Investigating the causes of fetal growth disorders
2024-06-18
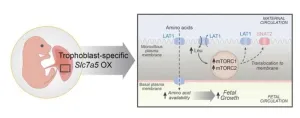
Common complications of pregnancy affecting fetal size may be caused by irregularities in the transport of amino acids across the placenta—a finding with therapeutic implications. Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) and fetal overgrowth affect 15-20% of pregnancies worldwide. Abnormal fetal growth is strongly linked to the development of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease in later life. Placental transport of essential amino acids is decreased in human IUGR and increased in fetal overgrowth, but whether this was a cause or consequence was unclear. Fredrick Rosario-Joseph and colleagues created a line of mice ...
Enzymes instead of cyanide: Researchers develop biocatalytic process for nitrile production
2024-06-18
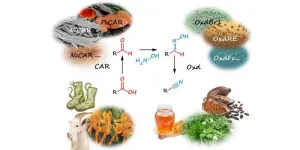
If the household cleaner emits a lemon-like odour, this may be due to a nitrile called citronellyl nitrile. These versatile chemical nitrile groups are also used in the manufacture of active pharmaceutical ingredients, superglue and chemical-resistant gloves. The prevalent production process used so far has required a chemical reaction of certain molecules with highly toxic cyanide. Margit Winkler from the Institute of Molecular Biotechnology at TU Graz, together with Ludmila Martínková from the Institute of Microbiology at the Czech Academy of Sciences, ...
New study reveals promising drug target for treating osteoporosis
2024-06-18
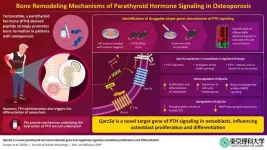
Osteoporosis is a skeletal condition that leads to the weakening of bones, making them porous, fragile, and prone to breakage. A whopping 8.9 million fractures are caused by osteoporosis annually, with one fracture occurring every three seconds! The aging population is the most vulnerable to primary osteoporosis, given, their frailty, and often, requires long-term therapy and support. Advances in healthcare and the corresponding rise in the aging population have put a strain on available resources, underscoring the need for effective therapies against osteoporosis.
Induction of parathyroid hormone (PTH) signaling using the PTH-derived ...
Breakthrough may clear major hurdle for quantum computers
2024-06-18
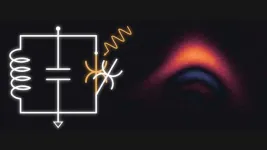
The potential of quantum computers is currently thwarted by a trade-off problem. Quantum systems that can carry out complex operations are less tolerant to errors and noise, while systems that are more protected against noise are harder and slower to compute with. Now a research team from Chalmers University of Technology, in Sweden, has created a unique system that combats the dilemma, thus paving the way for longer computation time and more robust quantum computers.
For the impact of quantum computers to be realised in society, quantum researchers first need to deal with some major obstacles. So far, errors and noise stemming from, for example, ...
Authority's physical proximity means greater obedience. New look at results of famous experiment
2024-06-18
Who should be spared pain, hurt or disappointment, and who should be harmed? This internal dilemma accompanied the participants of the Milgram experiment, say experts from SWPS University. They have revisited the causes of obedience in that famous study and showed that the experimenter's physical proximity promote subjects' obedience, while the learner's physical proximity decreases it.
American social psychologist Stanley Milgram's demonstration of the human tendency to show extreme obedience to authority was one of the most ...
Large wildfires create weather that favors more fire
2024-06-18
A new UC Riverside study shows soot from large wildfires in California traps sunlight, making days warmer and drier than they ought to be.
Many studies look at the effect of climate change on wildfires. However, this study sought to understand the reverse — whether large fires are also changing the climate.
“I wanted to learn how the weather is affected by aerosols emitted by wildfires as they’re burning,” said lead study author and UCR doctoral candidate James Gomez.
To find his answers, Gomez analyzed peak fire days and ...
Election administration performance linked to counties’ economic, racial makeup
2024-06-18
PULLMAN, Wash. – Voters who are neither wealthy nor white are more likely to live in counties with fewer resources available to make sure ballots are counted on time, a new election index revealed.
Researchers developed the County Election Administration index, detailed in the Election Law Journal, to evaluate election performance by county rather than just by state. Election administration encompasses the policies and processes that ensure election access, integrity and accuracy. Despite voter fraud claims in the last presidential election, researchers found that overall election performance ...
Blood markers detect rare forms of dementia as well as the neurological diseases ALS and PSP
2024-06-18
In a study with 991 adults, scientists at DZNE show that the most common forms of frontotemporal dementia (FTD) as well as the neurological diseases amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) can be recognised by blood testing. Their procedure is not yet ready for routine medical use, but in the long term it could facilitate disease diagnosis and advance the development of new therapies already now. The findings published in the journal “Nature Medicine” are based ...
Restored rat-free islands could support hundreds of thousands more breeding seabirds
2024-06-18
Hundreds of thousands more breeding pairs of seabirds could return to remote island archipelagos if invasive rats were removed and native vegetation restored – a new paper finds.
In a first of its kind study, researchers also calculated that there are enough fish in the seas surrounding the remote tropical islands that were the focus of the research within hunting range of seabirds to support these restored populations.
This is an important factor that has not been considered in previous island restoration studies and could become ...
University of the Witwatersrand chooses Figshare to support its open data goals
2024-06-18
Figshare, a leading provider of institutional repository infrastructure that supports open research, is pleased to announce that the University of the Witwatersrand Library has chosen Figshare to support its research community with archiving, publishing, sharing and promoting their datasets.
The University of the Witwatersrand (Wits) – a leading research institution in South Africa based in Johannesburg, ranked as the second best university in Africa 2024 (jointly with Stellenbosch University) – will ...
Cancer survivors are at increased risk of disease throughout life
2024-06-18
Swedish researchers have surveyed all people under the age of 25 who have had cancer since 1958. The study, led by researchers at Linköping University and Region Östergötland, shows that cancer survivors are at greater risk for cardiovascular diseases, other cancers and other diagnoses later in life. In addition, the researchers saw that socioeconomic factors played a role in survival.
Since 1958, Sweden has registered all cancer patients in the National Cancer Register. Swedish researchers have now used this register to study all cancer survivors who had cancer as a child, adolescent or adult to examine outcomes in later life. The results have been published ...
Fishy parenting? Punishing offspring encourages cooperation
2024-06-18
Osaka, Japan — While there is an increasing consensus among humans that corporal discipline of children does more harm than good, fish may disagree.
Ryo Hidaka, Shumpei Sogawa, Masanori Kohda and Satoshi Awata from Osaka Metropolitan University have demonstrated that a fish species employs physical punishment to elicit helping efforts from their offspring, indicating advanced social and cognitive skills previously thought to be unique to higher vertebrates.
The results of their study were published online in Animal Behaviour on April 6.
For millennia, human societies have used punishment ...
Rethinking English essay scores: The argument for argument over grammar
2024-06-18
To get high scores at essay writing tests, learners of English as a foreign language need to focus on good arguments more than on complex grammar. The Kobe University finding challenges conventional approaches to test preparation and scoring rubrics.
Writing essays is a well-established tool for monitoring progress in learning English as a foreign language, as it provides a snapshot of a student’s mastery of grammar and vocabulary. Especially in Japan, where English language tests are often required for university admission and students closely follow advice on how to achieve high scores on these tests, a “good essay” is often seen as one that demonstrates ...
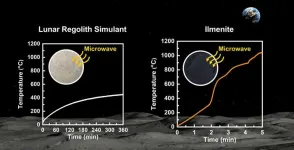
Laying the foundation for lunar base construction; elucidating lunar soil-microwave interactions
2024-06-18
The United States’ NASA aims to construct a lunar base through the Artemis program, a manned lunar exploration initiative. However, the practical reality of what general public envision for the space base differs somewhat from well-known science fiction movies. To build a base on the Moon using abundant and diverse construction materials, significant transportation costs are involved. All these materials must be launched from Earth using rockets.
Because transporting construction materials from Earth to the ...
Surge in fatal opioid overdoses in Ontario shelters, report finds
2024-06-18
Researchers from the Ontario Drug Policy Research Network (ODPRN) at St. Michael’s Hospital and Public Health Ontario analyzed health data from the Office of the Chief Coroner of Ontario and ICES, and found that there were 210 accidental opioid-related toxicity deaths within shelters between January 2018 to May 2022, with the number of deaths more than tripling during the study period (48 before the pandemic versus 162 during the pandemic).
Statistics Canada data shows that the annual number of emergency beds in Ontario grew by only 15% (6,764 to 7,767) between 2018 and 2022.
“People who use Ontario’s shelter system are not only facing housing instability, but ...
Teachers report worse pay and well-being compared to similar working population
2024-06-18
With more working hours and lower average base pay, the well-being of U.S. teachers continues to be worse than that of similar working adults – a consistent pattern since 2021, according to a new RAND survey.
Managing student behavior, low salary and administrative work outside of teaching were the top-ranked sources of stress for teachers in 2024. Teachers reported working an average of 53 hours per week; 15 of these hours – or roughly one quarter of their working hours – were outside of their contracts. This compares to 44 hours per week for similar working adults. Only 36% of teachers said their base pay was adequate compared with 51% of similar ...
Study proposes novel hypothesis to explain occupation of Brazil’s southern coast 2,000 years ago
2024-06-18
An important chapter of the history of human occupation on the coast of Brazil is being rewritten by Brazilian researchers affiliated with the University of São Paulo’s Museum of Archeology and Ethnology (MAE-USP) and supported by FAPESP.
In an article published in the journal PLOS ONE, the group, which also includes researchers in Santa Catarina state, South Brazil, and in other countries (the United States, Belgium and France), shows that the sambaqui builders of Galheta IV, an archeological ...
The declining diet of Japan’s youth
2024-06-18
Researchers from the University of Tokyo performed the first study to quantify highly processed food consumption and to investigate its association with diet quality among Japanese children and adolescents. Highly processed foods (HPFs) accounted for over one-fourth of the total energy intake amongst youths. Consumption was negatively associated with the intake of healthy foods, such as fruits, vegetables and pulses, and positively associated with the consumption of confectioneries.
It's common knowledge that poor-quality diets are considered major risk factors for many health issues and even noncommunicable ...
How targeted nutrients can fight cancer
2024-06-18
An international research team has discovered a new way to effectively treat cancer, by using nutrients to reactivate suppressed metabolic pathways in cancer cells.
The researchers used a common amino acid, tyrosine, packaged as a nanomedicine, to change the metabolism of melanoma, a deadly skin cancer, and prevent cancer growth.
Australia has the highest rate of skin cancer in the world. This new approach could be combined with current therapies to better treat melanoma. The technique also has the potential to treat other types of cancer.
The study, Nutrient-delivery and metabolism reactivation therapy for melanoma, was led by Professor Wenbo ...
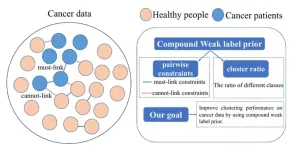
Constrained clustering with weak label prior
2024-06-18
Clustering is widely exploited in data mining. It has been proved that embedding weak label prior into clustering is effective to promote its performance. Previous researches mainly focus on only one type of prior. However, in many real scenarios, two kinds of weak label prior information, e.g., pairwise constraints and cluster ratio, are easily obtained or already available. How to incorporate them to improve clustering performance is important but rarely studied.
To deal with this problem, a research team led by Chenping ...
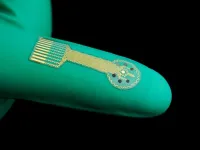
New “smart bandages” hold potential for revolutionizing the treatment of chronic wounds
2024-06-18
Chronic wounds, which include diabetic ulcers, surgical wounds, pressure injuries, and other problems, are deadlier than many people realize. Patients with chronic wounds have a five-year survival rate around 70%, worse than that of breast cancer, prostate cancer and other serious diseases. Treating wounds is also expensive, costing an estimated $28 billion each year in the U.S. alone.
A team of researchers from the Keck School of Medicine of USC and the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) is developing a series of cutting-edge technologies to revolutionize wound care, including smart bandages that would automatically sense and ...
Rapid test of cerebrospinal fluid decreases time to diagnosis for brain tumors
2024-06-18
A test that looks for genetic hallmarks of brain cancers in samples of cerebrospinal fluid can decrease the time to diagnosis and eliminate the need for invasive brain biopsies for some patients. Mass General Brigham experts in neurosurgery, cancer and pathology worked together to develop a rapid, genotyping test that can detect key mutations associated with brain cancers from samples taken during a lumbar puncture. The team evaluated the technique known as TetRS (Targeted Rapid Sequencing) among 70 patients admitted to Massachusetts General Hospital with new central nervous system ...
Cyberbullying and sexual harassment rampant in esports
2024-06-18
It’s one of the fastest growing industries globally, raking in millions for the best players and attracting a huge fanbase, but a new Australian study has revealed the dark side of professional video gaming: cyberbullying and sexual harassment.
Even though the esports industry is a diverse community, cyberbullying is rampant in this virtual world, and cis-gendered and trans-gendered women players are disproportionately more likely to be sexually harassed than men.
Despite women making up 46% of the world’s three billion video gamer players, according to a new paper published in Entertainment Computing, women who play professionally (16% of esports competitors ...
New study shows mechanisms of Hagfish burrowing into deep sea sediment
2024-06-18
Scientists at the Schmid College of Science and Technology at Chapman University developed a novel way to observe the elusive burrowing behavior of hagfish. Dr. Douglas S Fudge and his team created a specialized tank of transparent gelatin in order to visualize how the hagfish behave and locomote within sediments.
Hagfishes are bottom-dwelling marine animals that are capable of producing startling amounts of defensive slime when they are provoked. Understanding the burrowing activities of hagfishes could lead to increased knowledge of sediment turnover in marine benthic habitats, new insights into the reproductive behavior of hagfishes or ...
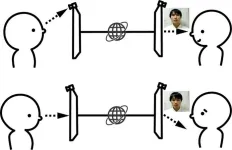
Study suggests at-camera gaze can increase scores in simulated interviews
2024-06-18
Eye-contact has a significant impact on interpersonal evaluation, and online job interviews are no exception. In addition to the quality of a resume, the direction of the interviewee’s gaze might help (or hinder) their chances of securing the job.
Researchers published their results in Scientific Reports on May 31.
The study simulated online job interviews. Twelve students who participated in the study as a role of interviewees presented themselves twice, once looking directly at a web camera, and the other looking towards the screen. ...
[1] ... [1107]
[1108]
[1109]
[1110]
[1111]
[1112]
[1113]
[1114]
1115
[1116]
[1117]
[1118]
[1119]
[1120]
[1121]
[1122]
[1123]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.