Yuan elevated to IEEE senior member
2024-06-10
Jinghui Yuan, an R&D staff member in the Applied Research for Mobility Systems group at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, has been elevated to a senior member of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, or IEEE.
Senior member status is the highest grade of IEEE and requires extensive experience that reflects professional accomplishments. Only 10% of IEEE’s more than 450,000 members achieve this level.
As a transportation engineer in the Buildings and Transportation Science Division, Yuan’s research focuses on intelligent transportation systems, crash risk prediction, big data analytics, deep learning, traffic simulation and ...
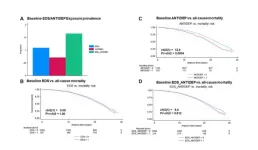
Passive heat exposure increases stress on the heart, posing risk to adults with history of CAD
2024-06-10
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 10 June 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. ...
Feeling rough after your COVID shot? Congrats, it’s working!
2024-06-10
Feeling Rough After Your COVID Shot? Congrats, It’s Working!
Headache, chills, tiredness may be evidence of a supercharged defense, according to UCSF-led study.
Fewer than 1 in 4 people in the United States have received last year’s updated COVID-19 vaccine, despite a death toll of more than 23,000 Americans this year.
One of the most common reasons for bypassing the COVID vaccine is concern about side effects like tiredness, muscle and joint pain, chills, headache, fever, nausea and feeling generally unwell. But a new study, led by UC San Francisco, has found that the symptoms indicate a robust immune response that is likely to ...
Depression, antidepressants, epigenetic age acceleration, and mortality in postmenopausal women
2024-06-10
“The study examined the impact of depressive symptoms, antidepressant use, and epigenetic age acceleration on all-cause mortality in postmenopausal women.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 10, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 10, entitled, “Relationships of depression and antidepressant use with epigenetic age acceleration and all-cause mortality among postmenopausal women.”
In this new study, researchers May A. Beydoun, Hind A. Beydoun, Jason Ashe, Michael F. Georgescu, Steve Horvath, Ake Lu, Anthony S. Zannas, ...
Researchers engineer new approach for controlling thermal emission
2024-06-10
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — If a material absorbs light, it will heat up. That heat must go somewhere, and the ability to control where and how much heat is emitted can protect or even hide such devices as satellites. An international team of researchers, including those from Penn State, has developed a novel method for controlling this thermal emission, with what they called promising implications for thermal management and thermal camouflage technologies.
The team published their work on June 7 in the print edition of Science.
Led by researchers at The University of Manchester’s National Graphene Institute ...
UTA honors two faculty for distinguished scholarship
2024-06-10
The University of Texas at Arlington is honoring two faculty for their outstanding contributions to scholarship with the Distinguished Record of Research or Creativity Award.
Sam W. Haynes, professor of history, and Jaehoon Yu, professor of physics, are the 2024 recipients of the award, which recognizes faculty who have achieved a distinguished record of scholarship over an extended period.
“Jae and Sam have each been at UTA for more than 20 years, and they have each truly made an impact in the lives of the students we prepare for future careers,” said Kate C. Miller, vice president of research and innovation. "In addition, their contributions ...
New research describes the leisure motivations that underpin young U.S. adults' recreational cannabis use
2024-06-10
As of 2024, 24 states including Virginia and Maryland, and DC have legalized the adult recreational use of cannabis. As laws change, citizens' perceptions of the drug and reasons for using the drug have also shifted. In 2020, 34.5% of adults aged 18-25 reported using cannabis in the previous 12 months, according to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Health experts seek to better understand the broader implications of legalizations and individuals’ motivations and attitudes related to cannabis use.
New ...
UC San Diego develops first-in-kind protocol for creating ‘wired miniature brains’
2024-06-10
Researchers worldwide can now create highly realistic brain cortical organoids — essentially miniature artificial brains with functioning neural networks — thanks to a proprietary protocol released this month by researchers at the University of California San Diego.
The new technique, published in Nature Protocols, paves the way for scientists to perform more advanced research regarding autism, schizophrenia and other neurological disorders in which the brain’s structure is usually typical, but electrical activity is altered. That’s according to Alysson Muotri, Ph.D., corresponding author and ...
Lone Star State: Tracking a low-mass star as it speeds across the Milky Way
2024-06-10
It may seem like the Sun is stationary while the planets in its orbit are moving, but the Sun is actually orbiting around the Milky Way galaxy at an impressive rate of about 220 kilometers per second — almost half a million miles per hour. As fast as that may seem, when a faint red star was discovered crossing the sky at a noticeably quick pace, scientists took notice.
Thanks to the efforts of a citizen science project called Backyard Worlds: Planet 9 and a team of astronomers from around the country, a rare hypervelocity ...
Researchers demonstrate the first chip-based 3D printer
2024-06-10
CAMBRIDGE, MA – Imagine a portable 3D printer you could hold in the palm of your hand. The tiny device could enable a user to rapidly create customized, low-cost objects on the go, like a fastener to repair a wobbly bicycle wheel or a component for a critical medical operation.
Researchers from MIT and the University of Texas at Austin took a major step toward making this idea a reality by demonstrating the first chip-based 3D printer. Their proof-of-concept device consists of a single, millimeter-scale photonic ...
Making remanufacturing profitable
2024-06-10
Returning end-of-life products to as-new condition is called remanufacturing and can be an essential element in a circular economy. But for more industrial companies to take an interest in it, remanufacturing needs to be economically viable. In a doctoral thesis from Linköping University, Johan Vogt Duberg has investigated how this can be accomplished.
“It’s possible to take advantage of increased environmental awareness to gain economic benefits. With remanufacturing, the costs of raw materials can be reduced, new customer groups found and ...
NSF awards additional $9.8 Million for Delta, DeltaAI
2024-06-10
The National Center for Supercomputing Applications was recently awarded $4.9 million of supplemental funding from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) for Delta and an additional $4.9 million for DeltaAI to expand the potential capabilities of the soon-to-launch system by nearly 50 percent.
NCSA originally received nearly $25 million from NSF in 2023 to deploy and operate DeltaAI, an advanced computing and data resource that will be a companion system to Delta. DeltaAI will triple NCSA’s AI-focused computing capacity and ...
Breakthrough in creating cyclic peptide opens the way for new antibiotics
2024-06-10
A discovery made by scientists at King’s College London could speed up efforts to produce new antibiotics in the fight against antimicrobial resistance.
In a paper published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, scientists from the Department of Chemistry share a new, rapid method for making cyclic peptides – an important class of antibiotic molecules. The approach takes minutes rather than the hours or days it normally takes, helping overcome a major challenge in antibiotic development.
Lead author Dr Sarah Barry, from the Department of Chemistry at King’s College London, ...
Unregulated sales of a toxic and hallucinogenic mushroom endanger public health
2024-06-10
Americans’ interest in a potentially harmful “magic mushroom” is soaring, with Google searches skyrocketing 114 percent from 2022 to 2023, according to a new study by researchers at the University of California San Diego Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human Longevity Science. In a paper published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, the scientists suggest that the growing market for Amanita muscaria may be sparked in part by emerging clinical research supporting the safety and efficacy of psilocybin as a treatment ...
Alarming trends call for action to define the future role of food in nation’s health
2024-06-10
CHICAGO, June 10, 2024 — The cost of nutritious food and the lack of access to it are of significant concern to U.S. consumers. That’s according to a new national poll of public attitudes on food and nutrition conducted by Zogby Analytics on behalf of Research!America and the American Heart Association. Nearly 7 in 10 (68%) respondents recognize healthy eating habits as an important factor in improving a person’s chance for a long and healthy life. Yet more than half (53%) say the United ...
Case studies show how quasi-governmental organizations could strengthen climate adaptation governance
2024-06-10
The politicization of climate issues and the unsynchronized efforts of stakeholders are hindering the effectiveness of climate adaptation governance in the U.S. According to a new study(Link is external) published by Princeton researchers, the design characteristics of quasi-governmental organizations (QGOs) could provide insights on how to depoliticize climate information sources and foster multi-level stakeholder coordination.
Quasi-governmental organizations are entities that have a combination of public and private characteristics, utilizing both for-profit and not-for-profit ...
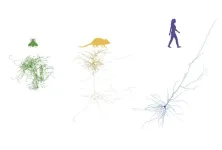
Brain’s structure hangs in ‘a delicate balance’
2024-06-10
When a magnet is heated up, it reaches a critical point where it loses magnetization. Called “criticality,” this point of high complexity is reached when a physical object is transitioning smoothly from one phase into the next.
Now, a new Northwestern University study has discovered that the brain’s structural features reside in the vicinity of a similar critical point — either at or close to a structural phase transition. Surprisingly, these results are consistent across brains from humans, mice and fruit flies, which suggests the finding might be universal.
Although the researchers don’t ...
Protein study could help researchers develop new antibiotics
2024-06-10
A bacterial enzyme called histidine kinase is a promising target for new classes of antibiotics. However, it has been difficult to develop drugs that target this enzyme, because it is a “hydrophobic” protein that loses its structure once removed from its normal location in the cell membrane.
Now, an MIT-led team has found a way to make the enzyme water-soluble, which could make it possible to rapidly screen potential drugs that might interfere with its functions.
The researchers created their new version ...
Two can play that game: juvenile dolphins who play together are more successful as adults
2024-06-10
Juvenile social play predicts adult reproductive success in male bottlenose dolphins, a new study has found.
Fresh findings published today in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences led by researchers from the University of Bristol and University of Western Australia, show that juvenile male dolphins with strong social bonds practice adult-like reproductive behaviours when playing together, and those juvenile males who spend more time practicing will father more offspring as adults. The study provides rare evidence for a link between juvenile social play and reproductive success in a wild animal.
In collaboration with international colleagues, the ...
Wire-cut forensic examinations currently too unreliable for court, new study says
2024-06-10
A research article published June 10 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences highlights the importance of careful application of high-tech forensic science to avoid wrongful convictions.
In a study with implications for an array of forensic examinations that rely on “vast databases and efficient algorithms,” researchers found the odds of a false match significantly increase when examiners make millions of comparisons in a quest to match wires found at a crime scene with the tools allegedly used to cut them.
The rate of mistaken identifications could be as high as one in 10 or more, concluded ...
SNMMI elects Jean-Luc C. Urbain, MD, Ph.D., FASNC, as President-Elect at 2024 Annual Meeting
2024-06-10
Toronto, Ontario—Jean-Luc C. Urbain, MD, PhD, FASNC, professor of Radiology/Nuclear Medicine and Medicine, has been named president-elect of the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI). SNMMI introduced a new slate of officers during its 2024 Annual Meeting, held June 8-11 in Toronto.
“As SNMMI president-elect, I plan to focus on bringing and integrating radiopharmaceutical theranostics into the clinic to benefit as many patients as possible. This will require an emphasis ...
UNC-Chapel Hill researchers create skin-inspired sensory robots to provide medical treatment
2024-06-10
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill scientists have created innovative soft robots equipped with electronic skins and artificial muscles, allowing them to sense their surroundings and adapt their movements in real-time, according to the paper, “Skin-Inspired, Sensory Robots for Electronic Implants,” in Nature Communications.
In their research, funded by the National Science Foundation and the National Institutes of Health, the robots are designed to mimic the way muscles and skin work together in animals, making them more effective and safer to use inside the body. The e-skin integrates various sensing materials, such as silver nanowires ...
Researchers use 3D visualization to predict, prevent hurricane damage
2024-06-10
Beginning annually on June 1, hurricane season poses a major threat to Texas coastal communities, causing both physical and financial damage to the areas they hit. This damage can be staggering; when Hurricane Harvey hit in 2017, it cost Galveston $132.73 billion in damages. Texas A&M University researchers have collaborated to understand the impacts of storm surge floods before they occur to potentially reduce the level of damage. Their study was published in “Urban Informatics.”
The researchers have implemented 3D visualization technology to identify the potential outcomes of hurricane flooding ...
Kepplinger, Vidyashankar to receive funding for conference
2024-06-10
David Kepplinger, Assistant Professor, Statistics, and Anand Vidyashankar, Professor, Statistics, are set to receive funding from the National Science Foundation for: “Conference: Building a robust community: Joint International Conference on Robust Statistics and Conference on Data Science, Statistics, and Data Science.”
Kepplinger and Vidyashankar will receive $20,993 from NSF for this award. Funding will begin in July 2024 and will end in late June 2025.
The funding will support 15–20 students and early-career researchers to participate in the joint International Conference on Robust Statistics (ICORS) and the Conference ...
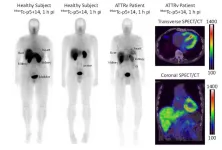
Novel radiotracer produces high quality images of “Alzheimer’s disease of the heart”
2024-06-10
Toronto, Ontario—A newly developed radiotracer can generate high quality and readily interpretable images of cardiac amyloidosis, a condition referred to as the “Alzheimer’s disease of the heart.” As the first amyloid-specific and pan-amyloid binding radiotracer designed for planar and SPECT/CT imaging, 99mTc-p5+14 could play an important role in early detection and treatment of cardiac amyloidosis. This research was presented at the 2024 Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Annual Meeting.
Systemic amyloidosis is an incurable disease in which abnormal amounts of ...
[1] ... [1119]
[1120]
[1121]
[1122]
[1123]
[1124]
[1125]
[1126]
1127
[1128]
[1129]
[1130]
[1131]
[1132]
[1133]
[1134]
[1135]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.