(Press-News.org) Researchers at Tulane University are leading a groundbreaking study to seek a more effective treatment for trichomoniasis, an infection that, despite being the most common curable sexually transmitted infection (STI) worldwide, continues to fly under the radar.
The five-year, multi-center study is funded by a $9.2 million National Institutes of Health grant and will compare the effectiveness of a recently approved medication, secnidazole, against the current standard treatment, metronidazole, using a 1,200-person cohort across Louisiana, Alabama and Florida. Despite decades of use as the primary trichomoniasis medication, treatment by metronidazole continues to have a 10% breakthrough rate.
“More than 10 percent of people who take the recommended treatment still have it. That is just unacceptable. We need better options” said Dr. Patty Kissinger, professor of epidemiology at Tulane School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine. “The problem is trichomoniasis is the most common treatable STI, but there are often no symptoms, and the CDC has not recommended screening among asymptomatic people, so the public doesn’t know about it.”
Trichomoniasis, which infects about 156 million people annually worldwide, is caused by trichomonas vaginalis, a parasite that thrives in the genital tract of both men and women and causes inflammation. Those infected have a 1.5 times higher susceptibility to HIV. For expecting mothers, it can cause pre-term birth and increase risk for perinatal morbidity. African American women are also four times more likely to have trichomoniasis.
“Trichomoniasis affects millions but remains a highly neglected STI,” Kissinger said. “We’re hoping this study leads to better treatment options and increased awareness that we hope will encourage more screening.”
Because of the lack of inclusion in STI screenings and scant symptoms, those infected can go years before realizing they have trichomoniasis.
This is the third in a series of studies funded by the NIH to refine treatment for trichomoniasis. This is the first study in the series to include men in its cohort and the first-ever study to compare the effectiveness of secnidazole with metronidazole.
Questions remain as to why metronidazole continues to have a high breakthrough rate. The prior NIH studies found that metronidazole is most effective when administered in multiple doses, but the breakthrough rate may be attributed to patients missing doses or having sex with partners before treatment is completed, creating a cycle of reinfection.
The secnidazole treatment would only require one dose, although some concerns remain about the cost of the medication, Kissinger said.
Trichomoniasis affects more than 3 million people in the United States and is particularly prevalent in the Deep South where the study is being conducted.
“We need better treatments for this STI,” Kissinger said. “If this is successful, we could control it and encourage more screening that could reduce perinatal morbidity and maybe even reduce the chances of some people getting HIV.”
END
It’s the most common STI you’ve never heard of. Will this newly developed drug provide the cure?
2024-08-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Texas A&M researchers find that aoudad, bighorn sheep share respiratory pathogens
2024-08-27
By Courtney Price, Texas A&M College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences
A team of researchers at the Texas A&M College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences (VMBS) has discovered that aoudad — an animal in the sheep and goat family — can catch and spread many of the same respiratory pathogens that can impact desert bighorn sheep, a native species in Texas that often shares its habitat with aoudad.
The new research, recently published in the journal PLOS ONE, will help wildlife conservationists better understand the complex relationship between ...
CRF announces TCT 2024 late-breaking clinical trials and science
2024-08-27
NEW YORK – August 27, 2024 – The Cardiovascular Research Foundation® (CRF®) is pleased to announce the late-breaking clinical trials and science to be featured at TCT® 2024. As the annual scientific symposium of CRF® and the world’s premier educational meeting specializing in interventional cardiovascular medicine, TCT® 2024 will be held October 27-30 in Washington, D.C. at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center.
For over three decades, TCT® has been at the forefront of innovation, education, and collaboration in interventional ...
Not sure how to stand out as a leader on Zoom calls? It starts with how you communicate, new study shows
2024-08-27
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- More companies are embracing remote work, and with that comes a need for more frequent communication. Teamwork through a screen isn’t always the same as having a group in the same room, so how are companies cultivating leaders in these virtual settings?
New research involving a collaboration between Binghamton University, State University of New York schools and research centers shows how, in virtual teams where nonverbal cues are limited, a person’s engagement and influence in conversations can significantly shape whether they’re perceived as a leader.
But taking charge of the conversation isn’t enough, the study found; for leadership ...
Prenatal smoking risks academic achievement of unborn babies
2024-08-27
Smoking harms almost every part of your body. But if you smoke when pregnant, the toxic chemicals in tobacco will also harm your unborn baby, with new research showing that it could lead to reduced academic outcomes at school.
In a systematic review of 19 studies and 1.25 million participants, researchers at the University of South Australia along with a team at Curtin University, SAHMRI, Harvard University and others* found that 79% of studies reported reduced academic achievement in children exposed to maternal prenatal smoking.
An additional meta-analysis of eight primary studies with 723,877 participants ...
The importance of brand strength when designing group and individual sales incentives in brand-managed retail sales settings
2024-08-27
Researchers from Wake Forest University and University of California-Riverside published a new Journal of Marketing article that examines the dynamic BMR retail context and investigates the sales incentives there.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Group or Individual Sales Incentives? What is Best for Brand-Managed Retail Sales Operations?” and is authored by Wenshu Zhang, Jia Li, and Subramanian Balachander.
Should a brand adopt group or individual sales incentives for its retail sales force? Could differences in brand strength or brand equity affect how brands incentivize their sales ...
Discovery gives answers to parents of children with rare disease
2024-08-27
Shortly after Kelly Cervantes’ daughter Adelaide was born, she started having terrible seizures. Doctors were unable to give her a solution, or even a cause.
“We never had an overarching diagnosis for her, which was extraordinarily frustrating and isolating,” she says. “If we did, we could join groups or talk to people who had various symptoms in common. We also had no idea what her prognosis looked like, or if we could have other children.”
Over time her condition worsened and sadly she died five days before her fourth birthday.
“She ...
UT Health San Antonio School of Dentistry names director of Center for Pain Therapeutics and Addiction Research
2024-08-27
SAN ANTONIO, Aug. 27, 2024 – Kenneth M. Hargreaves, DDS, PhD, professor of endodontics at the School of Dentistry of The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio), has been named inaugural director of the school’s Center for Pain Therapeutics and Addiction Research.
Hargreaves, who chaired the Department of Endodontics at the school for 26 years, is a world-renowned expert in pain research and has served as principal or co-principal investigator on numerous National Institutes of Health, Department of Defense and foundation-funded projects totaling more than $139 million.
Just recently, his research proposal, ...
Researchers develop affordable, rapid blood test for brain cancer
2024-08-27
Researchers at the University of Notre Dame have developed a novel, automated device capable of diagnosing glioblastoma, a fast-growing and incurable brain cancer, in less than an hour. The average glioblastoma patient survives 12-18 months after diagnosis.
The crux of the diagnostic is a biochip that uses electrokinetic technology to detect biomarkers, or active Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors (EGFRs), which are overexpressed in certain cancers such as glioblastoma and found in extracellular vesicles.
“Extracellular vesicles or exosomes are unique ...
NREL advances method for recyclable wind turbine blades
2024-08-27
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) see a realistic path forward to the manufacture of bio-derivable wind blades that can be chemically recycled and the components reused, ending the practice of old blades winding up in landfills at the end of their useful life.
The findings are published in the new issue of the journal Science. The new resin, which is made of materials produced using bio-derivable resources, performs on par with the current industry standard of blades made from a thermoset resin and outperforms certain thermoplastic resins intended to be recyclable.
The researchers built a prototype 9-meter blade to ...
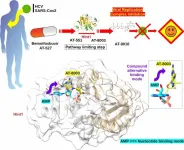
Atomic resolution of the broad-spectrum antiviral drug cascade to facilitate the design of antiviral drugs
2024-08-27
Atomic resolution of the broad-spectrum antiviral drug cascade to facilitate the design of antiviral drugs
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002743
Article Title: The activation cascade of the broad-spectrum antiviral bemnifosbuvir characterized at atomic resolution
Author Countries: France, United States, Germany
Funding: see manuscript END ...