(Press-News.org) Among uncircumcised men in Kenya, compensation in the form of food vouchers worth approximately U.S. $9 or $15, compared with lesser or no compensation, resulted in a modest increase in the prevalence of circumcision after 2 months, according to a study published by JAMA. The study is being released to coincide with its presentation at the International AIDS Conference.
Following randomized trials that demonstrated that medical male circumcision reduces men's risk of HIV acquisition by 50 percent to 60 percent, UNAIDS and the World Health Organization recommended the scale-up of voluntary medical male circumcision (VMMC) in 14 countries in eastern and southern Africa. Despite considerable scale-up efforts, most countries are far short of target goals. Novel strategies are needed to increase VMMC uptake. Potential barriers include concerns about lost wages during and after the procedure, according to background information in the article.
Harsha Thirumurthy, Ph.D., of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and colleagues studied 1,504 uncircumcised men (25 to 49 years of age) in Nyanza region, Kenya, who were randomly assigned to 1 of 3 intervention groups or a control group. Participants in the intervention groups received varying amounts of compensation conditional on VMMC uptake at 1 of 9 study clinics within 2 months of enrollment. Compensation took the form of food vouchers worth approximately U.S. $2.50, $8.75, or $15, which reflected a portion of transportation costs and lost wages associated with getting circumcised. The control group received no compensation.
The researchers found VMMC uptake within 2 months was higher in the $8.75 group (6.6 percent [25 of 381]) and the $15 group (9.0 percent [34 of 377]) than in the $2.50 group (1.9 percent [7 of 374]) and the control group (1.6 percent [6 of 370]). Further analysis indicated that compared with participants in the control group, those in the $15 and $8.75 groups were significantly more likely to get circumcised; those enrolled in the $2.50 group were not. The difference in VMMC uptake between the $8.75 and $15 groups was not significant.
"There was also a significant increase in VMMC uptake among married and older participants, groups that have been harder to reach previously. The interventions also significantly increased the likelihood of circumcision uptake among participants at higher risk of acquiring HIV. This latter result is especially promising from an HIV prevention standpoint," the authors write.
"The overall increase in VMMC uptake within 2 months, as a result of providing compensation, was modest, with an increase of at most 7.4 percent in the U.S. $15.00 group. This increased uptake was in a population with an estimated circumcision prevalence of 35.6 percent. Evaluation of scaled-up implementation of the intervention is needed to determine whether it will help achieve higher circumcision coverage over longer periods of time."
INFORMATION:
(doi:10.1001/jama.2014.9087; Available pre-embargo to the media at http://media.jamanetwork.com)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, financial disclosures, funding and support, etc.
Study examines incentives to increase medical male circumcision to help reduce risk of HIV
2014-07-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fecal transplants let packrats eat poison
2014-07-21
Salt Lake City – Woodrats lost their ability to eat toxic creosote bushes after antibiotics killed their gut microbes. Woodrats that never ate the plants were able to do so after receiving fecal transplants with microbes from creosote-eaters, University of Utah biologists found.
The new study confirms what biologists long have suspected: bacteria in the gut – and not just liver enzymes – are "crucial in allowing herbivores to feed on toxic plants," says biologist Kevin Kohl, a postdoctoral researcher and first author of the paper published online today in the journal ...
Why are more people in the UK complaining about their doctors?
2014-07-21
The report – "Understanding the Rise in Fitness to Practise Complaints from Members of the General Public" – is published today.
An increase in complaints has been seen across the UK, which suggests wider social trends rather than localised issues. A large number of complaints did not progress because the issues raised could not be identified, which suggests that the GMC is receiving complaints outside its remit. According to the report, this points towards problems with the wider complaint-handling system and culture.
While the report does not point to any specific ...
UEA research shows oceans vital for possibility for alien life
2014-07-21
Researchers at the University of East Anglia have made an important step in the race to discover whether other planets could develop and sustain life.
New research published today in the journal Astrobiology shows the vital role of oceans in moderating climate on Earth-like planets.
Until now, computer simulations of habitable climates on Earth-like planets have focused on their atmospheres. But the presence of oceans is vital for optimal climate stability and habitability.
The research team from UEA's schools of Maths and Environmental Sciences created a computer ...
New findings show strikingly early seeding of HIV viral reservoir
2014-07-20
BOSTON – The most critical barrier for curing HIV-1 infection is the presence of the viral reservoir, the cells in which the HIV virus can lie dormant for many years and avoid elimination by antiretroviral drugs. Very little has been known about when and where the viral reservoir is established during acute HIV-1 infection, or the extent to which it is susceptible to early antiretroviral therapy (ART).
Now a research team led by investigators at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) in collaboration with the U.S. Military HIV Research Program has demonstrated that ...
Metabolic enzyme stops progression of most common type of kidney cancer
2014-07-20
PHILADELPHIA -- In an analysis of small molecules called metabolites used by the body to make fuel in normal and cancerous cells in human kidney tissue, a research team from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania identified an enzyme key to applying the brakes on tumor growth. The team found that an enzyme called FBP1 – essential for regulating metabolism – binds to a transcription factor in the nucleus of certain kidney cells and restrains energy production in the cell body. What's more, they determined that this enzyme is missing from all kidney ...
Scientists map one of most important proteins in life -- and cancer
2014-07-20
Scientists reveal the structure of one of the most important and complicated proteins in cell division – a fundamental process in life and the development of cancer – in research published in Nature today (Sunday).
Images of the gigantic protein in unprecedented detail will transform scientists' understanding of exactly how cells copy their chromosomes and divide, and could reveal binding sites for future cancer drugs.
A team from The Institute of Cancer Research, London, and the Medical Research Council Laboratory of Molecular Biology in Cambridge produced the first ...
Marmoset sequence sheds new light on primate biology and evolution
2014-07-20
HOUSTON – (July 20, 2014) – A team of scientists from around the world led by Baylor College of Medicine and Washington University in St. Louis has completed the genome sequence of the common marmoset – the first sequence of a New World Monkey – providing new information about the marmoset's unique rapid reproductive system, physiology and growth, shedding new light on primate biology and evolution.
The team published the work today in the journal Nature Genetics.
"We study primate genomes to get a better understanding of the biology of the species that are most closely ...
Speedy computation enables scientists to reconstruct an animal's development cell by cell
2014-07-20
Recent advances in imaging technology are transforming how scientists see the cellular universe, showing the form and movement of once grainy and blurred structures in stunning detail. But extracting the torrent of information contained in those images often surpasses the limits of existing computational and data analysis techniques, leaving scientists less than satisfied.
Now, researchers at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute's Janelia Research Campus have developed a way around that problem. They have created a new computational method to rapidly track the three-dimensional ...
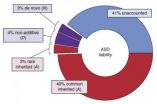
Common gene variants account for most genetic risk for autism
2014-07-20
Most of the genetic risk for autism comes from versions of genes that are common in the population rather than from rare variants or spontaneous glitches, researchers funded by the National Institutes of Health have found. Heritability also outweighed other risk factors in this largest study of its kind to date.
About 52 percent of the risk for autism was traced to common and rare inherited variation, with spontaneous mutations contributing a modest 2.6 percent of the total risk.
"Genetic variation likely accounts for roughly 60 percent of the liability for autism, ...
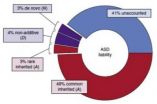
Genetic risk for autism stems mostly from common genes
2014-07-20
PITTSBURGH—Using new statistical tools, Carnegie Mellon University's Kathryn Roeder has led an international team of researchers to discover that most of the genetic risk for autism comes from versions of genes that are common in the population rather than from rare variants or spontaneous glitches.
Published in the July 20 issue of the journal "Nature Genetics," the study found that about 52 percent of autism was traced to common genes and rarely inherited variations, with spontaneous mutations contributing a modest 2.6 percent of the total risk. The research team — ...