem Cell, is the first to report that glial cells from MS patients have intrinsic hallmarks of disease, independent of immune system influences, which points to the power of stem cells for revealing new disease biology and to the need for ...
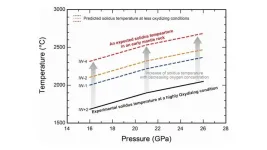
Uncovering the role of oxygen concentration in the formation of early earth magma ocean
2024-08-26
It is widely accepted that the early Earth largely consisted of molten magma, forming a global ocean of magma. This extreme state of Earth was likely caused by the intense heat generated from accretionary impacts, meaning the collision of smaller celestial bodies with Earth. Understanding the formation of this magma ocean is crucial for comprehending Earth’s formation. A major problem with current magma ocean formation models is the lack of consensus on the melting temperatures of deep mantle rocks. Models explaining Earth’s core formation use a specific ...
Early galaxies were not too big for their britches after all
2024-08-26
When astronomers got their first glimpses of galaxies in the early universe from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, they were expecting to find galactic pipsqueaks, but instead they found what appeared to be a bevy of Olympic bodybuilders. Some galaxies appeared to have grown so massive, so quickly, that simulations could not account for them. Some researchers suggested this meant that something might be wrong with the theory that explains what the universe is made of and how it has evolved since the big bang, known as the standard model of cosmology.
According to a new study in The Astrophysical Journal led by University of Texas at Austin graduate student ...
SwRI showcases latest warfighter research at military health research symposium
2024-08-26
SAN ANTONIO — August 26, 2024 — Southwest Research Institute will highlight its capacity to advance military medicine and human performance at the Military Health System Research Symposium, August 26-29, in Kissimmee, Florida.
“Southwest Research Institute has a long history of working with several DOD agencies,” said Senior Research Engineer Kreg Zimmern of SwRI’s Chemistry and Chemical Engineering Division. “SwRI offers multidisciplinary expertise, allowing us to manage government contracts ...
Scientific consensus can strengthen pro-climate attitudes in society
2024-08-26
Climate scientists have long agreed that humans are largely responsible for climate change. A new study, co-led by Bojana Većkalov from the University of Amsterdam and Sandra Geiger from the University of Vienna, finds that communicating the scientific consensus about climate change can clear up misperceptions and strengthen beliefs about the existence and the causes of climate change. The team surveyed over 10,000 people from 27 countries on 6 continents. The study has just been published in the renowned journal Nature Human Behaviour.
Scientific consensus identifying humans as primarily responsible ...
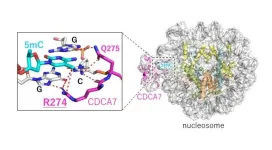
Unraveling the role of CDCA7 in maintenance of DNA methylation
2024-08-26
DNA methylation, a process by which methyl groups are added to DNA molecules, is essential for the maintenance of DNA and the overall health of an organism. Disruptions in the standard DNA methylation patterns can lead to immunodeficiency and diseases such as cancer. Helicase lymphoid-specific (HELLS) is an enzyme that facilitates DNA methylation by remodeling the nucleosome - the tightly packed structure of DNA wound around histone proteins. The absence of HELLS or its activator, cell division cycle associated 7 (CDCA7) is known to be a factor that leads to the disruption of DNA methylation. Mutations in the genes that code for HELLS and CDCA7 cause rare disorder immunodeficiency, ...
Study finds salamanders are surprisingly abundant in northeastern forests
2024-08-26
RESTON, Va. — Two recent amphibian-focused studies shed light on the ecological importance of red-backed salamanders, while confirming that proactive measures would prevent costly impacts from a wildlife disease spreading across Europe that has not yet reached North America.
Scientists knew that red-backed salamanders were abundant in eastern North America, but a recent study found their densities and biomass across the region were much higher than expected. The study authors estimated an average of ...
Old chemo drug, new pancreatic cancer therapy?
2024-08-26
The fight against cancer is an arms race, and one of the most effective weapons in clinicians’ arsenals is immunotherapy. Immune checkpoint therapy has become the standard for treating several types of cancer. However, the Nobel Prize-winning strategy is ineffective for most pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) patients.
“Immune checkpoint therapy is only an option in rare cases of PDAC,” Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor Douglas Fearon says. “It’s only effective for patients with a specific subtype of PDAC—that’s less than 5% of all cases.”
Until recently, it was thought that PDAC didn’t ...
Shakespeare in sign language, seen through AI
2024-08-26
A new study uses co-creation with reference communities to develop an app for sign language machine translation (SLMT). The research team designed a theatrical performance in sign language, seen through the eyes of artificial intelligence (AI), as one of the methodologies. “Historically, deaf people have been excluded from the development of automatic translation technologies,” says Shaun O’Boyle, Research Fellow in the School of Inclusive and Special Education (Dublin City University DCU). “This has often caused backlash and resistance from deaf communities, as the projects were designed and ...
PLOS and the University of South Carolina announce APC-free Open Access publishing agreement
2024-08-26
SAN FRANCISCO — The University of South Carolina and the Public Library of Science (PLOS) today announced a three-year Open Access agreement that allows researchers to publish in PLOS journals[1] without incurring article processing charges (APC). This partnership brings together two organizations that believe researchers should be able to access content freely and make their work available publicly, regardless of their access to funds.
“The evidence is undeniable — open research enables the convergence of ...
Why children can’t pay attention to the task at hand
2024-08-26
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Scientists have learned that children find it hard to focus on a task, and often take in information that won’t help them complete their assignment. But the question is, why?
In a new study, researchers found that this “distributed attention” wasn’t because children’s brains weren’t mature enough to understand the task or pay attention, and it wasn’t because they were easily distracted and lacked the control to focus.
It now appears that kids distribute their attention broadly either out of simple curiosity or because their working memory isn’t developed enough to complete a task without “over ...
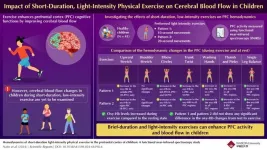
Short-duration, light-intensity exercises improve cerebral blood flow in children
2024-08-26
Cognitive functions, also known as intellectual functions, encompass thinking, understanding, memory, language, computation, and judgment, and are performed in the cerebrum. The prefrontal cortex (PFC), located in the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex, handles these functions. Studies have shown that exercise improves cognitive function through mechanisms such as enhanced cerebral blood flow, structural changes in the brain, and promotion of neurogenesis. However, 81% of children globally do not engage in enough physical activity, leading to high levels of sedentary behavior and insufficient exercise. This lack of physical ...
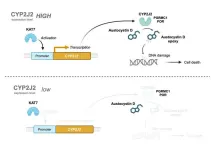
Exploring the role of cytochrome oxygenases in augmenting austocystin D-mediated cytotoxicity
2024-08-26
Austocystin D, a natural compound produced by fungi, has been recognized for its cytotoxic effects and anticancer activity in various cell types. It exhibits potent activity even in cells that express proteins associated with multidrug resistance, attracting significant global research interest. Austocystin D promotes cell death by damaging their DNA, a process which might be dependent on cytochrome P450 (CYP) oxygenase enzymes. Notably, austocystin D has shown significant activity against cancer cells with increased CYP expression. However, the specific role and function of the CYP2J2 enzyme in the cytotoxicity of austocystin D remain ...
[1] ... [971]
[972]
[973]
[974]
[975]
[976]
[977]
[978]
979
[980]
[981]
[982]
[983]
[984]
[985]
[986]
[987]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.