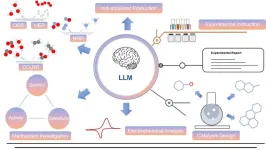
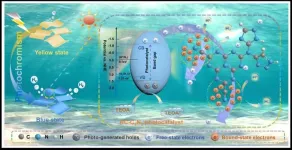
Large language model in electrocatalysis
2024-06-11
Large language models, outstanding representatives of modern technology, have significant impacts on various fields of modern society. These models, constructed by billions of neurons, incorporate the extensive knowledge accumulated by humans so far, possessing the exceptional abilities to chat with people around the world fluently. Their human-like intelligence enables them to tackle various challenges of modern society and shows great potential for applications in various fields.
Recently, a research team led by Prof. Ziyun Wang from the University of Auckland in New Zealand delved into the potential applications of large language models in the field ...
Bound-state electrons synergy over photochromic high-crystalline C₃N₅ nanosheets in enhancing charge separation for photocatalytic H₂ production
2024-06-11
Photocatalytic water splitting, a sustainable energy strategy, utilizes solar energy to produce clean hydrogen fuel. While it offers a promising solution to the global energy crisis and environmental pollution, the slow kinetics of photogenerated electron-hole pairs result in low activity for most semiconductor materials, even with sacrificial agents. To that end, integrating electron traps and reactive centers could be a feasible strategy to enhance charge separation and catalytic performance.
In ...
Engagement key to eliminating prejudice: Uncovering the process of feeling understood
2024-06-11
Osaka, Japan - A research group at Osaka University has uncovered how the view of other people and groups changes when individuals feel that they are understood by others by conducting an experimental study on the relationship between Japanese and Chinese people. The study shows that the role of felt understanding largely derives from a reduction in prejudice toward the other person.
Feeling understood by other people is a crucial determinant for positive interpersonal and intergroup relationships; however, the psychology behind this determinant was not well understood.
In ...
1 in 7 adults have experienced someone threaten to share their intimate images: new research
2024-06-11
A global study on the prevalence of sexual extortion among adults has found the issue to be more widespread than initially thought.
Sexual extortion, or sextortion, is a form of image-based sexual abuse which includes making threats to share intimate photos or videos of a victim unless they comply with the perpetrator’s behavioral or financial demands.
The research, led by RMIT University in partnership with Google, surveyed over 16,000 adults across Australia, North and Central America, Europe and Asia and found 14.5% of respondents reported being victims of sextortion, while 4.8% admitted to being perpetrators.
LGBTQ+ ...
Treating rare skin diseases by transplanting healthy skin
2024-06-11
Researchers from Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine in Japan have successfully treated the skin diseases epidermolytic ichthyosis (EI) and ichthyosis with confetti (IWC) by transplanting genetically healthy skin to inflamed areas. Transplanting healthy skin to inflamed areas has been used as a treatment option for severe burn injuries. They applied this technique from a common disease to rare diseases. Their research could pave the way for a new and effective treatment strategy for these challenging skin disorders. The study was published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
EI and IWC are rare genetic skin disorders caused by mutations in one of the two genes ...
Revealed: tricks used by opioid giant to mold doctors’ minds
2024-06-11
Opioid giant Mallinckrodt, selling more than Purdue Pharma in the US, was forced by the courts to publish more than 1.3 million internal documents.
In The BMJ today, researchers Sergio Sismondo and Maud Bernisson sift through nearly 900 contracts which together reveal a carefully coordinated effort to shape medical attitudes toward pain medicine.
Pharmaceutical companies have a long history of managing physician and public opinion, explain the authors. For example, by recruiting physicians to serve as influencers, planting articles in scientific journals, coordinating conference presentations, and developing continuing medical education (CME) courses.
Amid surging ...
Lab-grown ‘mini-guts’ could help in development of new and more personalized treatments for Crohn’s disease
2024-06-11
Cambridge scientists have grown ‘mini-guts’ in the lab to help understand Crohn’s disease, showing that ‘switches’ that modify DNA in gut cells play an important role in the disease and how it presents in patients.
The researchers say these mini-guts could in future be used to identify the best treatment for an individual patient, allowing for more precise and personalised treatments.
Crohn’s disease is a form of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). It is a life-long condition characterised by inflammation of the digestive tract that affects around one in 350 people in the UK, with one in four presenting before the age of 18. Even at its mildest, it ...
How the brain is affected by Huntington’s Disease
2024-06-11
The genetic disease Huntington’s not only affects nerve cells in the brain but also has widespread effects on microscopic blood vessels according to research.
These changes to the vasculature were also observed in the pre-symptomatic stages of the disease, demonstrating the potential for this research for predicting brain health and evaluating the beneficial effects of lifestyle changes or treatments.
Huntington’s disease is an inherited genetic condition leading to dementia, with a progressive decline in a person’s movement, memory, and cognition. There is currently no ...
MOLLER experiment baselined and moving forward
2024-06-11
NEWPORT NEWS – The U.S. Department of Energy’s Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility is moving forward on a project to gain new insight into the interactions of electrons. The MOLLER experiment will make an extremely precise measurement of the electron’s force field to learn about specific and rare interactions with other subatomic particles. On May 28, the experiment received approvals of both Critical Decision 2 and Critical Decision 3 from the DOE.
The MOLLER research program was established at Jefferson Lab as a DOE Major Item of Equipment (MIE) project to build the equipment required to support the experiment.
These ...
Engaging with patients for better treatments and outcomes for smell and taste disorders
2024-06-11
PHILADELPHIA (June 10, 2024) – Researchers and patient advocates from the Monell Chemical Senses Center, Smell and Taste Association of North America (STANA), and Thomas Jefferson University came together during the COVID-19 pandemic to incorporate patient voices in efforts to prioritize research areas focused on improving care for people with smell and taste disorders.
To this end, in 2022 these collaborators conducted a survey and listening sessions with patients, caregivers, and family members affected by impaired smell or taste. They asked about their individual perceptions of the effectiveness of treatments, among other topics. Using an online questionnaire, ...
Study shows first evidence of sex differences in how pain can be produced
2024-06-10
Research suggests that males and females differ in their experience of pain, but up until now, no one knew why. In a recent study published in BRAIN, University of Arizona Health Sciences researchers became the first to identify functional sex differences in nociceptors, the specialized nerve cells that produce pain.
The findings support the implementation of a precision medicine-based approach that considers patient sex as fundamental to the choice of treatment for managing pain.
“Conceptually, this paper is a big advance in our ...
Hubble finds surprises around a star that erupted 40 years ago
2024-06-10
Astronomers have used new data from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and the retired SOFIA (Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy) as well as archival data from other missions to revisit one of the strangest binary star systems in our galaxy – 40 years after it burst onto the scene as a bright and long-lived nova. A nova is a star that suddenly increases its brightness tremendously and then fades away to its former obscurity, usually in a few months or years.
Between April and September 1975, the binary system HM Sagittae (HM Sge) grew 250 times brighter. Even more unusual, it did not rapidly fade away as novae commonly do, but has ...
NASA’s Webb opens new window on supernova science
2024-06-10
Peering deeply into the cosmos, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope is giving scientists their first detailed glimpse of supernovae from a time when our universe was just a small fraction of its current age. A team using Webb data has identified 10 times more supernovae in the early universe than were previously known. A few of the newfound exploding stars are the most distant examples of their type, including those used to measure the universe's expansion rate.
"Webb is a supernova ...
May research news from the Ecological Society of America
2024-06-10
The Ecological Society of America (ESA) presents a roundup of four research articles recently published across its six esteemed journals. Widely recognized for fostering innovation and advancing ecological knowledge, ESA’s journals consistently feature illuminating and impactful studies. This compilation of papers explores how wolf reintroduction affects other carnivores, how drought and grazing snails together drive salt marsh productivity, the key to an invasive fish’s success and the plight of backyard trees, ...
Taking the fall: How stunt performers struggle with reporting head trauma
2024-06-10
In the heart-pounding action scenes of your favorite blockbuster, it's not always the A-list actor taking the risks but the unsung heroes—stunt performers—who bring those breathtaking moments to life. However, behind the glamour lies a grim reality: the reluctance of these daredevils to report head trauma, fearing it could jeopardize their careers.
In the recently released blockbuster, “The Fall Guy,” audiences get a behind-the-scenes look at what stunt professionals go through to create those most thrilling moments, and although this film celebrates these skilled professionals, it does not highlight the impact the stunts can have on their health.
Ohio ...
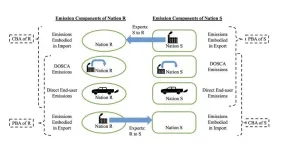
Income inequality and carbon dioxide emissions have a complex relationship
2024-06-10
Income inequality and carbon dioxide emissions for high-income nations such as the United States, Denmark and Canada are intrinsically linked – but a new study from Drexel University has taken a deeper look at the connection and found this relationship is less fixed, can change over time, and differ across emission components. The findings could help countries set a course toward reducing emissions of the harmful greenhouse gas and alleviating domestic income inequality at the same time.
The ...
Yuan elevated to IEEE senior member
2024-06-10
Jinghui Yuan, an R&D staff member in the Applied Research for Mobility Systems group at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, has been elevated to a senior member of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, or IEEE.
Senior member status is the highest grade of IEEE and requires extensive experience that reflects professional accomplishments. Only 10% of IEEE’s more than 450,000 members achieve this level.
As a transportation engineer in the Buildings and Transportation Science Division, Yuan’s research focuses on intelligent transportation systems, crash risk prediction, big data analytics, deep learning, traffic simulation and ...
Passive heat exposure increases stress on the heart, posing risk to adults with history of CAD
2024-06-10
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 10 June 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. ...
Feeling rough after your COVID shot? Congrats, it’s working!
2024-06-10
Feeling Rough After Your COVID Shot? Congrats, It’s Working!
Headache, chills, tiredness may be evidence of a supercharged defense, according to UCSF-led study.
Fewer than 1 in 4 people in the United States have received last year’s updated COVID-19 vaccine, despite a death toll of more than 23,000 Americans this year.
One of the most common reasons for bypassing the COVID vaccine is concern about side effects like tiredness, muscle and joint pain, chills, headache, fever, nausea and feeling generally unwell. But a new study, led by UC San Francisco, has found that the symptoms indicate a robust immune response that is likely to ...
Depression, antidepressants, epigenetic age acceleration, and mortality in postmenopausal women
2024-06-10
“The study examined the impact of depressive symptoms, antidepressant use, and epigenetic age acceleration on all-cause mortality in postmenopausal women.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 10, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 10, entitled, “Relationships of depression and antidepressant use with epigenetic age acceleration and all-cause mortality among postmenopausal women.”
In this new study, researchers May A. Beydoun, Hind A. Beydoun, Jason Ashe, Michael F. Georgescu, Steve Horvath, Ake Lu, Anthony S. Zannas, ...
Researchers engineer new approach for controlling thermal emission
2024-06-10
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — If a material absorbs light, it will heat up. That heat must go somewhere, and the ability to control where and how much heat is emitted can protect or even hide such devices as satellites. An international team of researchers, including those from Penn State, has developed a novel method for controlling this thermal emission, with what they called promising implications for thermal management and thermal camouflage technologies.
The team published their work on June 7 in the print edition of Science.
Led by researchers at The University of Manchester’s National Graphene Institute ...
UTA honors two faculty for distinguished scholarship
2024-06-10
The University of Texas at Arlington is honoring two faculty for their outstanding contributions to scholarship with the Distinguished Record of Research or Creativity Award.
Sam W. Haynes, professor of history, and Jaehoon Yu, professor of physics, are the 2024 recipients of the award, which recognizes faculty who have achieved a distinguished record of scholarship over an extended period.
“Jae and Sam have each been at UTA for more than 20 years, and they have each truly made an impact in the lives of the students we prepare for future careers,” said Kate C. Miller, vice president of research and innovation. "In addition, their contributions ...
New research describes the leisure motivations that underpin young U.S. adults' recreational cannabis use
2024-06-10
As of 2024, 24 states including Virginia and Maryland, and DC have legalized the adult recreational use of cannabis. As laws change, citizens' perceptions of the drug and reasons for using the drug have also shifted. In 2020, 34.5% of adults aged 18-25 reported using cannabis in the previous 12 months, according to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Health experts seek to better understand the broader implications of legalizations and individuals’ motivations and attitudes related to cannabis use.
New ...
UC San Diego develops first-in-kind protocol for creating ‘wired miniature brains’
2024-06-10
Researchers worldwide can now create highly realistic brain cortical organoids — essentially miniature artificial brains with functioning neural networks — thanks to a proprietary protocol released this month by researchers at the University of California San Diego.
The new technique, published in Nature Protocols, paves the way for scientists to perform more advanced research regarding autism, schizophrenia and other neurological disorders in which the brain’s structure is usually typical, but electrical activity is altered. That’s according to Alysson Muotri, Ph.D., corresponding author and ...
Lone Star State: Tracking a low-mass star as it speeds across the Milky Way
2024-06-10
It may seem like the Sun is stationary while the planets in its orbit are moving, but the Sun is actually orbiting around the Milky Way galaxy at an impressive rate of about 220 kilometers per second — almost half a million miles per hour. As fast as that may seem, when a faint red star was discovered crossing the sky at a noticeably quick pace, scientists took notice.
Thanks to the efforts of a citizen science project called Backyard Worlds: Planet 9 and a team of astronomers from around the country, a rare hypervelocity ...
[1] ... [1110]
[1111]
[1112]
[1113]
[1114]
[1115]
[1116]
[1117]
1118
[1119]
[1120]
[1121]
[1122]
[1123]
[1124]
[1125]
[1126]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.