Forensic scientists unlocking unique chemical signatures in tires
New approach could provide law enforcement additional tools to track down those who flee a crime scene
2021-04-26
(Press-News.org) Skid marks left by cars are often analyzed for their impression patterns, but they often don't provide enough information to identify a specific vehicle. UCF Chemistry Associate Professor Matthieu Baudelet and his forensics team at the National Center for Forensic Science, which was established at UCF in 1997, may have just unlocked a new way to collect evidence from those skid marks.
The team recently published a study in the journal Applied Spectroscopy that details how they are classifying the chemical profile of tires to link vehicles back to potential crime scenes.
"Tire evidence is often overlooked in forensics," says Baudelet. "In cases of hit and runs or accidents involving multiple cars the chemical signature of the tires have the potential to be integral information to the investigation."
The team used laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) on each sample. The technique focuses a laser onto the tire sample, which creates a microscopic plasma that emits light according to the chemical elements present. The spectroscopy comes in because it analyzes this light and matches it to the corresponding chemicals. It's the same technique that instruments aboard the Mars rovers (Curiosity and Perseverance) use to determine what kinds of elements are found within the rocks of Mars.
"The process is as complicated as it is fun," says Baudelet. "The whole idea is that tire evidence holds a lot of data. They have patterns, but these pattern impressions do not give all the answers. It became a question of 'Can we use their chemical composition to obtain information from the tires?'"
Baudelet and his graduate student, John Lucchi, started testing their idea by recreating skid marks in the laboratory using road materials like concrete and asphalt. By pressing a tire into the surface at the same velocity as a moving vehicle, a braking impression is made on the laboratory controlled "road" from the tire. This in turn gives the team a chance to analyze the chemical composition of the tire and the road material and make chemical comparisons.
Every tire is expected to have its own chemical signature and, as such, a unique, corresponding skid mark. One current challenge is identifying how elements on the road like oil, rainwater, and other cars interfere and change that signature. Baudelet says the National Center for Forensic Science has been working on overcoming these interference challenges with other evidence for years.
Now that the process shows promise, the team will focus on establishing statistical reliability. Standards for police evidence are justifiably high, so next steps involve reproducible, dependable protocols, Baudelet says. Ultimately, he would like to know his team's work provided justice and closure to cases of hit-and-run and vehicle violence.
"We're still working but so far we've made a lot of progress," Baudelet says. "I feel that this can be a great supplementation to the methods currently being used in forensics and law enforcement."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-26
A genome by itself is like a recipe without a chef - full of important information, but in need of interpretation. So, even though we have sequenced genomes of our nearest extinct relatives - the Neanderthals and the Denisovans - there remain many unknowns regarding how differences in our genomes actually lead to differences in physical traits.
"When we're looking at archaic genomes, we don't have all the layers and marks that we usually have in samples from present-day individuals that help us interpret regulation in the genome, like RNA or cell structure," said David Gokhman, a postdoctoral fellow in biology at Stanford University.
"We ...
2021-04-26
Gossip is often considered socially taboo and dismissed for its negative tone, but a Dartmouth study illustrates some of its merits. Gossip facilitates social connection and enables learning about the world indirectly through other people's experiences.
Gossip is not necessarily spreading rumors or saying bad things about other people but can include small talk in-person or online, such as having a private chat during a Zoom meeting. Prior research has found that approximately 14% of people's daily conversations are gossip, and primarily neutral in tone.
"Gossip is ...
2021-04-26
Powered flight in animals -that uses flapping wings to generate thrust- is a very energetically demanding mode of locomotion that requires many anatomical and physiological adaptations. In fact, the capability to develop it has only appeared four times in the evolutionary history of animals: on insects, pterosaurs, birds and bats.
A research paper published in 2020 in the scientific journal Current Biology concluded that, apart from birds -the only living descendants of dinosaurs-, powered flight would have originated independently in other three groups of dinosaurs. A conclusion that makes a great impact, as it increases the number of vertebrates that would have developed this costly mode of locomotion, ...
2021-04-26
A major hurdle to developing new and effective treatments for drug addiction is better understanding how exactly it manifests itself before, during and after chronic use. In a paper published online in the April 21, 2021 issue of the journal eNeuro, an international team of researchers led by scientists at University of California San Diego School of Medicine describe the creation of two unique collections of more than 20,000 biological samples collected from laboratory rats before, during and after chronic use of cocaine and oxycodone.
Developed by the Preclinical Addiction Research Consortium, located in the Department of Psychiatry at UC San Diego School of Medicine and at Skaggs School of Pharmacy ...
2021-04-26
Corn is America's top agricultural crop, and also one of its most wasteful. About half the harvest--stalks, leaves, husks, and cobs-- remains as waste after the kernels have been stripped from the cobs. These leftovers, known as corn stover, have few commercial or industrial uses aside from burning. A new paper by engineers at UC Riverside describes an energy-efficient way to put corn stover back into the economy by transforming it into activated carbon for use in water treatment.
Activated carbon, also called activated charcoal, is charred biological material that has been treated to create millions of microscopic pores that increase how much the material can absorb. It has many industrial ...
2021-04-26
How often have you laid in bed scrolling through news stories, social media or responding to a text? After staring at the screen, have you ever found that it is harder to fall asleep?
It's widely believed that the emitted blue light from phones disrupts melatonin secretion and sleep cycles. To reduce this blue light emission and the strain on eyes, Apple introduced an iOS feature called Night Shift in 2016; a feature that adjusts the screen's colors to warmer hues after sunset. Android phones soon followed with a similar option, and now most smartphones have some sort of night mode function that claims ...
2021-04-26
The process designed to harvest on Earth the fusion energy that powers the sun and stars can sometimes be tricked. Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics laboratory have derived and demonstrated a bit of slight-of-hand called "quasi-symmetry" that could accelerate the development of fusion energy as a safe, clean and virtually limitless source of power for generating electricity.
Fusion reactions combine light elements in the form of plasma -- the hot, charged state of matter composed of free electrons and atomic nuclei that makes up 99 percent of the visible universe ...
2021-04-26
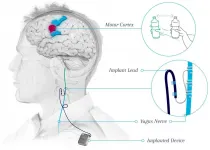
LOS ANGELES -- Every year, more than 795,000 people in the United States have a stroke. Of these, approximately 80% lose arm function and as many as 50-60% of this population still experience problems six months later.
Traditionally, stroke patients try to regain motor function through physical rehabilitation, where patients re-learn pre-stroke skills, such as eating motions and grasping. However, most patients eventually plateau and stop improving over time.
Now, results of a clinical trial published in The Lancet gives patients new hope in their recovery.
Patients who received a novel treatment that combines vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) and rehabilitation showed ...
2021-04-26
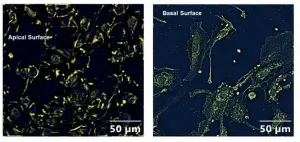
A new study performed in human lung airway cells is one of the first to show a potential link between exposure to organophosphate pesticides and increased susceptibility to COVID-19 infection. The findings could have implications for veterans, many of whom were exposed to organophosphate pesticides during wartime.
Exposure to organophosphate pesticides is thought to be one of the possible causes of Gulf War Illness, a cluster of medically unexplained chronic symptoms that can include fatigue, headaches, joint pain, indigestion, insomnia, dizziness, respiratory disorders and memory problems. More than 25% of Gulf War veterans are estimated to experience this condition.
"We have identified a basic mechanism linked with inflammation that could increase susceptibility to COVID-19 infection ...
2021-04-26
During infection, SARS-CoV-2 binds to a cellular receptor known as angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) before entering a cell and replicating. Because it is not well established whether common blood pressure medications can increase the levels of ACE2, there has been some concern that patients taking these medications might be more susceptible to COVID-19.
In a new study, researchers led by Hans Ackerman, MD, DPhil, in the Laboratory of Malaria and Vector Research (LMVR) at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, found that mice treated with an ACE inhibitor blood pressure medication showed increased levels of ACE2. However, mice that received both an ACE inhibitor and a different blood pressure medicine known as an angiotensin ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Forensic scientists unlocking unique chemical signatures in tires
New approach could provide law enforcement additional tools to track down those who flee a crime scene