Allison Institute announces appointment of two immunobiology experts as associate members
2024-06-05
HOUSTON ― The James P. Allison Institute at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center today announced the appointment of its newest members, Susan Bullman, Ph.D., and Xi Chen, Ph.D., to further the institute’s ongoing work of impactful immunobiology research. These accomplished researchers, joining as associate members, bring valuable expertise in studying how the intratumoral microbiome and the immune microenvironment influence patient responses to immunotherapy.
As Allison Institute members, Bullman and Chen will lead impactful research programs aligned with the institute’s ...
Focused Ultrasound Foundation designates Virginia Tech as a Center of Excellence
2024-06-05
The Focused Ultrasound Foundation has designated Virginia Tech as a Focused Ultrasound (FUS) Center of Excellence, making it the sixth such center in the United States and one of only 12 in the world.
“Virginia Tech possesses significant strengths in the FUS field, and it is an honor to recognize them as a Center of Excellence,” said Neal F. Kassell, founder and chairman of the Focused Ultrasound Foundation. “With distinguished experts across the colleges of engineering, science, veterinary medicine, and medicine, ...
US public opinion on social media is warming to nuclear energy, but concerns remain
2024-06-05
Images
The U.S. public displays more positive than negative sentiment toward nuclear energy but concerns remain about waste, cost and safety, according to an analysis of 300,000 posts on X (formerly Twitter) by University of Michigan researchers.
The study was recently published in Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews.
Identifying public concerns and misconceptions about nuclear energy can target efforts to bridge these gaps as nuclear energy will play a large role in goals to decarbonize ...
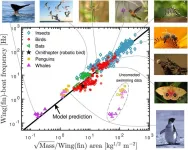
Flapping frequency of birds, insects, bats and whales described by universal equation
2024-06-05
A single universal equation can closely approximate the frequency of wingbeats and fin strokes made by birds, insects, bats and whales, despite their different body sizes and wing shapes, Jens Højgaard Jensen and colleagues from Roskilde University in Denmark report in a new study in the open-access journal PLOS ONE, publishing June 5.
The ability to fly has evolved independently in many different animal groups. To minimize the energy required to fly, biologists expect that the frequency that animals flap their wings should be determined by the natural resonance frequency of the wing. However, finding a universal mathematical description of flapping flight has proved ...
Pro-inflammatory diets are associated with higher levels of the heart failure biomarker NT-proBNP, with potential implications for cardiovascular risk, per study of more than 10,000 US adults
2024-06-05
Pro-inflammatory diets are associated with higher levels of the heart failure biomarker NT-proBNP, with potential implications for cardiovascular risk, per study of more than 10,000 US adults
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0304289
Article Title: Association between dietary inflammatory index and NT-proBNP levels in US adults: A cross-sectional analysis
Author Countries: China
Funding: The study was funded by the Yan'an Science and Technology Plan Project (Grant No. 2022SLSFGG-025).The funders ...
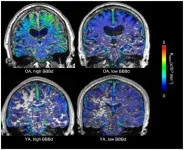
Normal ageing might be associated with increased blood-brain barrier permeability in regions also vulnerable in Alzheimer's Disease, in small study comparing healthy brains of the young and old
2024-06-05
Normal ageing might be associated with increased blood-brain barrier permeability in regions also vulnerable in Alzheimer's Disease, in small study comparing healthy brains of the young and old
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0299764
Article Title: Associations between regional blood-brain barrier permeability, aging, and Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers in cognitively normal older adults
Author Countries: USA
Funding: Research reported in this publication was supported ...
Evidence-based design or Feng Shui in hospital rooms might benefit patients
2024-06-05
In an online study, virtual hospital rooms designed according to the principles of evidence-based design or the principles of Feng Shui were associated with greater potential benefit for viewers than virtual representations of standard hospital rooms. Emma Zijlstra of Hanze University of Applied Sciences in the Netherlands and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on June 5.
Hospital designers might consider employing specific design principles in an effort to improve patients’ experiences. Growing evidence suggests ...
US Islamist extremist co-offenders form close-knit groups driven by mutual contacts, homophily effects
2024-06-05
The formation of relationships within violent US Islamist extremist groups is highly driven by mutual contacts and the tendency for people to bond with others similar to themselves, according to new research. Anina Schwarzenbach, formally of Harvard University and the University of Maryland (currently affiliated with the University of Bern) and Michael Jensen of the University of Maryland present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on June 5, 2024.
Prior research on social structures within extremist networks have primarily ...
Simple headlines attract more online news readers
2024-06-05
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Online news consumers tend to click on simpler headlines that use more common words and more readable writing, a new study finds.
Researchers evaluated more than 30,000 real-world field experiments from the Washington Post and the online news site Upworthy to see how readers reacted to headlines of varying complexity.
In addition, a follow-up experiment showed that average readers paid more attention to simpler headlines and processed them more deeply – unlike journalists, who paid just as much attention to complex headlines.
The results show ...
Researchers unveil pioneering approach to combat age-related vision loss
2024-06-05
June 5, 2024 (Cambridge, MA) - Cirrus Therapeutics, the University of Bristol, and London’s Global University Institute of Ophthalmology have discovered a revolutionary treatment for age-related macular degeneration (AMD), the leading cause of vision loss among older adults.
Featured on the cover of the journal Science Translational Medicine, this breakthrough research reveals that boosting a specific protein, IRAK-M, in retinal cells could offer a new and highly effective therapy for AMD.
AMD ...
MSU research: What makes a good headline?
2024-06-05
EAST LANSING, Mich. – The competition for online attention in today’s news environment is fierce. High-quality news from credible sources must compete for attention with misinformation and a rapidly increasing amount of partisan content.
How can a news organization stand out as a reputable and trustworthy outlet while driving readers to its site?
The answer is simple: literally.
According to research from Michigan State University, news readers engage more with simple writing, suggesting journalists ...
Scientists identify ‘missing piece’ required for blood stem cell self-renewal
2024-06-05
UCLA scientists have identified a protein that plays a critical role in regulating human blood stem cell self-renewal by helping them sense and interpret signals from their environment.
The study, published in Nature, brings researchers one step closer to developing methods to expand blood stem cells in a lab dish, which could make life-saving transplants of these cells more available and increase the safety of blood stem cell-based treatments, such as gene therapies.
Blood stem cells, also known as hematopoietic stem cells, have the ability to make copies of themselves via a process called ...
Father's diet before conception influences children's health
2024-06-05
Dr. Raffaele Teperino, head of the "Environmental Epigenetics" research group at Helmholtz Munich, along with his research team, has examined the impact of paternal diet on children's health – specifically, the influence of diet before conception. The researchers focused on special small RNA molecules in sperm, known as mitochondrial tRNA fragments (mt-tsRNAs, see background). These RNAs play a key role in the inheritance of health traits by regulating gene expression.
For their study, the researchers used data from the LIFE Child cohort, which includes information from over 3,000 families. The analyses showed ...
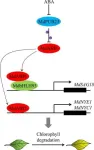
Fountain of youth for plants: E3 ligase's role in leaf longevity
2024-06-05
A new study uncovers the intricate molecular mechanisms that regulate leaf senescence in apple plants, focusing on the crucial role of the E3 ligase enzyme, MdPUB23, and its interaction with the ABI5 protein. This research provides valuable insights into how plants manage stress responses and maintain growth, offering potential applications in improving crop yield and stress resistance.
Leaf senescence is a vital phase in the life cycle of plants, impacting overall plant health and yield. Abscisic acid (ABA) ...
Drones and AI harnessed to monitor invasive stink bugs
2024-06-05
Researchers in Italy have unveiled the first successful application of commercial drones combined with artificial intelligence (AI) to monitor the invasive agricultural pest, Halyomorpha halys, commonly known as the brown marmorated stink bug. This research, published in the SCI journal Pest Management Science, marks a significant advancement in the use of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for automated monitoring of invasive species.
Halyomorpha halys is notorious for its extensive damage to orchard crops across North America and southern Europe. In Italy, this invasive pest caused an ...
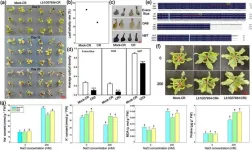
Unlocking salt resistance: sea lavender's genetic secret revealed
2024-06-05
Recent research has uncovered the genetic mechanisms behind sea lavender's (Limonium bicolor) salt tolerance by studying basic helix–loop–helix (bHLH) transcription factors. Identifying 187 bHLH genes, the study highlights their roles in salt gland development and stress responses. CRISPR-Cas9 validation demonstrated specific bHLH genes' critical role in enhancing salt tolerance, paving the way for future applications in crop improvement and saline soil management.
Basic helix–loop–helix (bHLH) transcription factors are essential for various plant processes, including ...
Six UTA faculty receive prestigious CAREER grants
2024-06-05
Six faculty members from The University of Texas at Arlington received more than $3.23 million in awards as part of the National Science Foundation’s (NSF) Faculty Early Career Development Program. Called CAREER, these awards are considered the NSF’s most prestigious for early-career faculty and are given to those who have the potential to serve as academic role models in research and education.
Between 2017 and 2022, UTA received nine CAREER awards; in 2023, it received six. Vice President of research and innovation Kate C. Miller called this “a true testament to the world-class research teams we’re assembling here in Arlington.”
“CAREER ...
Brain overgrowth dictates autism severity, new research suggests
2024-06-05
Some children with autism experience profound, lifelong difficulties like developmental delay, social struggles and even the inability to speak. Others experience more mild symptoms that improve with time.
The disparity in outcomes has been a mystery to scientists, until now. A new study, published in Molecular Autism by researchers at University of California San Diego, is the first to shed light on the matter. Among its findings: The biological basis for these two subtypes of autism develops in utero.
Researchers ...
MD Anderson Research Highlights for June 5, 2024
2024-06-05
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments at MD Anderson offer insights into a lower-intensity therapy combination for older patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), a novel T cell therapy for patients with bone marrow failure syndromes, a proof-of-concept study using MRI to detect metabolic changes inside tumors, a molecular target to overcome treatment resistance ...
New study finds many of the world’s most threatened species lack evidence of sufficient conservation efforts
2024-06-05
-With images-
A new study has revealed alarming gaps in the implementation of conservation interventions for thousands of the world's most threatened species.
The research, published in the journal Nature, shows that most terrestrial plant and animal species at risk of extinction from threats like habitat loss, over-exploitation for trade, and invasive species are not receiving the appropriate types of conservation efforts needed to protect them.
The study findings suggest that there is a serious mismatch between the ...
BU study: Black-specific incarceration rates are associated with Black firearm homicide rates
2024-06-05
(Boston)—Firearm-related injury remains a significant burden in the U.S. with more than 45,000 people dying from these injuries in 2020. Suicides continue to account for the majority of all gun deaths. The number of homicides due to gun violence decreased between 1990 and 2010, but the last decade has seen an uptick. Homicides now make up 45% of all gun-related deaths, and Black and other minorities are overrepresented among firearm homicide victims. Moreover, there has been a stark increase in incarcerated populations in the U.S since the 1980s largely due to differential drug sentencing, ...
New technique reveals how gene transcription is coordinated in cells
2024-06-05
The human genome contains about 23,000 genes, but only a fraction of those genes are turned on inside a cell at any given time. The complex network of regulatory elements that controls gene expression includes regions of the genome called enhancers, which are often located far from the genes that they regulate.
This distance can make it difficult to map the complex interactions between genes and enhancers. To overcome that, MIT researchers have invented a new technique that allows them to observe the timing of gene and enhancer activation in a cell. When a gene is turned on around the same time as a particular enhancer, it strongly suggests the enhancer ...
Major cause of inflammatory bowel disease discovered
2024-06-05
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute, working with UCL and Imperial College London, have discovered a new biological pathway that is a principal driver of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and related conditions, and which can be targeted using existing drugs.
About 5% of the world’s population, and one in ten people in the UK1, are currently affected by an autoimmune disease, such as IBD, the umbrella term for Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. These diseases are also becoming more common, with over half a million people living with IBD in the UK as of 2022, nearly double the 300,000 previously estimated2.
Despite increasing prevalence, current treatments do not ...
Cooperative proteins help the immune system identify and attack invaders
2024-06-05
LA JOLLA (June 5, 2024)—Bacteria, parasites, viruses—the immune system tackles them all. At the front line of the human immune response are cells called macrophages, which are responsible for correctly identifying intruders and then directing how the entire immune system responds. Researchers at the Salk Institute have now discovered a molecular mechanism that helps macrophages mount a coordinated response tailored to a specific immune challenge.
Activating macrophages requires the work of three versions of a protein complex called SWI/SNF: cBAF, ncBAF, and PBAF. Scientists already knew these variants had slightly different structures, but ...
Why do 1 in 10 Americans get eczema? Is it too much salt?
2024-06-05
Why Do 1 in 10 Americans Get Eczema? Is it Too Much Salt?
UCSF Study finds that changes in daily salt intake may explain eczema flares.
A high sodium diet may increase the risk of eczema, according to researchers at UC San Francisco (UCSF), who found that eating just one extra gram of sodium per day – the amount in a Big Mac – increases the likelihood of flares by 22%.
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic disease that causes dry, itchy skin. It’s one of ...
[1] ... [1128]
[1129]
[1130]
[1131]
[1132]
[1133]
[1134]
[1135]
1136
[1137]
[1138]
[1139]
[1140]
[1141]
[1142]
[1143]
[1144]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.