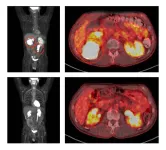
We may soon be able to detect cancer with AI
2024-06-20
A new paper in Biology Methods & Protocols, published by Oxford University Press, indicates that it may soon be possible for doctors to use artificial intelligence (AI) to detect and diagnose cancer in patients, allowing for earlier treatment. Cancer remains one of the most challenging human diseases, with over 19 million cases and 10 million deaths annually. The evolutionary nature of cancer makes it difficult to treat late-stage tumours.
Genetic information is encoded in DNA by patterns of the four bases—denoted by A, T, G and C—that make ...
Rate of cannabis use disorder during pregnancy increased over 20% after cannabis legalization in Canada
2024-06-20
In October 2018, Canada enacted the Cannabis Act in Canada (CAC), which legalised the non-medical use of cannabis. A new study has found that the rate of cannabis-related disorders diagnosed among pregnant women in the Canadian province of Québec increased by more than 20% after the enactment of the CAC, while rates for all other drug- and alcohol-related disorders remained stable. The study is published today in the scientific journal Addiction.
This study measured changes to the monthly rates of diagnosed cannabis-related disorders (CRDs) in the pregnant population in Québec. Since 2010 the monthly average number of CRDs has increased consistently, ...
Among cancer survivors, LGBTQ+ individuals report higher prevalence of chronic health conditions, disabilities, other limitations
2024-06-20
Bottom Line: Cancer survivors who identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer, or anything other than straight and cisgender (LGBTQ+) experience more chronic health conditions, disabilities, and other physical and cognitive limitations than non-LGBTQ+ cancer survivors; however, the prevalence of most conditions was highest among transgender or gender non-conforming (TGNC) individuals.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of ...
Improving crops with laser beams and 3D printing
2024-06-20
A demonstration of how new technologies can be used in 21st century crop breeding comes from just published research that combines Laser Scanning and 3D printing to create a detailed 3D model of a sugar beet plant. Taking the next step beyond having genetic information to guide intelligent breeding, the 3D plant models here capture the essential characteristics of the above-ground parts of the sugar beet plant and can be used for AI-assisted crop improvement pipelines. The sugar beet plant models are reproducible and fit for field use. All the research information, data, methodology, as well as the 3D printing files are freely ...
Government’s failure to fortify all flour and rice with sufficient folic acid will lead to avoidable birth defects, warns expert
2024-06-20
The UK government’s failure to fortify all flour and rice with the vitamin folic acid “will result in more deaths and birth defects every year that could have been prevented,” argues Professor Sir Nicholas Wald in The BMJ today.
He warns that the current government’s proposal to fortify only one type of flour (non-wholemeal wheat flour) at an inadequate level will prevent only about 20% of neural tube defects, much less than the approximate 80% that could be prevented with fully effective fortification.
“What the government has done is a useful ...
Walking brings huge benefits for low back pain, study finds
2024-06-20
Adults with a history of low back pain went nearly twice as long without a recurrence of their back pain if they walked regularly, a world-first study has found.
About 800 million people worldwide have low back pain, and it is a leading cause of disability and reduced quality of life.
Repeated episodes of low back pain are also very common, with seven in 10 people who recover from an episode going on to have a recurrence within a year.
Current best practice for back pain management and prevention suggests the combination of ...
Study finds one copy of protective genetic variant helps stave off early-onset Alzheimer’s disease
2024-06-19
KEY TAKEAWAYS
An international team, including researchers from Mass General Brigham, has been searching for protective genetic variants in a family that includes more than 1,000 individuals who are genetically predisposed to develop early onset Alzheimer’s disease in their 40s.
Previously, the researchers identified the “Christchurch variant” as potentially protective against Alzheimer’s based on one family member who had two copies of this variant and was expected to develop dementia in her ...
Combination targeted treatment produces lasting remissions in people with resistant aggressive B-cell lymphoma
2024-06-19
Embargoed for Release
Wednesday, June 19, 2024
5:00 p.m. ET Contact: NCI Press Office
240-760-6600
NCIPressOfficers@nih.gov
NOTE: A virtual briefing is scheduled for Tuesday, June 18, 2024, at 1:00 p.m. ET. Details below.
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have developed a non-chemotherapy treatment regimen that is achieving full remissions for some people with aggressive B-cell lymphoma that has come back or is no longer responding to standard treatments. The five-drug combination targets multiple molecular pathways that diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) tumors use to survive.
In ...
Common prostate drugs tied to lower risk of dementia with lewy bodies
2024-06-19
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, JUNE 19, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – Certain drugs used to treat urinary symptoms due to an enlarged prostate may be associated with a reduced risk of dementia with Lewy bodies, according to a study published in the June 19, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. Dementia with Lewy bodies is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that can cause memory and thinking issues, movement problems and issues such as hallucinations.
The results do not prove that these drugs reduce the risk of dementia ...
Drugs for enlarged prostate may also protect against dementia with Lewy bodies
2024-06-19
A new study suggests that certain drugs commonly used to treat enlarged prostate may also decrease the risk for dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB). This observational finding may seem surprising, but it mirrors previous work by the University of Iowa Health Care team that links the drugs to a protective effect in another neurodegenerative condition–Parkinson's disease.
The UI researchers think that a specific side effect of the drugs targets a biological flaw shared by DLB and Parkinson’s disease, as well as other neurodegenerative ...
Titan’s lakes may be shaped by waves
2024-06-19
Titan, Saturn’s largest moon, is the only other planetary body in the solar system that currently hosts active rivers, lakes, and seas. These otherworldly river systems are thought to be filled with liquid methane and ethane that flows into wide lakes and seas, some as large as the Great Lakes on Earth.
The existence of Titan’s large seas and smaller lakes was confirmed in 2007, with images taken by NASA’s Cassini spacecraft. Since then, scientists have pored over those and other images for clues to the moon’s mysterious ...
YALE EMBARGOED NEWS: Family psychiatric history: Effects on siblings of children with autism
2024-06-19
New Haven, Conn. — Children who have an older sibling with autism spectrum disorder (autism) are at greater risk of developmental vulnerabilities if they also have other relatives with neurodevelopmental or psychiatric conditions, according to a new study from the Yale Child Study Center.
Researchers found that the siblings of children with autism had an increase in the severity of social and communication difficulties — which are common in autism — if they had relatives with conditions such as schizophrenia or anxiety. Family histories of anxiety and intellectual disability were also associated ...
New technology provides electrifying insights into how catalysts work at the atomic level
2024-06-19
A team led by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) has invented a technique to study electrochemical processes at the atomic level with unprecedented resolution and used it to gain new insights into a popular catalyst material. Electrochemical reactions – chemical transformations that are caused by or accompanied by the flow of electric currents – are the basis of batteries, fuel cells, electrolysis, and solar-powered fuel generation, among other technologies. They also drive biological processes such as photosynthesis ...
Researchers create new class of materials called ‘glassy gels’
2024-06-19
Researchers have created a new class of materials called “glassy gels” that are very hard and difficult to break despite containing more than 50% liquid. Coupled with the fact that glassy gels are simple to produce, the material holds promise for a variety of applications.
Gels and glassy polymers are classes of materials that have historically been viewed as distinct from one another. Glassy polymers are hard, stiff and often brittle. They’re used to make things like water bottles or airplane windows. Gels – such as contact lenses – contain liquid and are soft and stretchy.
“We’ve created a class of materials ...
Tabulae Paralytica: Mapping the biology of spinal cord injury in unprecedented detail
2024-06-19
Scientists at EPFL have achieved a significant research milestone in the field of spinal cord injuries—mapping out the cellular and molecular dynamics of paralysis in unprecedented detail with their open-source project 'Tabulae Paralytica'. Grégoire Courtine and his team have integrated cutting-edge cell and molecular mapping technologies with artificial intelligence to chart the complex molecular processes that unfold in each cell after spinal cord injuries (SCI). Published in Nature, this seminal ...
When in drought: Researchers map which parts of the Amazon are most vulnerable to climate change
2024-06-19
In the late 2000s, Scott Saleska noticed something strange going on in the Amazon rainforest.
In 2005, a massive drought struck the region. Two years later, Saleska – a University of Arizona professor in the Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology – published surprising research that used satellite images to find that the drought resulted in more green growth in large swaths of the Amazon. On the other hand, field researchers saw plants brown and some die in response to the drought.
Research published today in the journal Nature reveals what caused the scientific mismatch. Shuli Chen, a doctoral degree candidate in ecology and evolutionary ...
Standardized OR handoffs significantly improve surgical communication and patient safety
2024-06-19
Key Takeaways
The introduction of a standardized handoff protocol substantially improved communication among OR staff, ensuring critical information was transferred consistently.
The enhanced communication reduced potential patient safety risks and highlighted the importance of standardized handoff tools in improving surgical outcomes.
CHICAGO (June 19, 2024) — A new study showcases a successful quality improvement program that significantly enhances surgical safety. By implementing a standardized handoff protocol, known as SHRIMPS, the study demonstrates how ...
Immune response study explains why some people don't get COVID-19
2024-06-19
Scientists have discovered novel immune responses that help explain how some individuals avoid getting COVID-19.
Using single-cell sequencing, researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, University College London (UCL), Imperial College London, the Netherlands Cancer Institute and their collaborators, studied immune responses against SARS-CoV-2 infection in healthy adult volunteers, as part of the world's first COVID-19 human challenge study1. Not all exposed participants went on to develop a COVID-19 infection, ...
New research illuminates the ecological importance of gray wolves in the American West
2024-06-19
Corvallis, OR — A study published today in the journal BioScience sheds light on the importance of gray wolves in western United States. Led by William Ripple, a scientist at Oregon State University and the Conservation Biology Institute, the research delves into the implications of large predator absence on plant and animal communities, and ecosystem functions. It calls attention to “shifting baselines” wherein increasingly degraded conditions are viewed as reflecting the historical state of a system.
"By the 1930s, wolves were largely absent from the American West, including its national parks. Most published ecological ...
Forgotten predators: Ecological understanding is often marred by the exclusion of extirpated species
2024-06-19
New research published in the journal BioScience describes how the removal large predators is often unrecognized in ecological scholarship, creating an issue of "shifting baselines," with profound implications for restoration efforts.
A team led by researchers from Oregon State University, including co-lead authors William J. Ripple and Christopher Wolf, reviewed 96 published studies from 1955 to 2021 that were conducted in 11 national parks where gray wolves had been extirpated. Their analysis found that ...
Inclusive care: Strategies to support infant feeding for parents with disabilities through WIC
2024-06-19
Philadelphia, June 19, 2024 – Infant feeding, involving breastfeeding, formula feeding, and the introduction of solid foods, is crucial for parenting. Pregnant and postpartum individuals with intellectual and developmental disabilities face challenges in infant feeding compared to parents without intellectual and developmental disabilities, often due to ableism and inaccessible care. The Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) program, a federal nutrition initiative, can address these disparities by offering inclusive and accessible support and counseling.
A recent research article in the Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior, published ...
Computer modelling shows where Arizona’s winter precipitation originates
2024-06-19
The Sun Corridor in Arizona in the semi-arid Southwestern U.S. is a land of seeming unlimited growth that is constantly colliding with physical constraints. It is mountainous but also home to a large valley that includes one of the fastest growing metropolitan areas in the U.S.
While experiencing explosive growth, the Phoenix metropolitan area faces an uncertain future due to prolonged drought and fluctuating seasonal water availability. Planning for the future, especially in terms of water, ...
STUDY: Sourcing genomically diverse seedlings to create climate-change resilient forests brings optimism for partnerships between science and practice
2024-06-19
The roots of the project formed during a CASRI conference in 2018 when experts from various organizations learned about red spruce genetic research being conducted by Keller’s lab and collaborators at University of Maryland with funding by the National Science Foundation. The group saw an opportunity to join forces to take an on-the-ground approach to utilizing the genetic data for red spruce restoration. In 2019, funding from the Wildlife Conservation Society’s Climate Adaptation Fund enabled this group to pursue science-informed restoration at scale.
“Science-informed ...
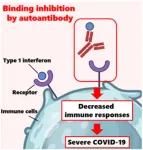
Could auto-antibodies be linked to severe COVID-19?
2024-06-19
Even though COVID-19 manifests as a mild and short-lived disease in most people, some suffer extremely severe symptoms; in the worst cases, these patients die due to complications such as respiratory failure or thromboembolism. It is well-known that factors such as age and underlying medical conditions like diabetes or immunodeficiencies increase vulnerability to severe COVID-19. However, some patients still experience severe COVID-19 without any apparent reason.
One possible explanation may lie in auto-antibodies, which are antibodies that erroneously target specific proteins produced by one’s own body. In normal circumstances, type I interferons ...
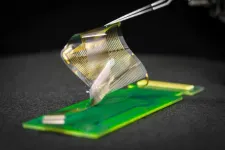
Breakthrough UC San Diego brain recording device receives FDA approval for a clinical trial
2024-06-19
Video: https://youtu.be/-7ggs6e2UXI?si=lnFqEscjJh-91n64
B-roll: https://youtu.be/pvNBa733ICw?si=DotUuQkxVgMQ0jY7
The Federal Drug Administration approved a clinical trial to test the effectiveness of an electronic grid that records brain activity during surgery, developed by engineers at the University of California San Diego.
The device with nanoscale sensors records electrical signals directly from the surface of the human brain in record-breaking detail. The grid’s breakthrough resolution could provide better guidance for planning and performing surgeries to remove brain tumors and treat drug-resistant epilepsy.
The grid’s higher resolution ...
[1] ... [1103]
[1104]
[1105]
[1106]
[1107]
[1108]
[1109]
[1110]
1111
[1112]
[1113]
[1114]
[1115]
[1116]
[1117]
[1118]
[1119]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.