Towards a new era in flexible piezoelectric sensors for both humans and robots
2024-06-12
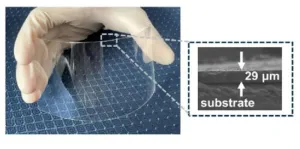
Flexible piezoelectric sensors are essential to monitor the motions of both humans and humanoid robots. However, existing designs are either are costly or have limited sensitivity. In a recent study, researchers from Japan tackled these issues by developing a novel piezoelectric composite material made from electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride nanofibers combined with dopamine. Sensors made from this material showed significant performance and stability improvements at a low cost, promising advancements ...
New study suggests kidney function is associated with tooth loss in postmenopausal women
2024-06-12
CLEVELAND, Ohio (June 12, 2024)—Kidneys play a critical role in overall health by removing waste products from the blood. When they fail to sufficiently filter out foreign elements, several serious, lifethreatening, medical conditions can result. A new study suggests that chronic kidney disease may also be linked with tooth loss. Results of the survey are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The Menopause Society.
A woman’s glomerular filtration rate shows how well her kidneys are functioning. ...
Breakthrough MEMS Huygens clock improves timekeeping precision and stability
2024-06-12
In a significant development for the miniaturization of electronic devices, a new study published in Engineering has reported the creation of a Microelectromechanical Systems (MEMS) clock that offers improved precision and stability. The clock, which utilizes the synchronization principle discovered by the Christiaan Huygens, consists of two synchronized MEMS oscillators and a frequency compensation system.
The research details how the MEMS Huygens clock enhances short-time stability, with the Allan deviation – a measure of the clock’s accuracy over time – improving by a factor of 3.73 from 19.3 ppb to 5.17 ppb at 1 second. The clock's long-term ...
HKUMed’s world-first ‘Liver-in-Cube’ wins a gold medal at International Exhibition of Inventions of Geneva, advancing precise cancer treatment
2024-06-12
Background
Liver cancer is the sixth most common cancer and third leading cause of cancer death globally. According to Hong Kong Cancer Registry data, there are approximately 1,800 new cases of liver cancer each year, with over 1,500 deaths, over 80% of which are advanced cases at first diagnosis. Patients with advanced liver cancer who are not suitable for surgical operations have limited treatment options. Traditional chemotherapy, targeted therapy and immunotherapy for treating advanced liver cancer often have a low response rate and severe side effects, thereby limiting their efficacy and hindering the patient’s quality ...
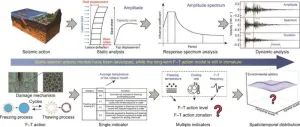
Nationwide zonation and durability assessment of China’s plateau infrastructure under freeze–thaw cycles
2024-06-12
In a bid to tackle the enduring problem of infrastructure durability in the face of relentless freeze–thaw (F–T) cycles, a team of researchers has published a new study in Engineering. The study focuses on the Chinese Plateau region, where the harsh effects of F–T cycles on concrete structures have led to concerns regarding their aging and subsequent performance deterioration.
The authors of the study emphasize that the existing national standards for designing frost-resistant concrete structures are insufficient, as they rely primarily on the coldest monthly average temperature without accounting for the intricate spatiotemporal variations, amplitude, and ...
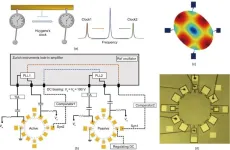
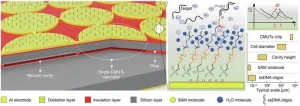
Innovative CMUT-based resonant biosensor offers enhanced DNA detection specificity
2024-06-12
In the latest study, researchers have successfully demonstrated a novel biosensor capable of detecting single-stranded DNA oligonucleotides with high specificity without needing external labels. This advancement paves the way for more accessible and efficient point-of-care diagnostics, as reported in a recent study published in Engineering.
The biosensor in question is based on capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers (CMUTs), which have shown promise for developing miniaturized, high-performance biosensing platforms. However, previous ...
Transparent organic–inorganic hybrid photoresist with highly tunable refractive index for advanced display
2024-06-12
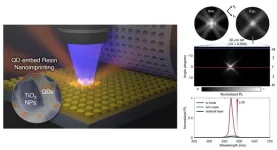
Researchers at Beijing University of Chemical Technology (BUCT) and BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd. (BOE) have developed a novel type of transparent organic–inorganic hybrid photoresist with highly tunable refractive index. The study published in Engineering presents the synthesis of transparent photoresist made of titanium dioxide nanoparticle-embedded acrylic resin with a tunable refractive index of up to 2.0 (589 nm) after being cured by ultraviolet (UV) light, while maintaining both a high transparency of over 98% in the visible ...
Quantum dots and metasurfaces: Deep connections in the nano world
2024-06-12
In relationships, sharing closer spaces naturally deepens the connection as bonds form and strengthen through increasing shared memories. This principle applies not only to human interactions but also to engineering. Recently, an intriguing study was published demonstrating the use of quantum dots to create metasurfaces, enabling two objects to exist in the same space.
Professor Junsuk Rho from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, the Department of Chemical Engineering, and the Department of Electrical Engineering, ...
Researchers at Houston Methodist find survival improves with open radical hysterectomy in early-stage cancer
2024-06-12
Early-stage cervical cancer patients see better survival and decreased recurrence rates after open radical hysterectomy than minimally invasive laparoscopic approaches, according to a 5-year study led by Houston Methodist researchers and published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“The findings from this and an initial study in 2018 led to the change in the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines established that same year that for radical hysterectomy we routinely perform an open approach. This latest study reaffirms this recommendation,” ...
Rise in global number of patient harms from 11 million to 18 million (59%) in 30 years
2024-06-12
The proportion of patient harms associated with medical procedures, treatment, and contact with healthcare systems rose by 59%, from 11 million to 18 million globally between 1990 and 2019, finds a data analysis published online in the journal BMJ Quality & Safety.
They outpaced the increase in the world’s population of 45% over the same period. And older people bore the brunt of these incidents, with the steepest rise among 65-69 year olds, the findings show.
In developed nations, over 50% of inpatient ...
Few UK people likely to be suitable for new Alzheimer’s drugs when they come on stream
2024-06-12
Few people in the UK with early stage Alzheimer’s disease are likely to be suitable for the latest drugs which aim to halt progress of the condition, yet many are nevertheless likely to be referred for these treatments, finds research published online in the Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery & Psychiatry.
The disease-modifying drugs, lecanemab and donanemab, slow cognitive decline in people with early stage Alzheimer’s disease. And they have been granted ‘breakthrough therapy’ ...
Retraction notice of previously press released research
2024-06-12
The research “Acupuncture for low back and/or pelvic pain during pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials,” published in the open access journal BMJ Open in 2022, has been retracted.
This research was press released in November 2022 under the title of “Acupuncture can relieve lower back/pelvic pain often experienced during pregnancy.”
Following publication of the research, various issues concerning its design and reporting methods came to light, none of which ...
Preparing for a world where Alzheimer’s disease is treatable
2024-06-12
Under strict embargo until Tuesday 11 June 2024 at 23.30 hours UK (BST) time
Preparing for a world where Alzheimer’s disease is treatable
Peer-reviewed | Observational study | People
Drugs with the potential to change the course of Alzheimer’s disease are expected to be approved by mid-year in the UK. Healthcare services may need to change to ensure that all patients have equitable access to these new modifying anti-amyloid therapies, according to research led by Queen Mary University of London and University College London (UCL).
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia. Of the 944,000 people living ...
Robot radiotherapy could improve treatments for eye disease
2024-06-12
Researchers from King’s, with doctors at King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, have successfully used a new robot system to improve treatment for debilitating eye disease.
The custom-built robot was used to treat wet neovascular age-related macular degeneration (AMD), administering a one-off, minimally invasive dose of radiation, followed by patients’ routine treatment with injections into their eye.
In the landmark trial, published today in The Lancet, it was found that patients then needed fewer injections to effectively control the disease, potentially saving around ...
Millions of insects migrate through 30-metre Pyrenees pass
2024-06-12
Over 17 million insects migrate each year through a single mountain pass on the border between France and Spain, new research shows.
University of Exeter scientists studied migrating insects in the Pass of Bujaruelo, a 30-metre gap between two high peaks in the Pyrenees.
The team visited the pass each autumn for four years, monitoring the vast number and variety of day-flying insects heading south.
The findings for this single pass suggest that billions of insects cross the Pyrenees each year, making it a key location for many migrating species.
The migrating insects ...
Should celebrities and influencers turn off their social media comments? A new study suggests they are less persuasive and likable when they do
2024-06-12
Researchers from University of Alabama and Vanderbilt University published a new Journal of Marketing study that examines the negative consequences that celebrities and influences incur when they disable social media comments.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “No Comments (From You): Understanding the Interpersonal and Professional Consequences of Disabling Social Media Comments” and is authored by Michelle Daniels and Freeman Wu.
Celebrities and influencers like Addison Rae, Hailey Bieber, ...
Painful truth about knee osteoarthritis: Why inactivity may be more complex than we think
2024-06-12
Knee osteoarthritis (OA) is a common cause of pain and joint stiffness. And while physical activity is known to ease symptoms, only one in 10 people regularly exercise.
Understanding what contributes to patients’ inactivity is the focus of a world first study from the University of South Australia. Here, researchers have found that people with knee OA unconsciously believe that activity may be dangerous to their condition, despite medical advice telling them otherwise.
The study found that of those surveyed, 69% of people with knee pain had stronger implicit (unconscious) beliefs that exercise ...
New study finds human-caused nitrous oxide emissions grew 40 percent from 1980-2020, greatly accelerating climate change
2024-06-12
Chestnut Hill, Mass. (6/11/24) – Emissions of nitrous oxide – a greenhouse gas more potent than carbon dioxide or methane – continued unabated between 1980 and 2020, a year when more than 10-million metric tons were released into the atmosphere primarily through farming practices, according to a new report by the Global Carbon Project.
Agricultural production accounted for 74 percent of human-driven nitrous oxide emissions in the 2010s – attributed primarily to the use of chemical fertilizers and ...
Study reveals significant increasing nitrous-oxide emissions from human activities, jeopardizing climate goals
2024-06-12
Emissions of nitrous-oxide (N2O) - a potent greenhouse gas - have continued to rise unabated over the past four decades, according to an international team of scientists.
The new report 'Global nitrous oxide budget (1980–2020)' is published in the journal Earth System Science Data. It is the most comprehensive accounting to date of nitrous-oxide emissions from human activities and natural sources.
It was led by researchers from Boston College in the US and involved an international team of scientists including researchers from the University of East Anglia (UEA), UK, under the umbrella of the Global Carbon Project. ...
Virtual reality as a reliable shooting performance-tracking tool
2024-06-11
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Virtual reality technology can do more than teach weaponry skills in law enforcement and military personnel, a new study suggests: It can accurately record shooting performance and reliably track individuals’ progress over time.
In the study of 30 people with a range of experience levels in handling a rifle, researchers at The Ohio State University found that a ballistic simulator captured data on the shooters’ accuracy, decision-making and reaction time – down to the millimeter in distance ...
New study explores the sun’s effects on the skin microbiome – it can create a damaged skin barrier
2024-06-11
The impact of solar radiation on skin has long been understood but what about UV’s effects on our skin's hidden world – its microbiome?
An article from American Society for Photobiology’s journal delved into existing knowledge on solar radiation’s impact on the skin microbiome and proposed innovative sun protection methods that safeguard both skin integrity and microbiome balance.
Experts offered insights into novel sun protection products designed to shield the skin and mitigate the effects of solar ...
States declare May 17 as NEC Awareness Day
2024-06-11
The NEC Society is leading the way toward a world without necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), a complex and often deadly intestinal disease affecting the most vulnerable infants. By bringing together families and elected officials, the NEC Society is raising the profile of this devastating neonatal disease. States nationwide have championed NEC Awareness Day Resolutions to recognize May 17.
The NEC Society’s families have partnered with elected officials to declare May 17 NEC Awareness Day in California, Colorado, Georgia, Louisiana, New York, Pennsylvania, and Utah, bringing much-needed attention to this leading cause ...
Precision medicine for sepsis in children within reach
2024-06-11
Sepsis – the leading cause of mortality in children around the world – can present with a wide range of signs and symptoms, making a one-size-fits-all treatment strategy ineffective. Pursuing a precision medicine approach for pediatric sepsis, researchers used artificial intelligence to analyze a large set of clinical data and find a distinct group of patients who might respond better to targeted treatments.
These children share clinical characteristics described as PHES, or persistent hypoxemia (abnormally low oxygen ...
New ACAAI position paper examines safety of receiving live vaccines while on dupilumab
2024-06-11
ARLINGTON HEIGHTS, Ill. (June 11, 2024) – A new position paper from the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (ACAAI) addresses the safety of administering live vaccines to patients who are currently being treated with dupilumab, a biologic therapy for various allergic conditions. The paper, The Use of Vaccines in Patients Receiving Dupilumab: A Systematic Review and Expert Delphi Consensus Recommendation: A Position Paper of the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, is published online in Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, ACAAI’s scientific journal. The panel conducting ...
St. Bernard Parish Hospital included among Becker’s 100 Great Community Hospitals
2024-06-11
CHALMETTE, La. – St. Bernard Parish Hospital (SBPH) has been named one of the 100 Great Community Hospitals in 2024 by Becker’s Hospital Review. This marks the second consecutive year St. Bernard Parish Hospital has earned the honor of being named a Great Community Hospital.
Many hospitals included on this year’s list have been recognized by rankings and rating organizations for their excellent clinical care, outstanding patient outcomes, and high performance in specialty services. Becker’s ...
[1] ... [1115]
[1116]
[1117]
[1118]
[1119]
[1120]
[1121]
[1122]
1123
[1124]
[1125]
[1126]
[1127]
[1128]
[1129]
[1130]
[1131]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.