Novel AI method could improve tissue, tumor analysis and advance treatment of disease
2024-06-06
Researchers at the University of Michigan and Brown University have developed a new computational method to analyze complex tissue data that could transform our current understanding of diseases and how we treat them.
Integrative and Reference-Informed tissue Segmentation, or IRIS, is a novel machine learning and artificial intelligence method that gives biomedical researchers the ability to view more precise information about tissue development, disease pathology and tumor organization.
The findings are published ...
Omega-3 therapy prevents birth-related brain injury in newborn rodents
2024-06-06
NEW YORK, NY--An injectable emulsion containing two omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil markedly reduced brain damage in newborn rodents after a disruption in the flow of oxygen to the brain near birth, a study by researchers at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons has found.
Brain injury due to insufficient oxygen is a severe complication of labor and delivery that occurs in one to three out of every 1,000 live births in the United States. Among babies who survive, the condition can lead to cerebral palsy, cognitive disability, epilepsy, pulmonary hypertension, and neurodevelopmental conditions.
“Hypoxic ...
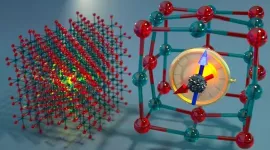
Calcium oxide’s quantum secret: nearly noiseless qubits
2024-06-06
Calcium oxide is a cheap, chalky chemical compound commonly used in the manufacturing of cement, plaster, paper, and steel. But the material may soon have a more high-tech application.
UChicago Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering researchers and their collaborator in Sweden have used theoretical and computational approaches to discover how tiny, lone atoms of bismuth embedded within solid calcium oxide can act as qubits — the building blocks of quantum computers and quantum communication devices. These qubits are described today in Nature Communications.
“This system has even better properties than we expected,” said Giulia Galli, Liew Family Professor ...
Innovative combination therapy shows promise for bladder cancer patients unresponsive to standard treatment
2024-06-06
TAMPA, Fla. (June 6, 2024) — In a groundbreaking advance that could revolutionize bladder cancer treatment, a novel combination of cretostimogene grenadenorepvec and pembrolizumab has shown remarkable efficacy in patients with Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG)-unresponsive non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Results from the phase 2 CORE-001 trial, published today in Nature Medicine, reveal a significant improvement in complete response rates and long-term disease control, offering new hope for patients with this challenging condition who face limited treatment options.
The trial included patients with BCG-unresponsive carcinoma in situ of the bladder, a condition that is notoriously ...
SFU Physics collaboration pushes an information engine to its limits
2024-06-06
The molecules that make up the matter around us are in constant motion. What if we could harness that energy and put it to use?
Over 150 years ago Maxwell theorized that if molecules’ motion could be measured accurately, this information could be used to power an engine. Until recently this was a thought experiment, but technological breakthroughs have made it possible to build working information engines in the lab.
With funding from the Foundational Questions Institute, SFU Physics professors John Bechhoefer and David Sivak teamed up to build an information engine and test its limits. Their work has greatly advanced ...
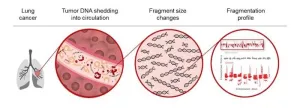
Artificial intelligence blood test provides a reliable way to identify lung cancer
2024-06-06
Using artificial intelligence technology to identify patterns of DNA fragments associated with lung cancer, researchers from the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and other institutions have developed and validated a liquid biopsy that may help identify lung cancer earlier.
In a prospective study published June 3 in Cancer Discovery, the team demonstrated that artificial intelligence technology could identify people more likely to have lung cancer based on DNA fragment patterns in the blood. The study enrolled about 1,000 participants with and without cancer who met the criteria for traditional lung ...
The ethical matrix: it's not just smart; it's the smart thing to do
2024-06-06
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the talk of the town, but far too often expediency has been the driver, not responsible innovation. The NYC Media Lab (NYCML) at NYU Tandon School of Engineering and Bertelsmann launched their 4th challenge this month, this time aimed at mentoring teams with projects that use AI to responsibly advance their fields.
The 2024 collaboration, The Ethical Matrix Challenge: Forging New AI Frontiers in Media, Communications, Education, and Healthcare, focuses on ethical AI and its power to have a real-world influence. The four selected teams have projects that can responsibly revolutionize the way ...
Study: Young athletes at risk for elevated blood pressure rates, future cardiovascular complications
2024-06-06
A substantial portion of young athletes are at risk of hypertension, according to a study presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Care of the Athletic Heart conference, taking place on June 6-8 in Washington.
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, occurs in 47% of adults in the U.S., according to CardioSmart.org. Over time, hypertension weakens the heart, blood vessels and kidneys, paving the way for potential stroke or heart attack. Often referred to as the “silent killer,” high blood pressure is a leading risk factor for heart disease and early death.
The 2017 ACC/American Heart Association Guideline for the Prevention, ...
Mpox continues to circulate at low numbers among gay and bisexual men who have sex with men
2024-06-06
While mpox cases have sharply declined since the 2022 global outbreak, they continue to occur in the U.S. among gay and bisexual men who have sex with men (GBMSM), according to a UCLA-led study from EMERGEncy ID NET, a multisite surveillance network funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Though no cases were found in women, children or the unhoused, vigilance and vaccination remain important, the researchers write.
The findings will be published June 6 in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, ...
How the cell cycle orchestra plays an unexpected new tune
2024-06-06
How the Cell Cycle Orchestra Plays an Unexpected New Tune
UCSF scientists discover that multiciliated cells adapt the well-known process of cell division to make hundreds of cilia.
The awe-inspiring process of cell division can turn a fertilized egg into a baby – or a cancerous cell into a malignant tumor. With so much at stake, nature keeps it tightly controlled in a process called the cell cycle that scientists thought they thoroughly understood.
But now it turns out there was more to know. Scientists ...
Exotic black holes could be a byproduct of dark matter
2024-06-06
For every kilogram of matter that we can see — from the computer on your desk to distant stars and galaxies — there are 5 kilograms of invisible matter that suffuse our surroundings. This “dark matter” is a mysterious entity that evades all forms of direct observation yet makes its presence felt through its invisible pull on visible objects.
Fifty years ago, physicist Stephen Hawking offered one idea for what dark matter might be: a population of black holes, which might have formed very soon after the Big Bang. Such “primordial” black holes would not have been the goliaths that we detect today, but ...
El Centro Regional Medical Center provides financial and operational updates
2024-06-06
El Centro Regional Medical Center (ECRMC), an affiliate of UC San Diego Health, today announced several financial and operational updates, demonstrating significant progress toward stabilizing and strengthening a critical health services asset in the Imperial Valley.
“Our goal is simple — to ensure that the people of El Centro and the broader Imperial Valley have long-term access to health care services,” said Pablo Velez, RN, PhD, chief executive officer, ECRMC. “Over the last year, the amazing team of dedicated physicians and staff at ECRMC have worked tirelessly in partnership with UC San Diego ...
ESMO Gynaecological Cancers Congress 2024: Event Announcement
2024-06-06
Lugano, Switzerland, 6 June 2024 – The ESMO Gynaecological Cancers Congress 2024 will be held in Florence, Italy, between 20-22 June, hosting international experts who will present and discuss the latest developments in the biology, diagnosis and therapy of gynaecological tumours. The management of rare gynaecological malignancies will be among the key areas covered in the scientific programme, available online.
The congress can be joined either in person or via the online platform.
Programme ...
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute partners with Massachusetts firefighters to address cancer risks
2024-06-06
BOSTON – Dana-Farber Cancer Institute is proud to announce the launch of the Direct Connect Partnership with Massachusetts Firefighters, marking a crucial step in addressing the heightened cancer risk faced by firefighters.
Dana-Farber’s Direct Connect program partners with employers who want to support their workforce across the spectrum of oncology needs and provides guided access to world-renowned expertise from cancer care specialists. Direct Connect has more than ...
Tepper School study offers a better way to make AI fairer for everyone
2024-06-06
n a new paper, researchers from Carnegie Mellon University and Stevens Institute of Technology show a new way of thinking about the fair impacts of AI decisions. They draw on a well-established tradition known as social welfare optimization, which aims to make decisions fairer by focusing on the overall benefits and harms to individuals. This method can be used to evaluate the industry standard assessment tools for AI fairness, which look at approval rates across protected groups.
"In assessing fairness, the AI community tries to ensure equitable treatment for groups that differ in economic level, race, ethnic background, gender, and other categories,” ...
People with autism turn to ChatGPT for advice on workplace issues
2024-06-06
A new Carnegie Mellon University study shows that many people with autism embrace ChatGPT and similar artificial intelligence tools for help and advice as they confront problems in their workplaces.
But the research team, led by the School of Computer Science's Andrew Begel, also found that such systems sometimes dispense questionable advice. And controversy remains within the autism community as to whether this use of chatbots is even a good idea.
"What we found is there are people with autism who are already using ChatGPT to ask questions that we think ChatGPT is partly well-suited and partly poorly suited for," said Begel, an associate professor ...
How do you know where a fish goes?
2024-06-06
When scientists want to study the long-distance movement of marine animals, they will instrument them with a small device called an acoustic transmitter – or tag – which emits unique signals or “pings.” These signals are picked up by receivers anchored to the seafloor that record the date and time of each detection when the tagged animal comes within range.
Data collected by the receivers are stored until they are retrieved by researchers and shared across members of cooperative acoustic telemetry networks. This information provides valuable insights into animal behavior, migration patterns, habitat preferences and ecosystem dynamics – all of which ...
People feel more connected to “tweezer-like” bionic tools that don’t resemble human hands
2024-06-06
Some say the next step in human evolution will be the integration of technology with flesh. Now, researchers have used virtual reality to test whether humans can feel embodiment—the sense that something is part of one’s body—toward prosthetic “hands” that resemble a pair of tweezers. They report June 6 in the journal iScience that participants felt an equal degree of embodiment for the tweezer-hands and were also faster and more accurate in completing motor tasks in virtual reality than when they were equipped with a virtual human hand.
“For our ...
Physical activity, cardiovascular status, mortality, and prediabetes in Hispanic and non-Hispanic adults
2024-06-06
About The Study: In this cohort study of U.S. Hispanic or Latino and non-Hispanic adults, lower moderate to vigorous physical activity levels were associated with cardiovascular disease or mortality among participants with normoglycemia but not participants with prediabetes. Adults with prediabetes may benefit from reducing sedentary behavior and improving multiple lifestyle factors beyond improving moderate to vigorous physical activity alone.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Robert C. Kaplan, Ph.D., email robert.kaplan@einsteinmed.edu.
To ...
Heavy lifetime cannabis use and mortality by sex
2024-06-06
About The Study: A positive association between cardiovascular disease mortality and heavy lifetime cannabis use was observed among females in this study. Longitudinal studies are needed in general populations to investigate the potential effects of cannabis on mortality.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Alexandre Vallee, M.D., Ph.D., email al.vallee@hopital-foch.com.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.15227)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
The rise of horse power ~4,200 years ago
2024-06-06
1. An international research team sequenced the genomes of hundreds of horse archaeological remains to track the historical rise of horse-based mobility around 4200 years ago in the Pontic-Caspian steppes.
2. The emergence of improved breeding techniques at the time considerably enhanced the yearly capacity of horse production, which helped spreading domestic horses like a wildfire across the whole Eurasian continent.
3. The massive human migrations that spread Indo-European languages outside the steppes around 5,000 years ago were not mediated by horses, contrarily to what was previously thought.
All domestic horses living on the planet today, whether racetrack ...
Adding nurse case managers to telehealth significantly lowers blood pressure in Black and Hispanic stroke survivors
2024-06-06
Low-income Black and Hispanic stroke survivors with uncontrolled hypertension had a more than two-fold reduction in blood pressure when they tracked it at home and sent their readings to a nurse case manager. The gains were in systolic blood pressure specifically at one year into the study and when compared to a similar group of patients who did not have access to a nurse.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone, the study is the first to examine differences in home blood pressure monitoring with or without nurse case management. Further, the findings, published online June 6 in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), addressed controlling hypertension in low-income ...
The gut’s stem cells get a new identity
2024-06-06
Two independent studies by Columbia scientists suggest that research into the gut’s stem cells over the past 15 years has been marred by a case of mistaken identity: Scientists have been studying the wrong cell.
Both studies were published online today in the journal Cell.
The gut’s stem cells are some of the hardest-working stem cells in the body. They work continuously throughout our lives to replenish the short-lived cells that line our intestines. About every four days, these cells—covering a surface about the size of a tennis court—are completely replaced.
Understanding these workaholic stem cells could help scientists turn ...
The World Cultural Council (WCC) is pleased to announce the names of the 2024 Awards
2024-06-06
SCIENCE
Professor Eske Willerslev, Professor of Evolutionary Biology at the University of Copenhagen and Prince Philip Professor at the University of Cambridge, has been selected as the winner of the Albert Einstein World Award of Science 2024.
The prize is granted in recognition of the numerous breakthroughs in evolutionary genetics Prof. Willerslev’s has made during his highly fruitful career. The award recognizes his pioneering contributions in establishing the field of Environmental DNA and the sequencing of ancient DNA to track the origins and interactions of human population groups.
During his doctoral studies, Prof. Willerslev published ...
Citrus saviors: discovering the genetic defense against Huanglongbing disease
2024-06-06
A recent study has pinpointed two key enzymes in Citrus sinensis that play a crucial role in the plant's defense mechanism against the Asian citrus psyllid (ACP), a vector for the lethal huanglongbing (HLB) disease. This research offers a promising lead in the battle against a disease that has caused significant losses in the citrus industry.
The citrus industry faces major challenges from Huanglongbing (HLB) disease, transmitted by the Asian citrus psyllid (ACP). Traditional control methods are often ineffective and environmentally harmful. The need for innovative and sustainable pest management strategies is ...
[1] ... [1125]
[1126]
[1127]
[1128]
[1129]
[1130]
[1131]
[1132]
1133
[1134]
[1135]
[1136]
[1137]
[1138]
[1139]
[1140]
[1141]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.