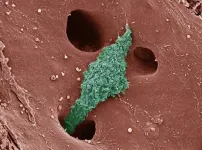
Single 5-nm quantum dot detection via microtoroid resonator photothermal microscopy
2024-08-23
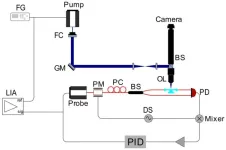
The detection of individual particles and molecules has opened new horizons in analytical chemistry, cellular imaging, nanomaterials, and biomedical diagnostics. Traditional single-molecule detection methods rely heavily on fluorescence techniques, which require labeling of the target molecules. In contrast, photothermal microscopy has emerged as a promising label-free, non-invasive imaging technique. This method measures localized variations in the refractive index of a sample's surroundings, resulting from light absorption by sample components, which induces temperature changes in the surrounding region. Whispering ...
Alzheimer’s drug may slow down cognitive decline in dementia with Lewy bodies
2024-08-23
Dementia with Lewy bodies is a type of dementia that is similar to both Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease but studies on long-term treatments are lacking. A new study from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden, published in Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association, highlights the potential cognitive benefits of cholinesterase inhibitor treatment.
Lewy body disease, which includes dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) and Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia, is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder, following Alzheimer’s disease. DLB accounts for approximately ...
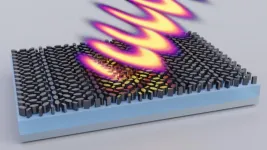
Researchers demonstrate metasurfaces that control thermal radiation in unprecedented ways
2024-08-23
NEW YORK, August 23, 2024 — In a groundbreaking advancement, researchers with the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) have experimentally demonstrated that metasurfaces (two-dimensional materials structured at the nanoscale) can precisely control the optical properties of thermal radiation generated within the metasurface itself. This pioneering work, published in Nature Nanotechnology, paves the way for creating custom light sources with unprecedented capabilities, ...
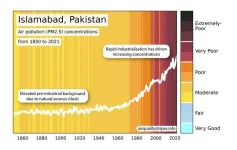
New images reveal global air quality trends
2024-08-23
University of Leeds News
Embargoed until 23 August 10:00 BST
A selection of AQ Stripes graphic images are available here
The global concentrations of one of the main air pollutants known to affect human health have been graphically illustrated for the first time by a team of scientists.
The Air Quality Stripes which were created by the University of Leeds, the University of Edinburgh, North Carolina State University, and the UK Met Office, starkly contrast the significant improvements in air quality across much of Europe with the alarming deterioration in parts ...
Spike mutations help SARS-CoV-2 infect the brain
2024-08-23
Still unknown what causes neurological complications of COVID-19 including ‘long COVID,’ ‘brain fog’ and loss of taste and smell
Viruses with a deletion in the spike protein are better able to infect the brains of mice
‘These findings suggest there might be treatments that could work better to clear the virus from the brain’
CHICAGO --- Scientists have discovered a mutation in SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, that plays a key role in its ability to infect the central nervous system. The findings may help scientists understand its neurological symptoms and the mystery of “long COVID,” and ...
Pesco-vegetarian diets best for reducing risk of death in elderly
2024-08-23
A variety of vegetarian diets appear to protect against risk of mortality and contributing conditions, with a pesco-vegetarian diet — which includes fish — providing the most protection against risk in very elderly people, according to a new study.
Researchers at Loma Linda University Health found that vegetarian diets are associated with lower risk for all-cause mortality and many cause-specific mortalities, especially among males and in middle-aged subjects. However, slightly higher risks were observed among very elderly vegetarians for neurological conditions such as stroke, dementia, and Parkinson’s Disease. Despite this, ...
Men infected with high-risk types of HPV could struggle with fertility
2024-08-23
Cervical cancer, the fourth most common cancer type in women, causes approximately 350,000 deaths each year, mainly in middle- and low-income countries. Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is known to cause 95% of these cases. Public health authorities in 37 countries currently vaccinate girls between nine and 14 years of age, before they typically start sexual activity.
HPV is also known to increase the risk of genital warts and cancers of the penis, anus, mouth, and throat in infected men, which is one of the reasons why the WHO and the US Center for Disease Control (CDC) ...
Scientists call for an update in environmental decision making that takes human rights into account
2024-08-23
Human wellbeing is connected to nature for food, climate regulation and culture, making the protection of nature a human rights matter.
Added to that, recent developments in international human rights law highlight that governments need to consider human-nature connections when making decisions that may affect the environment.
In a commentary published in npj Ocean Sustainability, an interdisciplinary group of researchers – including experts in ecosystem services, environmental governance, deep-sea ecology, and law – underscore that these developments should prompt a rethink of how any environmental decisions that hold the potential to impact biodiversity ...
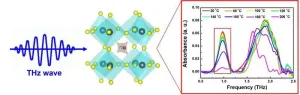
Terahertz detection: a novel approach to real-time monitoring of perovskite ageing
2024-08-23
Hybrid perovskites have great potential for use in advanced electronic devices like solar cells and LEDs. However, one major issue holding them back is that they don't last as long as needed for widespread commercial use. As these materials age, their performance drops, which is a big problem for both researchers and companies. To tackle this issue, it's important not only to improve the stability of these perovskites but also to develop methods for detecting how they age in real-time. By understanding how these materials degrade over time, we can make them more durable and efficient.
In a recent study, researchers led by Prof. Yiwen Sun at Shenzhen University used the terahertz ...
Colorful traits in primates ease tensions between groups
2024-08-23
Primate ornamentation plays a crucial role in communication not only within social groups but also between them, according to a new study. The research reveals that the males of species with overlapping home ranges often display vibrant colors or elaborate features, traits that may help reduce intergroup aggression by enabling quick assessments of potential rivals.
Ornaments are sexually selected traits that serve as powerful signals, often indicating an individual’s genetic quality, health or physical strength. These differences ...
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for August 2024
2024-08-23
AUGUST 2024 TIP SHEET: A mouthwash-like rinse to predict head and neck cancer recurrence, new research identifies biomarkers to predict which colon cancer patients benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy, the Dolphins Cancer Challenge and StacheStrong team up to boost brain cancer research, the CDC issues anal cancer screening guidelines for HIV patients based partly on research at Sylvester, and three Sylvester physicians who become the latest early-career faculty scholars are highlighted in this month’s tip sheet from Sylvester Comprehensive ...
Weight loss drug’s heart benefits extend to people with heart failure
2024-08-23
The anti-obesity medication semaglutide may help to prevent heart attacks and other major adverse cardiac events among overweight people who have cardiovascular disease, whether or not they also have heart failure, according to a new study led by UCL’s Professor John Deanfield.
The results follow previous research* from the same international team finding that weekly injections of semaglutide were linked to a 20% reduction in major adverse cardiac events (MACE) such as heart attacks and strokes for people with obesity or who were overweight and had cardiovascular disease.
The ...
Declining senses can impact mental health and loneliness in aging adults
2024-08-23
Most people — up to 94% of U.S. adults — experience at least some dulling of their senses with age, finding themselves squinting at screens, craving stronger flavors, and missing snatches of conversations more and more frequently. Researchers at the University of Chicago Medicine are looking into how these changes can go beyond mere inconvenience and actually worsen overall mental health in older adults.
“When your senses decline, you can't experience the world as well,” said Jayant Pinto, MD, a physician ...
NASA’s EXCITE mission prepared for scientific balloon flight
2024-08-23
Scientists and engineers are ready to fly an infrared mission called EXCITE (EXoplanet Climate Infrared TElescope) to the edge of space.
EXCITE is designed to study atmospheres around exoplanets, or worlds beyond our solar system, during circumpolar long-duration scientific balloon flights. But first, it must complete a test flight during NASA’s fall 2024 scientific ballooning campaign from Fort Sumner, New Mexico.
“EXCITE can give us a three-dimensional picture of a planet’s atmosphere and temperature by collecting data the whole time the world orbits its star,” said Peter Nagler, the mission’s principal ...
New gels could protect buildings during wildfires
2024-08-23
As climate change creates hotter, drier conditions, we are seeing longer fire seasons with larger, more frequent wildfires. In recent years, catastrophic wildfires have destroyed homes and infrastructure, caused devastating losses in lives and livelihoods of people living in affected areas, and damaged wildland resources and the economy. We need new solutions to fight wildfires and protect areas from damage.
Researchers at Stanford have developed a water-enhancing gel that could be sprayed on homes and critical infrastructure to help keep them from burning during wildfires. The research, published Aug. ...
U.S. National Science Foundation awards UT $18 million to study factors that lead to pandemics
2024-08-22
Professor of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology Nina Fefferman became a mathematician because she loves puzzles. She’s just been awarded $18 million from the U.S. National Science Foundation to solve one puzzle that has the potential to change the world: how, when and why an infection in a population will spread, or cause an epidemic or pandemic, rather than dying out.
Fefferman, director of the National Institute for Modeling Biological Systems and associate director of the UT One Health Initiative at the University ...
Mosquitoes sense infrared from body heat to help track humans down
2024-08-22
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — While a mosquito bite is often no more than a temporary bother, in many parts of the world it can be scary. One mosquito species, Aedes aegypti, spreads the viruses that cause over 100,000,000 cases of dengue, yellow fever, Zika and other diseases every year. Another, Anopheles gambiae, spreads the parasite that causes malaria. The World Health Organization estimates that malaria alone causes more than 400,000 deaths every year. Indeed, their capacity to transmit disease has earned mosquitoes the title of deadliest ...
DOD grants CU researchers $5 Million to study antibiotic-resistant wound infections in Ukraine
2024-08-22
Faculty members in the Department of Emergency Medicine at the University of Colorado School of Medicine have been awarded $5 million by the U.S. Department of Defense to work with partners in Ukraine on clinical and logistical challenges associated with modern large-scale combat operations and prolonged casualty care.
The overarching program — Research and Scalable Infrastructure to Improve Outcomes on the Front Lines of Ukraine by Advancing Treatment and Evaluation (RESOLUTE) — is focusing on collecting data related to antibiotic-resistant wound infections, which have substantially increased amid the military conflict.
The initial project — ...
3D body volume scanner uses AI to help predict metabolic syndrome risk
2024-08-22
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Mayo Clinic researchers are using artificial intelligence (AI) with an advanced 3D body-volume scanner – originally developed for the clothing industry – to help doctors predict metabolic syndrome risk and severity. The combination of tools offers doctors a more precise alternative to other measures of disease risk like body mass index (BMI) and waist-to-hip ratio, according to findings published in the European Heart Journal - Digital Health.
Metabolic syndrome can lead to heart attack, stroke and other serious health issues and affects over a third of the U.S. population and a quarter of people globally. ...
Building a COMPASS to navigate future pandemics
2024-08-22
Viruses like SARS-CoV-2 don’t respect boundaries, moving between species and continents and leaving destruction as they go. Beating the next pathogen with pandemic potential means getting good at crossing borders ourselves — between fields of study, between research universities, and between scientists and the wider community.
An $18 million grant announced by the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will put that goal within reach. The award brings together five universities and more than 20 researchers, academics, and public health experts to establish the Virginia Tech-led Center ...
Macrophage mix helps determine rate and fate of fatty liver disease
2024-08-22
Formerly known as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) is an inflammatory disease characterized by liver scarring or fibrosis that progressively impairs liver function.
It is a major risk factor for cirrhosis and liver cancer. And because treatment options are limited, MASH is the second leading cause for liver transplants in the United States after cirrhosis caused by chronic hepatitis C infection.
A better understanding of the pathological processes that drive MASH is critical to creating effective treatments. In a new paper published ...
Department of Energy announces $36 million to support energy-relevant research in underrepresented regions of America
2024-08-22
WASHINGTON, D.C. - Ensuring that scientific funding goes to states and territories that have typically received smaller fractions of federal research dollars in the past, the Department of Energy (DOE) today announced $36 million in funding for 39 research projects in 19 states via the Established Program to Stimulate Competitive Research (EPSCoR). The grants connect innovative ideas from scientists at eligible institutions with leading-edge capabilities at the DOE national laboratories.
Supporting scientists while building the expertise and capabilities critical for performing leading research ...
Analysis of 1,500 climate policies reveals only a small fraction achieved significant emission reductions
2024-08-22
A new machine learning analysis has revealed the most effective climate policies out of 1,500 implemented worldwide over the last two decades. Some of the success stories – numbered at about 63 – involve rarely studied policies and unappreciated policy combinations. “Our results provide a clear yet sobering perspective on the policy effort necessary for closing the remaining emissions gap of 23 billion tons carbon dioxide (CO2) by 2023,” write the authors. To achieve the Paris Agreement’s climate targets, it is essential to know which ...
Fatty-acid derived polymers yield recyclable and highly versatile adhesives
2024-08-22
Researchers have presented a new family of polymer adhesives that offer a sustainable and recyclable alternative to conventional polymer adhesives and can be used across a wide range of applications, from industrial adhesives to surgical superglues. The new chemical approach to aLA polymerization addresses the performance and environmental challenges of traditional polymers, providing environmentally friendly adhesive solutions. Polymer adhesives are ubiquitous in modern life and are widely used in many medical, consumer, and industrial products. Given this diversity, each adhesive material is often tailored ...
Governance needed to ensure biosecurity of biological AI models
2024-08-22
Concerns over the biosecurity risks posed by artificial intelligence (AI) models in biology continue to grow. Amid this concern, Doni Bloomfield and colleagues argue, in a Policy Forum, for improved governance and pre-release safety evaluations of new models in order to mitigate potential threats. “We propose that national governments, including the United States, pass legislation and set mandatory rules that will prevent advanced biological models from substantially contributing to large-scale dangers, such as the creation of novel or enhanced pathogens ...
[1] ... [982]
[983]
[984]
[985]
[986]
[987]
[988]
[989]
990
[991]
[992]
[993]
[994]
[995]
[996]
[997]
[998]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.