NYU Tandon researchers selected for National Artificial Intelligence Research Resource Pilot to enhance AI vision models
2024-06-17
An NYU Tandon School of Engineering project led by Chinmay Hegde – Associate Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering and the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering – is one of the first 35 initiatives selected for the National Artificial Intelligence Research Resource (NAIRR) Pilot by the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) and Department of Energy, a result of President Biden's Executive Order on the Safe, Secure and Trustworthy Development and Use of AI.
The NAIRR Pilot aims to connect U.S. researchers and educators with the computational power, data resources, ...
Investigating the origins of the crab nebula with NASA's Webb
2024-06-17
A team of scientists used NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope to parse the composition of the Crab Nebula, a supernova remnant located 6,500 light-years away in the constellation Taurus. With the telescope’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument) and NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera), the team gathered data that is helping to clarify the Crab Nebula’s history.
The Crab Nebula is the result of a core-collapse supernova from the death of a massive star. The supernova explosion itself was seen on Earth in 1054 CE and was bright enough to view during the daytime. The much fainter remnant observed today ...
The KIT ligand KITLG promotes portal vein tumor thrombosis by up-regulating COL4A1 through STAT3-SMAD2 signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma
2024-06-17
https://www.scienceopen.com/hosted-document?doi=10.15212/AMM-2023-0049
Announcing a new publication for Acta Materia Medica journal. Portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT), a severe complication of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), markedly influences patient prognosis by fostering a hypercoagulable state. However, its molecular underpinnings remain largely unexplored. This study sheds light on the critical role of the KIT ligand (KITLG) in modulating expression of the collagen gene COL4A1 via the STAT3-SMAD2 signaling pathway, thereby influencing platelet activation and PVTT development. Extensive analysis of PVTT tissue samples, ...
Recent Georgia Tech grad earns ACM Doctoral Dissertation Award for creating devices that look like stickers and can harvest energy from the environment
2024-06-17
ACM, the Association for Computing Machinery, today announced that Nivedita Arora, of Northwestern University is the recipient of the ACM Doctoral Dissertation Award for her dissertation “Sustainable Interactive Wireless Stickers: From Materials to Devices to Applications,” which demonstrated wireless and batteryless sensor nodes using novel materials and radio backscatter.
Arora’s research envisions creating sustainable computational materials that operate by harvesting energy from the environment and, at the end ...
Spinning up hurricane communications
2024-06-17
Forecasters can use images in social media to better communicate weather related hazards of hurricanes, according to a pair of new studies.
Scientists at the U.S. National Science Foundation National Center for Atmospheric Research (NSF NCAR) analyzed 2017 Twitter (now X) data related to two hurricanes – Harvey and Irma. The researchers found that forecast information communicated in the early stages of storm development, when the threat posed by a hurricane is uncertain, sets the stage for how people react to subsequent ...
How the ketogenic diet improves healthspan and memory in aging mice
2024-06-17
The ketogenic diet has its fanatics and detractors among dieters, but either way, the diet has a scientifically documented impact on memory in mice. Whlie uncovering how the high fat, low carbohydrate diet boosts memory in older mice, Buck scientists and a team from the University of Chile identified a new molecular signaling pathway that improves synapse function and helps explain the diet’s benefit on brain health and aging. Published in the June 5, 2024 issue of Cell Reports Medicine, the findings provide new directions for targeting the memory effects on a molecular level, without requiring a ketogenic diet or even the byproducts of it.
“Our ...
Brazilian scientists develop functional bread to help prevent asthma
2024-06-17
Brazilian researchers have developed functional bread with the potential to prevent asthma, a respiratory disorder responsible for some 350,000 hospitalizations per year in the SUS (Sistema Único de Saúde), the nation’s public healthcare network.
The formulation, for which a patent application has been filed in Brazil (BR1020210266465), is described in an article published in the journal Current Developments in Nutrition. It contains Saccharomyces cerevisiae UFMG A-905, ...
Potential new treatment option for diabetic retinopathy
2024-06-17
Potential New Treatment Option for Diabetic Retinopathy
OU researcher developing potential new treatment for diabetic retinopathy that could address the problem much earlier.
OKLAHOMA CITY, OKLA. – Patients with diabetes face a host of potential health problems as they work to manage the chronic disease. Still, one concern that seems to weigh heavily is the risk of losing their sight through a condition known as diabetic retinopathy.
Researchers at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences and Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK) Cancer Center are studying a new, revolutionary treatment for diabetic retinopathy that could change the prognosis ...
Paternal use of metformin during sperm production not associated with major birth defects
2024-06-17
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 17 June 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not ...
American diets have a long way to go to achieve health equity
2024-06-17
Poor diet continues to take a toll on American adults. It’s a major risk factor for obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain cancers, and more than one million Americans die every year from diet-related diseases, according to the Food and Drug Administration. Poor diet and food insecurity is also costly, attributing to an estimated $1.1 trillion in healthcare expenditures and lost productivity. These burdens also contribute to major health disparities by income, education, zip code, race, and ethnicity.
In a study from the Food is Medicine Institute at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University published today in ...
New ‘aging atlas’ provides a detailed map of how cells and tissues age
2024-06-17
A new aging atlas gives scientists an in-depth view of how individual cells and tissues in worms age and how different lifespan-extending strategies might stop the clock.
Aging impacts all the tissues in our body – from our muscles to our skin. Figuring out how individual tissues and cells age could help researchers better understand the aging process and aid in the development of anti-aging treatments.
Due to their short lifespans, simple body plans, and genetic similarity to humans, many researchers study aging in roundworms. To look at aging at the level of tissues and cells, a team of researchers from HHMI's Janelia ...
New technology allows researchers to precisely, flexibly modulate brain
2024-06-17
By Beth Miller
Human brain diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease, involve damage in more than one region of the brain, requiring technology that could precisely and flexibly address all affected regions simultaneously. Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have developed a noninvasive technology combining a holographic acoustic device with genetic engineering that allows them to precisely target affected neurons in the brain, creating the potential to precisely modulate selected cell ...
Origins of cumulative culture in human evolution
2024-06-17
Each of us individually is the accumulated product of thousands of generations that have come before us in an unbroken line. Our culture and technology today are also the result of thousands of years of accumulated and remixed cultural knowledge.
But when did our earliest ancestors begin to make connections and start to build on the knowledge of others, setting us apart from other primates? Cumulative culture — the accumulation of technological modifications and improvements over generations — allowed humans to adapt to a diversity of environments and challenges. But, it is unclear when cumulative culture first developed during hominin evolution.
A study published ...
Mitophagy and cancer: BNIP3/BNIP3L’s role in stemness, ATP production, proliferation, and cell migration
2024-06-17
“[...] our current work has provided a novel strategy to enrich for a sub-population of cancer cells, with high basal levels of mitophagy.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 17, 2024 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 11, entitled, “Mitophagy and cancer: role of BNIP3/BNIP3L as energetic drivers of stemness features, ATP production, proliferation, and cell migration.”
Mitophagy is a selective form of autophagy which permits ...
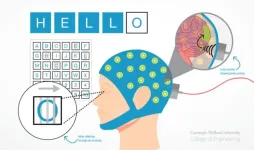
Breakthrough approach enables bidirectional BCI functionality
2024-06-17
Brain-computer interfaces or BCIs hold immense potential for individuals with a wide range of neurological conditions, but the road to implementation is long and nuanced for both the invasive and noninvasive versions of the technology. Bin He of Carnegie Mellon University is highly driven to improve noninvasive BCIs, and his lab uses an innovative electroencephalogram (EEG) wearable to push the boundaries of what’s possible. For the first time on record, the group successfully integrated a novel focused ultrasound stimulation to realize bidirectional BCI that both encodes and decodes brain waves using machine learning in a study with 25 human subjects. This work opens ...
Polarization and risk perception could play important roles in climate-policy outcomes
2024-06-17
Times of crises often call for strong and rapid action, but in polarized societies, strong top-down policies can backfire.
In a paper published on June 17, 2024, in Environmental Research Letters, SFI Applied Complexity Fellow Saverio Perri, SFI Science Board Fellow Simon Levin (Princeton University), and colleagues present a conceptual model of how these dynamics could play out in efforts to decarbonize our energy supply. The model illustrates the complex interplay between strong policies, people’s perception of risk, and the amount of polarization in a society. They show that in situations where the perception of risk is low — where the ...
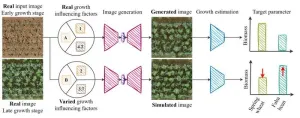
AI shows how field crops develop
2024-06-17
Researchers at the University of Bonn have developed software that can simulate the growth of field crops. To do this, they fed thousands of photos from field experiments into a learning algorithm. This enabled the algorithm to learn how to visualize the future development of cultivated plants based on a single initial image. Using the images created during this process, parameters such as leaf area or yield can be estimated accurately. The results have been published in the journal Plant Methods.
Which plants should I combine ...
African research funders in global spotlight through Dimensions indexing project
2024-06-17
African research is receiving a major visibility boost with the indexing of 10 national funders in Dimensions, the world’s largest linked research database.
This project is a collaboration with Digital Science, the Africa PID Alliance (APA), the Association of African Universities (AAU), the Training Centre in Communication (TCC Africa), and the Research Organization Registry (ROR).
“This project connects the research outputs from leading African funding bodies to the global research ecosystem,” said Joy Owango, Executive Director of TCC Africa ...
New study suggests cancer drug could be used to target protein connection that spurs Parkinson’s disease
2024-06-17
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
In studies with genetically engineered mice, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say they have identified a potentially new biological target involving Aplp1, a cell surface protein that drives the spread of Parkinson’s disease-causing alpha-synuclein.
The findings, published May 31 in Nature Communications, reveal how Aplp1 connects with Lag3, another cell surface receptor, in a key part of a process that helps spread harmful alpha-synuclein proteins to brain cells. Those protein buildups are hallmarks of Parkinson’s disease.
Notably, the researchers say, Lag3 is already the target of a combination ...
More than 1 in 10 patients at FQHCs experience major social risk factors
2024-06-17
A first-of-its-kind study found high rates of food insecurity, housing insecurity, financial strain, and/or a lack of transportation among patients at federally qualified health centers, particularly patients who were low-income or from racial/ethnic minority populations.
Federally qualified health centers (FQHCs) offer primary care services to 1 in 11 Americans, the majority of whom are low-income and/or underinsured and may not otherwise receive this care. While prior research has shown that 70 percent of FQHCs screen for social ...
Artificial intelligence accurately screens heart failure patients for clinical trial eligibility
2024-06-17
Generative Artificial Intelligence (Gen AI) can rapidly and accurately screen patients for clinical trial eligibility, according to a new study from Mass General Brigham researchers. Such technology could make it faster and cheaper to evaluate new treatments and, ultimately, help bring successful ones to patients.
Investigators assessed the accuracy and cost of a Gen AI process they named RAG-Enabled Clinical Trial Infrastructure for Inclusion Exclusion Review (RECTIFIER), that identifies patients who meet criteria for enrollment in ...
Unlocking the mystery behind the performance decline in a promising cathode material
2024-06-17
The first generation of lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles has been a remarkable success story. Yet, the question arises: What changes to battery materials will spur further advances to extend driving range and lower costs?
A better positive electrode, or cathode, for lithium-ion batteries has been the focus of intense past research. The cathode is one of the main components in batteries. Several candidates for cathode materials offer the prospect of batteries with much higher energy storage, leading to longer driving range. However, the capacity, or amount of current flowing out within a given time, tends to decline rapidly with charge-discharge cycling for reasons ...
A call for renaming clinical research partnerships
2024-06-17
PHILADELPHIA (June 17, 2024) - In a recently published opinion piece in BMJ Open, “Rhetoric of Research: A Call for Renaming the Clinical Research Partnership,” authors from Penn Nursing and Georgetown University School of Nursing, present a compelling argument for rethinking the language used to describe participants in clinical research. The opinion calls for a shift from the traditional term “patient participant” to “participant partner,” emphasizing the crucial role of participants in ...
SwRI breaks ground on new hypersonic engine research facility
2024-06-17
SAN ANTONIO — June 17, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) today celebrated the groundbreaking of the Center for Accelerating Materials and Processes (CAMP), a new facility that will support research and development for tomorrow’s high-speed aerospace engines.
“This project will help ensure the U.S. is a leader in high-speed propulsion research and development,” said Dr. Barron Bichon, director of SwRI’s Materials Engineering Department. “SwRI is committed to advancing this vital technology on behalf of Texas and the nation.”
Market forces including growth in global defense, air travel, ...
International Gemini Observatory and Subaru combine forces to discover first ever pair of merging quasars at cosmic dawn
2024-06-17
Since the very first instant after the Big Bang the Universe has been expanding. This means that the early Universe was considerably smaller and early-formed galaxies were more likely to interact and merge. Galaxy mergers fuel the formation of quasars — extremely luminous galactic cores where gas and dust falling into a central supermassive black hole emit enormous amounts of light. So when looking back at the early Universe astronomers would expect to find numerous pairs of quasars in close proximity to each other as their host galaxies undergo mergers. However, they have been surprised ...
[1] ... [1108]
[1109]
[1110]
[1111]
[1112]
[1113]
[1114]
[1115]
1116
[1117]
[1118]
[1119]
[1120]
[1121]
[1122]
[1123]
[1124]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.