(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON (June 14, 2023) – More than 500 adolescent mothers, caregivers and community members benefitted from a coordinated “collective impact” model to provide support aimed at addressing the litany of strains faced by teen parents, according to a case study published Wednesday in the journal Pediatrics.
Known as the District of Columbia Network for Parenting and Expectant Teens (DC NEXT), the model used well-tested pillars of community organization to provide services and care that bolstered the well-being of pregnant and expectant teens in the city. The case study found that the 3-year-old program, which included teen advisors to help guide the mission, could serve as a model in other areas with high rates of teen parents.
“There's no system of care for teen parents in Washington, D.C., or really anywhere in our country,” said Yael Smiley, M.D., Children’s National Hospital pediatrician and the study’s lead author. “Our coalition came together to connect the resources and the people who care about young parents and their families to improve their health, their outcomes, their well-being, and set them up for success. We fuse representatives from healthcare, education and housing policy — people who care about creating the very best outcomes possible.”
More than 140,000 teens became parents in 2021 in the United States. In Washington, D.C., more than 300 babies are born to teens each year, and the rate of births to young teens ages 15 to 17 is double the national average. These young parents often face barriers to childcare and education and poor birth outcomes, often stemming from a lack of access to prenatal care.
To address these obstacles, the network assembled a city-wide network in 2020 to follow the five pillars of an evidence-based “collective impact” model:
Create a common agenda
Design shared measurement systems
Host mutually reinforcing activities
Foster continuous communication
Rely on trusted backbone support
DC NEXT was housed at the District of Columbia Primary Care Association (DCPCA), which received the 3-year, $4.5 million federal grant and provided the leadership. At Children’s National, Dr. Smiley led a team that partnered with DCPCA and Howard University to direct a network of community clinics, nonprofits and other organizations whose mission was to support adolescent parents. Hundreds of client-facing staff members were trained to provide trauma-informed, human-centered care. DC NEXT also engaged directly with teen mothers through well-being surveys that led to improved access to essential programs, including resources for housing and food security. Over 550 young parents and caregivers have been impacted by the program.
The leadership quickly realized that the teen parents needed a voice and created a “context team” of paid teen advisors who provided insights into their unique experiences and needs as parents. They help set the agenda, choose program offerings and tailor communications to their peers.
“If the network can continue to grow and support young parents to achieve their health and well-being goals, the impact will be felt across generations,” said Dr. Smiley.
Media contact: Katie Shrader | media@childrensnational.org | 202-476-4500
###
About Children’s National Hospital
Children’s National Hospital, based in Washington, D.C., was established in 1870 to help every child grow up stronger. Today, it is the No. 5 children’s hospital in the nation. It is ranked No. 1 for newborn care for the sixth straight year and ranked in all specialties evaluated by U.S. News & World Report. Children’s National is transforming pediatric medicine for all children. The Children’s National Research & Innovation Campus opened in 2021, a first-of-its-kind pediatric hub dedicated to developing new and better ways to care for kids. Children’s National has been designated three times in a row as a Magnet® hospital, demonstrating the highest standards of nursing and patient care delivery. This pediatric academic health system offers expert care through a convenient, community-based primary care network and specialty care locations in the D.C. metropolitan area, including Maryland and Virginia. Children’s National is home to the Children’s National Research Institute and Sheikh Zayed Institute for Pediatric Surgical Innovation. It is recognized for its expertise and innovation in pediatric care and as a strong voice for children through advocacy at the local, regional and national levels. As a non-profit, Children's National Hospital relies on generous donors to help ensure that every child receives the care they need.
For more information, follow us on Facebook, Instagram, Twitter and LinkedIn.
END
Community-wide program to support teen parents serves as a model for engagement
2023-06-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New imaging technique captures COVID-19’s impact on the brain
2023-06-14
A University of Waterloo engineer’s MRI invention reveals better than many existing imaging technologies how COVID-19 can change the human brain.
The new imaging technique known as correlated diffusion imaging (CDI) was developed by systems design engineering professor Alexander Wong and recently used in a groundbreaking study by scientists at Baycrest’s Rotman Research Institute and Sunnybrook Hospital in Toronto.
“Some may think COVID-19 affects just the lungs,” Dr. Wong said. “What was found is that this new MRI technique that we created ...
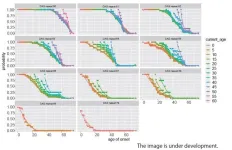
Prediction of age of onset of SCA3 and DRPLA by survival analysis using machine learning
2023-06-14
Niigata, Japan – Using machine learning, the Department of Neurology at Niigata University has developed a model to predict the asymptomatic probability at each age from the current age and number of CAG repeats in carriers of spinocerebellar degeneration. Polyglutamine diseases such as DRPLA and SCA3 are caused by an expansion of CAG repeats in the causative gene. In polyglutamine diseases, the number of CAG repeats is known to be inversely related to age of onset. Parametric survival analysis has traditionally been used to predict age of onset, but a more accurate prediction method has been desired. We ...
Remission rates of 1 in 100 people with type 2 diabetes in real world data
2023-06-14
Niigata, Japan - The phenomenon of improvement of glucose to levels in a normal range and cessation of the need for medication can occur in some patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes who are provided with lifestyle therapy, temporary pharmacotherapy, bariatric surgery, or combinations of these treatments. However, this phenomenon is not yet fully understood in routine care settings, and many factors remain to be clarified. Moreover, since there are differences in insulin secretion and resistance between East Asian and Western populations, the natural history of diabetes seems to differ widely between Western populations and East Asians.
Therefore, ...
Sharpening Occam’s Razor
2023-06-14
In science, the explanation with the fewest assumptions is most likely to be true. Called “Occam’s Razor,” this principle has guided theory and experiment for centuries. But how do you compare between abstract concepts?
In a new paper, philosophers from UC Santa Barbara and UC Irvine discuss how to weigh the complexity of scientific theories by comparing their underlying mathematics. They aim to characterize the amount of structure a theory has using symmetry — or the aspects of an object that remain the same when other changes are made.
After much ...
C-Path’s PSTC receives positive FDA response for drug-induced pancreatic injury biomarkers
2023-06-14
Safety biomarkers aim to provide an additional tool for detecting acute drug-induced pancreatic injury (DIPI) in phase 1 clinical trials
TUCSON, Ariz., June 13, 2023 — Critical Path Institute (C-Path) today announced that the Biomarker Qualification Program (BQP) at the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) in the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a Biomarker Letter of Support (LOS) for four pancreatic injury safety biomarkers identified and evaluated by C-Path’s Predictive Safety Testing Consortium's (PSTC) Pancreatic Injury Working Group (PIWG).
This set of biomarkers will help increase the ability ...
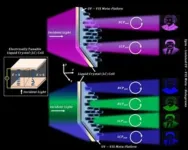
Breaking barriers: Advancements in meta-holographic display enable ultraviolet domain holograms
2023-06-14
The term meta means a concept of transcendence or surpassing, and when applied to materials, metamaterials encompass artificially engineered substances that exhibit properties not naturally found in the environment. Metasurfaces, characterized by their thinness and lightness, have garnered considerable interest as a potential component for incorporation into portable augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) devices to facilitate holographic generation. Nonetheless, it is important to note that metasurfaces have inherent limitations, such ...
Bhopal explosion may have heightened risk of disability and cancer among future generations
2023-06-14
The Bhopal gas explosion in 1984—one of India’s worst industrial disasters—may have heightened the risk of disability and cancer in later life among future generations, curbed their educational attainment, and prompted a fall in the proportion of male births the following year, suggests research in the open access journal BMJ Open.
The disaster is likely to have affected people across a substantially more extensive area than previous evidence suggested, say the researchers.
During the incident, toxic ...
NHS “flying blind” in attempt to tackle ethnic inequalities in care, warns expert
2023-06-14
The NHS will be “flying blind” in its attempts to meet its legal, and moral, obligation to eliminate ethnic inequalities in health and care until longstanding problems with the quality of ethnicity data are resolved, warns an expert in The BMJ today.
Inequalities in health and care between ethnic groups have been documented for decades, explains Sarah Scobie at the Nuffield Trust. But she argues that analysis by broad ethnic groups (white, Asian, black, and mixed) can mask substantial variation within them.
An accompanying infographic presents some of these disparities across a range ...
Timing of childhood adversity is associated with unique epigenetic patterns in adolescents
2023-06-14
BOSTON—Childhood adversity—circumstances that threaten to a child’s physical or psychological well-being--has long been associated with poorer physical and mental health throughout life, such as greater risks of developing cardiac disease, cancer, or depression. It remains unclear, however, when and how the effects of childhood adversity become biologically embedded to influence health outcomes in children, adolescents, and adults.
A team of researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of Mass General Brigham (MGB), previously showed that exposure to adversity between ages 3 to 5 has a ...
Lockdown children played on, study finds, despite being stuck at home
2023-06-14
Children displayed a resilient capacity to continue playing during peak COVID-19, a study has found, even though their options to do so became more limited while under stay-at-home orders.
The research, by academics at the University of Cambridge, interviewed children themselves about their playing habits during the pandemic. Without disputing the consensus that COVID-19 impeded children’s healthy development, it does suggest that they were able to adapt their play habits to their changed circumstances.
Children largely expressed ...