(Press-News.org) A comprehensive guideline from Osteoporosis Canada aims to help primary care professionals deliver care to optimize skeletal health and prevent fractures in postmenopausal females and males who are age 50 years and older. It is published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.221647.
With 25 recommendations and 10 good practice statements, this update to the 2010 guideline contains sections on exercise, nutrition, fracture risk assessment, treatment and more, reflecting advances in risk assessment, and nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic management of osteoporosis.
In Canada, there are more than 2 million people living with osteoporosis, defined as bone mineral density (BMD) at a level below peak bone mass, which increases risk of fracture. Fractures usually occur after a fall and can affect the hip, wrist, arm and spine, in particular.
"We are hopeful that this Canadian guideline will empower health care professionals and patients to have meaningful discussions on the importance of skeletal health and fracture prevention to preserve mobility and autonomy across adulthood," says Dr. Suzanne Morin, lead author and chair of the guideline steering committee.
The guideline is based on the latest evidence and included patient partners in developing the recommendations.
Key points:
Prior fracture is a strong risk predictor of subsequent fracture (particularly in the subsequent 12–24 months); however, other risk factors are also important to identify individuals who would benefit from pharmacotherapy.
The management of osteoporosis should be guided by the patient's risk of fracture based on clinical assessment, including risk for falls, and using a validated fracture risk assessment tool.
Exercise, nutrition, fall prevention and pharmacotherapy are key elements of the management strategy for fracture prevention, and should be individualized.
Clinicians and patients should collaborate in developing care plans that consider patients' priorities and preferences.
The guideline emphasizes key components to ensuring bone health and contains several recommendations for patients, including the following:
Exercise
Balance and functional training at least twice a week to reduce the risk of falls
Progressive resistance training at least twice a week, including exercises targeting abdominal and back extensor muscles
"Create a plan to do balance, functional, and strength training twice a week or more to prevent falls and fractures and improve functioning and quality of life," advises Dr. Lora Giangregorio, a coauthor and chair of the Exercise Working Group. "Progress the difficulty of the exercise program over time and monitor your progress."
Nutrition
For people who meet the recommended dietary allowance for calcium with a variety of calcium-rich foods, no supplementation to prevent fractures is needed.
Follow Health Canada's recommendation on vitamin D for bone health: 600 IU/d (age 51–70 yr) and 800 IU/d (age > 70 yr) for males and females.
Fracture risk assessment
A clinical assessment for osteoporosis and fracture that includes identifying risk factors and assessing for signs of undiagnosed vertebral fracture(s). This includes BMD testing in postmenopausal females and males who are
aged 50–64 years with a previous osteoporosis-related fracture or ≥ 2 clinical risk factors OR
aged ≥ 65 years with 1 clinical risk factor for fracture OR
aged ≥ 70 years
Pharmacotherapy is an important component of fracture prevention management and should be individualized.
Other guidelines
A guideline from the Canadian Task force on Preventive Health Care published in spring 2023 based on randomized controlled trials (RCTs) recommends risk assessment–first screening for the primary prevention of fragility fractures in females aged 65 years and older using the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool without BMD. The task force guideline recommends against screening younger females and males of any age. The Osteoporosis Canada guideline differs as it included a range of studies in addition to RCTs and several studies included men. The new guideline recommends screening in men and younger women, in contrast to the task force guideline.
"Identification and appropriate management of skeletal fragility in Canadians can reduce fractures, and preserve mobility, autonomy and quality of life in this population," says Dr Morin.
END
Comprehensive new Canadian guideline for skeletal health and fracture prevention
2023-10-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Five years of legal cannabis in Canada: mixed success
2023-10-10
Five years after cannabis legalization in Canada, it appears to be a mixed success, with social justice benefits outweighing health benefits, write authors in a commentary published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.230808.
Cannabis use was legalized in Canada in October 2018, with the goal to improve cannabis-related public health and safety, and reduce youth access and illegal activities related to cannabis. There was concern among some health ...
Mental health issues in Latinx middle schoolers may increase risk of sleep problems, obesity and unhealthy behaviors
2023-10-10
WASHINGTON (Oct. 10, 2023)--Latinx kids who experienced depression, anxiety or other mental health issues in middle school had a greater chance of developing sleep problems, unhealthy weight gain and sedentary behavior in high school, according to a study out today.
The research, led by a team at the George Washington University, suggests that unhealthy behaviors linked to mental health issues may start early in life and trigger obesity, high blood pressure, diabetes and other serious health problems.
“Our study suggests signs of depression ...
THE LANCET NEUROLOGY: Stroke could cause nearly 10 million deaths annually by 2050, mostly in LMICs, and cost up to US$2 trillion per year, new report warns
2023-10-10
Peer-reviewed / Modelling, Review, and Opinion / People
New World Stroke Organization-Lancet Neurology Commission forecasts future epidemiological and economic impacts of stroke, identifies evidence-based recommendations for improving the four pillars namely: surveillance, prevention, treatment and rehabilitation.
Epidemiological analysis projects stroke deaths will increase from 6.6 million in 2020 to 9.7 million in 2050, with an ever-widening gap between low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) and high-income countries (HICs). In 2050, 91% of stroke deaths are projected to be in LMICs compared to 9% in HICs, up from 86% in LMICs and 14% HICs ...
International team of scientists says identifying some foods as addictive could shift attitudes, stimulate research
2023-10-10
Researchers from the United States, Brazil, and Spain, including scientists with the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC, published an analysis in a special edition of the British Medical Journal with a timely and controversial recommendation: It’s time for an international shift in the way we think about ultra-processed food.
“There is converging and consistent support for the validity and clinical relevance of food addiction,” said Ashley Gearhardt, the article’s corresponding author and a psychology professor at the University of Michigan. “By acknowledging that certain types of processed foods have the properties of addictive substances, ...
History of parental infertility associated with small increased risk for birth defects among children conceived through fertility treatment
2023-10-09
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 9 October 2023
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. History of parental infertility associated ...
What is the impact of predictive AI in the health care setting?
2023-10-09
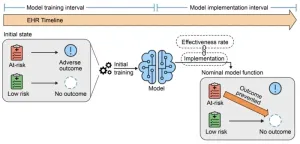
Models built on machine learning in health care can be victims of their own success, according to researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine and the University of Michigan. Their study assessed the impact of implementing predictive models on the subsequent performance of those and other models. Their findings—that using the models to adjust how care is delivered can alter the baseline assumptions that the models were “trained” on, often for worse—were detailed in the October 9 online issue of Annals of Internal Medicine: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-0949.
“We wanted to explore ...
Space weather disrupts nocturnal bird migration, study finds
2023-10-09
Graphics
It's well-known that birds and other animals rely on Earth's magnetic field for long-distance navigation during seasonal migrations.
But how do periodic disruptions of the planet's magnetic field, caused by solar flares and other energetic outbursts, affect the reliability of those biological navigation systems?
University of Michigan researchers and their colleagues used massive, long-term datasets from networks of U.S. Doppler weather radar stations and ground-based magnetometers—devices that measure the ...
Long-term lizard study challenges the rules of evolutionary biology
2023-10-09
Charles Darwin said that evolution was constantly happening, causing animals to adapt for survival. But many of his contemporaries disagreed. If evolution is always causing things to change, they asked, then how is it that two fossils from the same species, found in the same location, can look identical despite being 50 million years apart in age?
Everything changed in the past 40 years, when an explosion of evolutionary studies proved that evolution can and does occur rapidly — even from one generation to the next. Evolutionary biologists were thrilled, but the findings reinforced the same paradox: If evolution can happen so fast, then why do most species on Earth continue to ...
No lizard is an island
2023-10-09
Many species experience little to no change over long periods of time. Biologists often fall back on the same explanation for why this is true: that natural selection favors individuals with more moderate characteristics. Individuals with more extreme features — longer limbs, for example — have a disadvantage, while more moderate or average individuals are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their common features.
But new research from Washington University in St. Louis and the Georgia ...
Nature is inventive - the same substance is produced differently by plants
2023-10-09
Maize plants form special compounds derived from indole, the so-called benzoxazinoids. They are considered ecologically important because they act against a wide range of herbivores and reduce their feeding. Benzoxazinoids also exhibit antimicrobial properties and are thought to be involved in mediating plant-plant interactions. Their biosynthesis in maize has been known since the 1990s. Meanwhile, their biosynthetic pathway has been described in several grasses, but benzoxazinoids have also been found in other plant species. Their distribution is peculiar: While specialized metabolites often occur in specific evolutionary related plant species, benzoxazinoids ...