Social determinants of health linked with youth-onset prediabetes
2024-06-11
Food insecurity, low household income and not having private health insurance are associated with higher rates of prediabetes in adolescents, independent of race and ethnicity, according to a new JAMA Network Open study by University of Pittsburgh and UPMC researchers.
The findings suggest that screening for social determinants of health — the non-medical factors that influence a person's health and risk of disease — may help identify youth at risk of prediabetes, which could ultimately improve early interventions that prevent progression to type 2 diabetes.
“This study underscores the importance ...
Harvard, Google DeepMind researchers create realistic virtual rodent
2024-06-11
The agility with which humans and animals move is an evolutionary marvel that no robot has yet been able to closely emulate. To help probe the mystery of how brains control movement, Harvard neuroscientists have created a virtual rat with an artificial brain that can move around just like a real rodent.
Bence Ölveczky, professor in the Department of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology, led a group of researchers who collaborated with scientists at Google’s DeepMind AI lab to build a biomechanically realistic digital model of a rat. Using high-resolution data recorded from ...
Scientists unlock secrets of how the third form of life makes energy
2024-06-11
Scientists unlock secrets of how the third form of life makes energy.
An international scientific team has redefined our understanding of archaea, a microbial ancestor to humans from two billion years ago, by showing how they use hydrogen gas.
The findings, published today in Cell, explain how these tiny lifeforms make energy by consuming and producing hydrogen. This simple but dependable strategy has allowed them to thrive in some of Earth’s most hostile environments for billions of years.
The paper, led by Monash University Biomedicine Discovery Institute scientists, including ...
Would astronauts’ kidneys survive a roundtrip to Mars?
2024-06-11
The structure and function of the kidneys is altered by space flight, with galactic radiation causing permanent damage that would jeopardise any mission to Mars, according to a new study led by researchers from UCL.
The study, published in Nature Communications, is the largest analysis of kidney health in space flight to date and includes the first health dataset for commercial astronauts. It is published as part of a Nature special collection of papers on space and health.
Researchers have known that space flight causes certain health issues since the 1970s, in the ...
Depressive symptoms may hasten memory decline in older people
2024-06-11
Depressive symptoms are linked to subsequent memory decline in older people, while poorer memory is also linked to an increase in depressive symptoms later on, according to a new study led by researchers at UCL and Brighton and Sussex Medical School.
The study, published in JAMA Network Open, looked at 16 years of longitudinal data from 8,268 adults in England with an average age of 64.
The researchers concluded that depression and memory were closely interrelated, with both seeming to affect each other.
Senior author Dr Dorina Cadar, of the UCL Department of Behavioural Science & Health and Brighton and Sussex Medical School, said: “It is ...
New technique could help build quantum computers of the future
2024-06-11
Quantum computers have the potential to solve complex problems in human health, drug discovery, and artificial intelligence millions of times faster than some of the world’s fastest supercomputers. A network of quantum computers could advance these discoveries even faster. But before that can happen, the computer industry will need a reliable way to string together billions of qubits – or quantum bits – with atomic precision.
Connecting qubits, however, has been challenging for the research community. Some methods form qubits by placing ...
Trash-sorting robot mimics complex human sense of touch
2024-06-11
WASHINGTON, June 11, 2024 – Today’s intelligent robots can accurately recognize many objects through vision and touch. Tactile information, obtained through sensors, along with machine learning algorithms, enables robots to identify objects previously handled.
However, sensing is often confused when presented with objects similar in size and shape, or objects unknown to the robot. Other factors restrictive to robot perception include background noise and the same type of object with different shapes and sizes.
In Applied Physics Reviews, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Tsinghua University worked to break through the difficulties ...
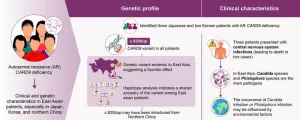
Shedding light on the origin of a genetic variant underlying fungal infections
2024-06-11
Researchers from Japan uncover the genetic diversity and regional patterns of CARD9 deficiency in patients susceptible to fungal diseases
Tokyo, Japan – Fungal infections pose life-threatening risks, especially when vital organs or the central nervous system are affected. Individuals harboring variants in the CARD9 gene are particularly susceptible to invasive fungal infections, given that the protein coded by this gene serves as a critical regulator of the immune system. A recent discovery ...
Humanitarian organizations showed flexibility and grit during COVID supply chain disruptions: study
2024-06-11
When the COVID-19 pandemic hit, it sent shock waves across global supply chains. But manufacturers and other businesses weren’t the only ones hit hard: local and international aid organizations, tasked with providing humanitarian assistance during times of crisis, suddenly had a major crisis of their own. How would they get the supplies they needed to carry out their crucial work?
According to a new study by the UBC Sauder School of Business, the organizations showed remarkable nimbleness and ingenuity — and while the pandemic was an unusual event, their approaches can provide powerful insights ...
Research on the visual rabbit illusion takes a leap forward
2024-06-11
Fukuoka, Japan—Researchers from Kyushu University have uncovered new variations to a traditional illusion, based on how we perceive the motion of flashing lights. Published on May 21 in i-Perception, the findings show that when three light flashes are presented in rapid succession in our side vision, our brain tends to perceive them in a straight line, with the second flash around the midpoint, no matter the actual location of the second flash. This research, which earned the journal’s Early Career Best Paper Prize this year, offers new perspectives on perceptual errors ...
Virus-like nanoparticles control the multicellular organization and reproduction of host bacteria
2024-06-11
Tsukuba, Japan—Viruses are ubiquitous in the environment, and organisms have developed various mechanisms to counter their threat. However, the genome of actinomycetes contains a highly conserved gene set encoding virus-like nanoparticles, although its biological significance has remained unclear.
In this study, researchers examined Streptomyces davawensis, an actinomycete species, and discovered that it produces virus-like particles that facilitate host reproduction. Extracellular DNA, which serves as a scaffold for multicellular organization, was significantly reduced in the colonies of mutant S. davawensis strains ...
Origins of fast radio bursts come into focus through polarized light
2024-06-11
TORONTO, ON, June 11, 2024 — What scientists previously thought about where Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs) come from is just the tip of the iceberg, according to new research led by astronomers at the University of Toronto. The mysteries of the millisecond-long cosmic explosions are unfolding with a new way of analyzing data from the Canadian Hydrogen Intensity Mapping Experiment (CHIME).
Published today in The Astrophysical Journal, the study details the properties of polarized light from 128 non-repeating FRBs — those from sources that have ...
Press registration opens for ACS Fall 2024
2024-06-11
WASHINGTON, June 11, 2024 — Journalists who register for the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS) will have access to about 10,000 presentations on topics including agriculture and food, energy and fuels, health and medicine, sustainability, and more. ACS Fall 2024 is a hybrid meeting being held virtually and in person in Denver on Aug. 18-22, with the theme “Elevating Chemistry.”
ACS considers requests for press credentials and complimentary meeting registration from reporters (staff and freelance) and public information officers at government, nonprofit and educational institutions. Please ...
New plasma escape mechanism could protect fusion vessels from excessive heat
2024-06-11
The furious exhaust heat generated by a fusing plasma in a commercial-scale reactor may not be as damaging to the vessel’s innards as once thought, according to researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL), Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the ITER Organization (ITER).
“This discovery fundamentally changes how we think about the way heat and particles travel between two critically important regions at the edge of a plasma during fusion,” said PPPL Managing Principal Research Physicist Choongseok Chang, who led ...
Endocrine Society urges passage of the Right to IVF Act
2024-06-11
WASHINGTON—The Endocrine Society endorses the Right to IVF Act, which was introduced by Senators Cory Booker (D-NJ), Patty Murray (D-WA) and Tammy Duckworth (D-IL) to protect and expand nationwide access to fertility treatment, including in vitro fertilization (IVF), and urges the Senate to pass the Right to IVF Act on June 12th to ensure that the freedom to start and grow a family is protected and accessible to everyone in the United States.
Infertility affects an increasing number of individuals. ...
FAU Harbor Branch launches ‘eConch’ to grow and conserve the queen conch
2024-06-11
The queen conch (Aliger gigas) is a prized delicacy long harvested for food and revered for its beautiful shell. With a lifespan between 25 to 40 years, the queen conch is second only to the spiny lobster fishery and is the most important molluscan fishery in the Caribbean region.
Deeply rooted in the way of life in the Caribbean, many island communities depend on queen conch for their livelihoods. However, intensive fishing and habitat degradation from urbanization and climate change have caused conch populations ...
Surprisingly high levels of toxic gas found in Louisiana
2024-06-11
The toxic gas ethylene oxide, at levels thousand times higher than what is considered safe, was detected across parts of Louisiana with a cutting-edge mobile air-testing lab. The concentrations found dwarfed Environmental Protection Agency estimates for the region.
The findings, led by Johns Hopkins University environmental engineers, suggest significantly higher cancer risks for people who live near facilities that manufacture and use ethylene oxide, as well as a need for more accurate and reliable tools to monitor emissions.
“I don’t think there’s any census track in the area that wasn’t at higher risk for cancer than we would deem acceptable,” said ...
Soil bacteria respire more CO2 after sugar-free meals
2024-06-11
When soil microbes eat plant matter, the digested food follows one of two pathways. Either the microbe uses the food to build its own body, or it respires its meal as carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere.
Now, a Northwestern University-led research team has, for the first time, tracked the pathways of a mixture of plant waste as it moves through bacteria’s metabolism to contribute to atmospheric CO2. The researchers discovered that microbes respire three times as much CO2 from lignin carbons (non-sugar aromatic units) compared to cellulose carbons (glucose sugar units), which both add structure and support ...
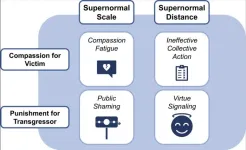
Human evolution and online morality
2024-06-11
In a Review article, Claire Robertson and colleagues explore how human morality, which evolved in the context of small in-person groups, functions on the internet with over five billion users. Evolved human responses, such as compassion for victims and urges to punish transgressors, operate differently online, the authors argue. The internet exposes users to large quantities of extreme morally relevant stimuli in the form of 24-hour news and intentionally outrageous content from sometimes physically distant locations. Subjecting human brains to this ...
Price sensitivity to unhealthy foods
2024-06-11
Consumer data shows people with obesity are more price-sensitive than others when it comes to buying unhealthy foods, suggesting a food tax could be an effective public health measure. Taxes on sugar-sweetened beverages have become a commonly employed policy to improve public health. Less common are taxes on unhealthy foods, such as candy, cookies, or potato chips--and there is little data on whether such taxes would improve public health. Ying Bao and colleagues examined whether individuals of various ...
Book bans as political action
2024-06-11
In the 2021–2022 school year, schools banned books more often than ever before in United States history. Katie Spoon, Isabelle Langrock, and colleagues analyzed data from PEN America on 2,532 book bans that occurred during the year, in combination with county-level administrative data, book sales data, and a novel crowd-sourced dataset of author demographic information. The research team found that people of color are several times more likely to be the authors of banned books than White authors and that a considerable proportion of banned books, both fictional and historical, feature characters of color. About 37% of banned books were children’s ...
New study shows metabolic and bariatric surgery prevents pre-diabetes from developing into type 2 diabetes in most patients
2024-06-11
Patients with pre-diabetes and severe obesity who had metabolic and bariatric surgery were 20-times less likely to develop full-blown type 2 diabetes over the course of 15 years than patients with the condition who did not have surgery, according to a new study* presented today at the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting.
Only 1.8% of patients progressed to a diagnosis of diabetes in five years after metabolic surgery (Roux-en-Y gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy), which rose to 3.3% in 10 years and 6.7% after 15 years. The protective effect against diabetes was higher ...
New studies suggest benefit of total robotic metabolic and bariatric surgery over conventional laparoscopy
2024-06-11
SAN DIEGO – June 11, 2024 – Two new studies* presented today at the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting suggest total robotic metabolic and bariatric surgery may result in shorter operative times, reduced lengths of stay and lower complications compared to laparoscopic approaches.
In one study, researchers from AdventHealth in Celebration, FL examined the outcomes of a single surgeon who performed 809 metabolic and bariatric operations – 498 totally robotic and 311 laparoscopic -- between 2020 and 2023. They found total robotic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) resulted in significantly shorter ...
Bariatric surgery more effective and durable than new obesity drugs and lifestyle intervention
2024-06-11
SAN DIEGO – June 11, 2024 – Systematic reviews* of medical literature between 2020 to 2024 show bariatric surgery, also known as metabolic or weight-loss surgery, produces the greatest and most sustained weight loss compared to GLP-1 receptor agonists and lifestyle interventions. The study was presented today at the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting.
Researchers found lifestyle interventions such as diet and exercise resulted in an average weight loss of 7.4% but that weight was generally regained within 4.1 years. GLP-1s and metabolic ...
For Republican men, environmental support hinges on partisan identity
2024-06-11
PULLMAN, Wash. – Who proposes a bill matters more to Republican men than what it says—at least when it comes to the environment, a recent study found.
In an experiment with 800 adults, researchers used an article describing a hypothetical U.S. Senate bill about funding state programs to reduce water pollution to test partisan preferences, changing only the political affiliation of the proposal’s sponsors. Democrats in the study who favored the proposal supported the legislation no matter who proposed it and at higher levels than the Republican participants. Republicans’ support varied, however, dropping about 18% when it was described as being ...
[1] ... [1117]
[1118]
[1119]
[1120]
[1121]
[1122]
[1123]
[1124]
1125
[1126]
[1127]
[1128]
[1129]
[1130]
[1131]
[1132]
[1133]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.