Desert hero unveiled: Cissus quadrangularis genome decodes drought survival tactics
2024-06-06
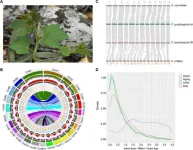
In a recent study, scientists have unlocked the genetic secrets of Cissus quadrangularis, a plant that flourishes in the harshest of desert climates. The discovery of its adaptive traits and the Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) pathway marks a significant leap forward in the quest for drought-resistant crops.
As water scarcity looms as a major threat to global ecosystems and food production, the quest to understand how plants like Cissus quadrangularis conquer arid landscapes is more critical than ever. The genetic blueprint of such species could hold the key to enhancing ...
Afib patients on low doses of blood thinners have more bleeding episodes than those on standard doses
2024-06-06
(WASHINGTON, June 6, 2024) – Patients with atrial fibrillation (Afib) who took low doses of blood-thinning medications known as direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) experienced more bleeding episodes during the first three months of treatment and about one in five had high blood levels of the medications, compared with similar patients who took standard doses of the same medications, according to a study published in Blood Advances.
Patients with Afib, a common type of arrhythmia, or ...
Severity of calls to US poison centers increases sharply for both adults, kids
2024-06-06
America’s poison centers are fielding increasingly severe cases that are dramatically more likely to lead to severe harm or death in both adults and children, a new study from the University of Virginia School of Medicine reveals.
The number of calls about intentional exposures that resulted in death among adults increased a whopping 233.9% between the beginning of 2007 and the end of 2021, the study reveals. “Intentional exposures” include cases such as suicide attempts, use of illegal drugs and ...
Novel diamond quantum magnetometer for ambient condition magnetoencephalography
2024-06-06
Magnetoencephalography (MEG) is a biomedical imaging technique used for mapping brain activity by recording magnetic fields produced by the naturally occurring electrical currents generated by neurons in the brain, using very sensitive magnetometers. Currently, MEG requires a magnetically shielded room for operation. Achieving MEG that works in normal environments, without the need for magnetic shielding, is a major goal. This would enable daily diagnosis, brain-machine interfaces, and fundamental research on brain function.
Magnetometers using diamond quantum sensors with nitrogen–vacancy (NV) centers are promising candidates for realizing ambient ...
Novel lipopeptide proves lethal against Staphylococcus areus
2024-06-06
A novel antibacterial lipopeptide produced by the bacterium Serratia marcescens has been shown to be highly effective in killing Staphylococcus aureus – one of the most important pathogens occurring in humans.
Staphylococcus aureus is one of the five most common causes of hospital-acquired infections and is often the cause of life-threatening infections following surgery. Since the introduction of antibiotics in the early 1940s, S. aureus has by now developed resistance against most classes of antibiotics, ...
Harposporium incensis sp. nov., a South American cordycipitoid species exhibiting inter-phylum host-jumping and having potential as a biological control agent for pest management
2024-06-06
The genus of Harposporium belongs to the Ascomycota of the Fungi kingdom, the class Sortariomycetes, the order Hypocreales, and the family Ophiocordyceiaceae, is a common genus of soil fungi. The species of Harposporium are pathogens of nematodes, with some also infecting rotifers or tardigrades, and has significant ecological value. In recent years, studies have shown that a few species of the genus Harposporium can also parasitize insects or other invertebrates, such as H. janus, which can infect beetles in the Coleoptera family. However, so far, it has not been found that the same species in this genus can parasitize different invertebrates in both sexual and asexual stages. Is there a ...
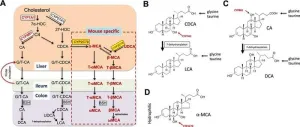
Balancing act between digestion and liver health through bile acids
2024-06-06
Bile acids are essential molecules the liver produces that play a critical role in digestion. They help us absorb fat-soluble vitamins and cholesterol from our food. However, bile acids can become a double-edged sword. While they are necessary for proper digestion, high concentrations can also be toxic to the liver.
Recent research is shedding light on the complex relationship between bile acids and liver health. Scientists have identified new ways in which bile acids interact with cellular stress responses, impacting how the liver functions in diseases ...
Cleveland clinic-led study links sugar substitute to increased risk of heart attack and stroke
2024-06-06
June 6, 2024, Cleveland: Cleveland Clinic researchers found higher amounts of the sugar alcohol xylitol are associated with increased risk of cardiovascular events like heart attack and stroke.
The team, led by Stanley Hazen, M.D., Ph.D., confirmed the association in a large-scale patient analysis, preclinical research models and a clinical intervention study. Findings were published today in the European Heart Journal.
Xylitol is a common sugar substitute used in sugar-free candy, gums, baked ...
Vigorous exercise may preserve cognition in high-risk patients with hypertension
2024-06-06
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – June 6, 2024 – People with high blood pressure have a higher risk of cognitive impairment, including dementia, but a new study from researchers at Wake Forest University School of Medicine suggests that engaging in vigorous physical activity more than once a week can lower that risk.
The findings appear online today in Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association.
“We know that physical exercise offers many benefits, including lowering blood pressure, improving heart health and potentially delaying cognitive decline,” said Richard Kazibwe, ...
Sanders-Brown study: Long-read RNA sequencing reveals key gene expressions in Alzheimer’s disease
2024-06-06
LEXINGTON, Ky. — Researchers at the University of Kentucky Sanders-Brown Center on Aging are working to develop a pre-symptomatic disease diagnostic tool for Alzheimer’s disease.
“While the need for better treatments is clear, such treatments will not be very meaningful if they are administered after symptoms have onset. By then, Alzheimer’s disease has been ravaging the brain for decades to the point the brain can no longer compensate for the extreme cellular death,” said Mark ...
Women with excess weight as a teen or young adult may have higher stroke risk by age 55
2024-06-06
Research Highlights:
Women with excess weight at age 14 or 31 may have increased ischemic (clot caused) stroke risk before age 55. The same ischemic stroke risk was not found in men.
Losing excess weight after adolescence may not eliminate the stroke risk.
These findings are according to a study conducted in Finland that followed more than 10,000 people from birth into their 50s.
Researchers suggest health care professionals pay attention to overweight and obesity in young people and work with them to promote healthy eating and physical activity from an early age.
Embargoed ...
New glioblastoma treatment reaches human brain tumor and helps immune cells recognize cancer cells
2024-06-06
· Major advance for treatment of deadly brain cancer
· Clinical trial launched at Northwestern to test treatment
· Ultrasound microbubbles open blood-brain barrier to admit chemotherapy and immunotherapy cocktail
CHICAGO --- In a major advance for the treatment of the deadly brain cancer glioblastoma, Northwestern Medicine scientists used ultrasound technology to penetrate the blood-brain barrier and provide a small dose of a chemotherapy and immunotherapy drug cocktail. The study found that this treatment ...
Using oceanography to understand fronts and cyclones on Jupiter
2024-06-06
New research led by Lia Siegelman, a physical oceanographer at UC San Diego’s Scripps Institution of Oceanography, shows that the roiling storms at the planet Jupiter’s polar regions are powered by processes known to physicists studying Earth’s oceans and atmosphere. The geophysical commonalities spanning the 452 million miles between the two planets could even help facilitate an improved understanding of those processes on Earth.
Siegelman first made the connection between our planet and the gas giant in 2018 when she noticed a striking similarity between images of Jupiter’s huge cyclones and the ocean turbulence she was studying. ...
Ohio State develops searchable database for Alzheimer’s research
2024-06-06
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A searchable database is now ready to help study Alzheimer’s disease.
Neuroscience and biomedical informatics researchers at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine created the comprehensive, user-friendly repository.
The free database – known as ssREAD – is outlined in a manuscript published online in Nature Communications.
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia, accounting for up to 80% of cases. An estimated 6.7 million Americans who are age 65 and older are living with Alzheimer's dementia today, according ...
Lifesaving childbirth blood loss intervention is highly cost-effective
2024-06-06
Economic analysis of the E-MOTIVE trial finds that average cost per patient of drape and treatment to save women’s lives incurs minimal additional cost compared with usual care, while significantly improving health outcomes.
The additional cost to achieve the improved outcome could be as little as 30 US cents extra- on average, compared to usual care.
Post-partum haemorrhage currently affects 14m women around the world and leads to 70,000 deaths a year which is equivalent to one woman dying every 6 minutes
A lifesaving package including early detection and bundled treatment for ...
Hidden challenges of tooth loss and dentures revealed in new study
2024-06-06
The hidden challenges faced by people with tooth loss and dentures has been identified by new research from the University of Sheffield.
Improvements in dental care, more people living longer and the social value placed on having a healthy smile has led to people keeping their own teeth longer, but it has also led to an increasing number of people needing some kind of restoration work including crowns, bridges and implants.
Many of these treatments remain unobtainable for most people due to the availability of NHS dentists and the high cost of private dental work. Removable dentures are often the only viable option for anyone experiencing tooth loss with an estimated ...
How medical models can transform agriculture
2024-06-06
Nano-agriculture: Sustainable solutions for global food security
PITTSBURGH—Researchers in the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering at Carnegie Mellon University are using findings from nanomedicine and digital twin technologies to understand the new field of Plant Nanobiotechnology, address unsustainable agricultural practices, and meet increasing global food demands.
Currently, agriculture accounts for 14-28% of global greenhouse gas emissions and 70% of all freshwater withdraws. This, in addition to a range of other factors from extreme weather ...
World-first study into precision medicine for high-risk childhood cancer yields extraordinary results
2024-06-06
WORLD-FIRST STUDY INTO PRECISION MEDICINE FOR HIGH-RISK CHILDHOOD CANCER YIELDS EXTRAORDINARY RESULTS
VIDEO - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bwyugwVwNzc
In a world-first, Australian researchers and clinicians have shown that precision medicine – where treatment is tailored to an individual child’s cancer – leads to significantly improved outcomes in children with high risk cancer.
In a study published this week in the leading international journal Nature Medicine, the researchers found that precision medicine (also called personalised medicine) was shown to be superior to standard or non-guided therapy, both in terms of clinical response and survival.
A staggering ...
Better farming through nanotechnology
2024-06-06
Advanced technologies enable the controlled release of medicine to specific cells in the body. Scientists argue these same technologies must be applied to agriculture if growers are to meet increasing global food demands.
In a new Nature Nanotechnology journal review paper, scientists from UC Riverside and Carnegie Mellon University highlight some of the best-known strategies for improving agriculture with nanotechnology.
Nanotechnology is an umbrella term for the study and design of microscopically small things. How small? A nanometer is one billionth of a meter, or about 100,000 times smaller ...
First-of-its-kind test can predict dementia up to nine years before diagnosis
2024-06-06
Peer Reviewed | Observational study | People
Researchers at Queen Mary University of London have developed a new method for predicting dementia with over 80% accuracy and up to nine years before a diagnosis. The new method provides a more accurate way to predict dementia than memory tests or measurements of brain shrinkage, two commonly used methods for diagnosing dementia.
The team, led by Professor Charles Marshall, developed the predictive test by analysing functional MRI (fMRI) scans to detect changes in the brain’s ‘default mode network’ (DMN). The DMN connects regions of the brain ...
Popular chatbot is a politically left-leaning EU supporter
2024-06-06
With the European Parliament elections now underway, millions of EU citizens are finalizing their decisions about which political party best represents their views.
But anyone using LlamaChat, one of the major new AI chatbots, is very likely to be confronted with biased answers. It turns out that the large language model developed by Meta, upon which LlamaChat is based, has clear political leanings. This has been demonstrated in a new study from the University of Copenhagen in which Department of Computer Science researchers examined the language model's knowledge of political groups in the European Parliament. Moreover, they tested LlamaChat’s ...
Doctors advise caution as energy drinks may trigger life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias in patients with genetic heart diseases
2024-06-06
Philadelphia, June 6, 2024 – A new study in Heart Rhythm, the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society, the Cardiac Electrophysiology Society, and the Pediatric & Congenital Electrophysiology Society, published by Elsevier, examined the potential dangers of consuming energy drinks for patients with genetic heart diseases. A cohort of 144 sudden cardiac arrest survivors was examined at Mayo Clinic, of which seven patients (5%) had consumed one or more energy drinks in close proximity to their cardiac ...
Only around half of individuals disclose or believe they should reveal having an STI prior to sexual intercourse, research to-date suggests
2024-06-06
A review of research to-date reveals the complex nature of revealing a diagnosis of a sexually transmitted infection (STI) to a partner ahead of engaging in sexual activity.
With individuals experiencing a variety of feelings and emotions related to the prospect of disclosure, the research shows that only around half or fewer individuals felt able to disclose their diagnosis to a partner before sexual engagement.
Peer-reviewed results, published today in The Journal of Sex Research, also show a similar number of people believed they should have to disclose having a STI to a partner prior to engaging in sexual intercourse.
In order ...
Climate crisis puts Australia’s ski industry on slippery slope, but not all hope is lost
2024-06-06
Australia’s ski industry is at risk of major disruptions and shorter seasons if the current level of climate pollution continues, according to new modelling from Protect Our Winters Australia (POW) and The Australian National University (ANU).
The report found the average ski season across all resorts in Australia will be 44 days shorter by 2050 under a mid-greenhouse gas emissions scenario and 55 days shorter under a high-emissions scenario.
It also shows that despite a dramatic decline in snowfall under mid- and high-emissions scenarios, the ...
Tiny roundworms carve out unique parasitic niche inside pseudoscorpion’s protective covering
2024-06-06
CORVALLIS, Ore. – The early worm gets the arachnid, fossil research by an Oregon State University scientist has shown.
In a parasitic first, a Baltic amber specimen has revealed that millions of years ago tiny worms known as nematodes were living inside of and feeding on the outer protective layer of pseudoscorpions.
“This is very strange,” said George Poinar Jr., who has a courtesy appointment in the OSU College of Science. “No other invertebrate-associated nematodes are known to have this detailed habit.”
Findings were published in Historical Biology.
Pseudoscorpions are a highly diverse lineage of arachnid, said Poinar, an international expert in ...
[1] ... [1126]
[1127]
[1128]
[1129]
[1130]
[1131]
[1132]
[1133]
1134
[1135]
[1136]
[1137]
[1138]
[1139]
[1140]
[1141]
[1142]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.