International collaboration enabled participatory stock assessment on glass eel fisheries in West Java, Indonesia
2024-03-29
Joint Press Release with IPB University, WWF Indonesia, and WWF Japan
<Summary Text>
Appropriate fishery management requires an understanding of the target species' stock dynamics. However, in the Northern Hemisphere, illegal trade and IUU (Illegal, Unreported, and Unregulated) fisheries make the assessment of recruiting glass eels extremely difficult. Contrary, we have successfully collected sufficient data on glass eel fisheries for detailed statistical analysis based on a community-based participatory assessment. This study was conducted by NGOs, experts, and a broad range of stakeholders ...
Enhanced melanoma vaccine offers improved survival for men
2024-03-29
A second-generation melanoma vaccine being developed at UVA Cancer Center improves long-term survival for melanoma patients compared with the first-generation vaccine, new research shows. Interestingly, the benefit of the second-generation vaccine was greater for male patients than female patients. That finding could have important implications for other cancer vaccines, the researchers say.
The vaccine developers, led by Craig L. Slingluff Jr., MD, found that they could enhance the effectiveness of their melanoma vaccine by simultaneously stimulating important immune cells known as “helper ...
Nearly one-third of patients with TBI have marginal or inadequate health literacy
2024-03-29
Waltham — March 26, 2024 — Low health literacy is a problem for a substantial proportion of people with moderate to severe traumatic brain injury (TBI), according to research published in The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation (JHTR). The official journal of the Brain Injury Association of America, JHTR is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
Angelle M. Sander, PhD, FACRM, Professor in the H. Ben Taub Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation at Baylor College of Medicine and Director of TIRR Memorial Hermann’s Brain Injury Research Center, ...
Genetic causes of cerebral palsy uncovered through whole-genome sequencing
2024-03-29
A Canadian-led study has identified genes which may be partially responsible for the development of cerebral palsy.
Cerebral palsy (CP), a condition that affects the development of motor skills in children, is the most common childhood-onset physical disability. CP can have different causes, such as infections, injuries, or lack of oxygen before or during birth, but the genetic contributors to CP have remained largely unknown.
Novel research from scientists at The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids), the Research Institute of the McGill University ...
Modesty and boastfulness – perception depends on usual performance
2024-03-29
When people present themselves as capable or humble, the way this influences other people’s evaluations of one’s true ability and character depends on one’s usual performance. Kobe University and University of Sussex researchers thus add an important factor in our understanding of how the relationship between self-presentation and perception develops with age.
People want to be liked. Amongst the many ways of achieving this, making statements about oneself to manipulate other people’s evaluation is called “self-presentation.” Both the ability to do so and the effect this has on others’ evaluation of one’s ability ...
Do sweeteners increase your appetite? New evidence from randomised controlled trial says no
2024-03-29
University of Leeds news
Embargo: Thursday 28 March 2024, 23:30 UK time
Do sweeteners increase your appetite? New evidence from randomised controlled trial says no
Replacing sugar with artificial and natural sweeteners in foods does not make people hungrier – and also helps to reduce blood sugar levels, a significant new study has found.
The double blind randomised controlled trial found that consuming food containing sweeteners produced a similar reduction in appetite sensations and appetite-related hormone responses ...
Women with obesity do not need to gain weight during pregnancy, new study suggests
2024-03-29
The guidelines for weight gain during pregnancy in obese women have long been questioned. New research from Karolinska Institutet supports the idea of lowering or removing the current recommendation of a weight gain of at least 5 kg. The results are published in The Lancet.
International guidelines from the US Institute of Medicine (IOM) state that women with obesity should gain a total of 5 to 9 kg during pregnancy, compared to 11.5 to 16 kg for normal-weight women. The guidelines have long been questioned, but there has been no evidence to warrant a re-examination.
A new study from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden now shows that there are no increased health risks for either the mother or ...
Individuals with multiple sclerosis face substantially greater risk of hospitalisation and death from COVID-19, despite high rates of vaccination
2024-03-28
Authors say the findings underscore the urgent need for preventive measures for people with MS who are inadequately protected by COVID-19 vaccination alone.
*Please mention the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2024, Barcelona, 27-30 April) if using this material*
New real-world research being presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2024) in Barcelona, Spain (27-30 April) reveals that people living with multiple sclerosis (MS) face a much higher ...
Study shows obesity in childhood associated with a more than doubling of risk of developing multiple sclerosis in early adulthood
2024-03-28
New research to be presented at this year’s European Congress on Obesity in Venice, Italy (12-15 May) shows that having obesity in childhood is associated with a more than doubling of the risk of later developing multiple sclerosis. The study is by Professor Claude Marcus and Associate Professor Emilia Hagman, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, and colleagues.
Emerging evidence implies a link between high BMI in adolescence and an increased risk of Multiple Sclerosis (MS). Yet, most studies evaluating this association are cross-sectional, have retrospective design with self-reported data, have used solely genetic correlations, or use paediatric ...
Rice Emerging Scholars Program receives $2.5M NSF grant to boost STEM education
2024-03-28
Rice University’s Emerging Scholars Program (RESP) has received a five-year, $2.5 million grant from the National Science Foundation. The funding aims to bolster achievements in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) among students from under-resourced families and communities.
The grant will enable RESP to expand its reach and impact, offering increased support to its scholars via summer tuition scholarships, housing subsidies and research stipends. The number of scholars in the program will increase from 40 to 50 in Summer 2024 and to 60 in Summer 2025.
“Rice ...
Virtual rehabilitation provides benefits for stroke recovery
2024-03-28
A stroke often impacts a person’s ability to move their lower body from the hips down to the feet.
This leads to diminished quality of life and mental health in addition to increased susceptibility to falls. But now, UBC Okanagan researchers are exploring new treatment methods to help bridge the service delivery gap, and recovery outcomes, for patients after a stroke.
“Shortened length of inpatient stays and continued challenges in transitioning back to the community—including poor access to continued stroke rehabilitation services—have resulted in substantial unmet recovery needs,” ...
Generative AI develops potential new drugs for antibiotic-resistant bacteria
2024-03-28
With nearly 5 million deaths linked to antibiotic resistance globally every year, new ways to combat resistant bacterial strains are urgently needed.
Researchers at Stanford Medicine and McMaster University are tackling this problem with generative artificial intelligence. A new model, dubbed SyntheMol (for synthesizing molecules), created structures and chemical recipes for six novel drugs aimed at killing resistant strains of Acinetobacter baumannii, one of the leading pathogens responsible for antibacterial resistance-related deaths.
The researchers described their model and experimental validation of these new compounds in a study published March 22 in the journal ...
Biofuels could help island nations survive a global catastrophe, study suggests
2024-03-28
A major global catastrophe could disrupt trade in liquid fuels used to sustain industrial agriculture, impacting the food supply of island nations like New Zealand that depend on oil imports.
A new study in the journal Risk Analysis suggests that New Zealand and other island nations dependent on imported fuel can plan for future emergencies by stepping up their production of biofuel from locally grown crops (like canola) and farming more fuel-efficient crops (like wheat and potatoes rather than dairy).
In the event of a major disruption in liquid fuel imports, results showed that New ...
NJIT research team discovering how fluids behave in nanopores with NSF grant
2024-03-28
A research team from New Jersey Institute of Technology is uncovering mysteries surrounding fluids in nanoporous materials, and has been recently awarded a grant from the National Science Foundation (NSF) to support this research.
The research is focused on the elasticity, or compressibility, of fluids in these nanopores. Understanding the elastic properties of fluids has significant implications across multiple disciplines. Engineering applications, geological exploration, materials science and environmental studies ...
New study shows association of historical housing discrimination and shortfalls in colon cancer treatment
2024-03-28
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – A nationwide study of 196 cities shows that housing discrimination from 90 years ago still casts a historical shadow of inequities in colon cancer care today, S.M. Qasim Hussaini, M.D., of the University of Alabama at Birmingham and colleagues at the American Cancer Society and Johns Hopkins School of Public Health report in the journal JCO Oncology Practice.
In the 1930s, the federally sponsored Home Owners’ Loan Corporation, or HOLC, used racial composition to map out residential areas worthy of receiving mortgage loans and those areas to avoid. Neighborhoods ...
Social media use may help to empower plastic surgery patients
2024-03-28
Waltham — March 28, 2024 — For patients considering or undergoing plastic and reconstructive surgery (PRS) procedures, using social media to gather information and answer questions can enhance patient empowerment – potentially leading to increased autonomy and better decision-making, reports a study in the April issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Our study suggests that connecting to social media is associated with meaningful increases in empowerment for PRS patients, ...
Q&A: How to train AI when you don't have enough data
2024-03-28
Artificial intelligence excels at sorting through information and detecting patterns or trends. But these machine learning algorithms need to be trained with large amounts of data first.
As researchers explore potential applications for AI, they have found scenarios where AI could be really useful — such as analyzing X-ray image data to look for evidence of rare conditions or detecting a rare fish species caught on a commercial fishing boat — but there's not enough data to accurately train the algorithms.
Jenq-Neng Hwang, University of Washington professor of electrical and computer and engineering, specializes in these issues. ...
Wayne State University researchers uncover potential treatment targets for Zika virus-related eye abnormalities
2024-03-28
DETROIT - A groundbreaking study published in the journal iScience presents crucial insights into the ocular effects of Zika virus infection during pregnancy and offers promising avenues for therapeutic intervention.
Produced by a team of researchers in the Department of Ophthalmology, Visual and Anatomical Sciences at the Wayne State University School of Medicine, the paper, “Targeting ABCG1 and SREBP-2 mediated cholesterol homeostasis ameliorates Zika virus-induced ocular pathology,” provides compelling evidence of the ...
Discovering Van Gogh in the wild: scientists unveil a new gecko species
2024-03-28
You’ve probably seen nature depicted in art, but how often do you see an artwork hiding in nature?
When they saw the back of a lizard in the Southern Western Ghats, a group of scientists from the Thackeray Wildlife Foundation in India were reminded of Van Gogh’s The Starry Night. As soon as they figured out it was a new species, it was only apt to name it in honour of the famous painter.
“Cnemaspis vangoghi is named for Dutch painter Vincent Van Gogh (1853–1890) as the striking colouration of the new species is reminiscent of one of his most iconic paintings, The ...
Small birds spice up the already diverse diet of spotted hyenas in Namibia
2024-03-28
Hyenas are generalist predators (and scavengers) with a broad range of prey species. They are known for hunting (or scavenging) larger mammals such as antelopes and occasionally feed on smaller mammals and reptiles. Being flexible in the choice of prey is a strategy of generalists – and this even extends to small passerine birds, as scientists from the Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (Leibniz-IZW) and the University of Ljubljana observed in Namibia: Spotted hyenas pursued red-billed queleas, picked them from the ground or the surface of a waterhole and swallowed them whole, at a success rate of approximately one bird every three minutes. These observations were described ...
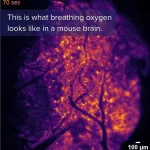
Imaging detects transient “hypoxic pockets” in the mouse brain
2024-03-28
Using a bioluminescent oxygen indicator, Felix Beinlich and colleagues discovered a spontaneous, spatially defined occurrence of “hypoxic pockets” in the mouse brain. Their technique offers a way to learn more about brain oxygen tension (pO2), a measure of oxygen delivery and demand in brain tissue that changes dynamically but is not well understood. The findings could have implications for how rest and exercise affect pO2 in the human brain, including the role of these activities in conditions such as dementia, Beinlich et al. suggest. The researchers used a genetically encoded bioluminescent oxygen indicator called Green NanoLuc in mouse cortical astrocytes to ...
Dissolved organic matter could be used to track and improve the health of freshwaters
2024-03-28
The dissolved organic matter (DOM) from hundreds of plant and animal remains could be used to track and possibly restore the health of freshwater bodies, Andrew J. Tanentzap and Jérémy A. Fonvielle write in this Perspective. The broad range of compounds, or chemodiversity, of DOM has multiple effects in freshwaters, including providing nutrients to support food web productivity, reducing or enhancing contamination from pollutants, and influencing the metabolism of microorganisms important to the biogeochemical cycle. DOM may also reduce the heat that ...
Indoor air quality standards in public buildings would boost health and economy, say international experts
2024-03-28
There should be mandatory indoor air quality standards, say an international group of experts led by Professor Lidia Morawska.
Professor Morawska, Vice-Chancellor Fellow at the University of Surrey and Distinguished Professor at Queensland University of Technology, led the appeal to the World Health Organization to recognise the airborne transmission of the virus which causes COVID-19 early in the pandemic – and help minimise it.
Now, in a paper published by the prestigious journal Science, Professor Morawska's international team recommends setting standards for ventilation rate and three key indoor pollutants: carbon ...
Positive associations between premenstrual disorders and perinatal depression
2024-03-28
Women affected by premenstrual disorders have a higher risk of perinatal depression compared with those who do not, according to research published March 28th in the open access journal PLOS Medicine. The relationship works both ways: those with perinatal depression are also more likely to develop premenstrual disorders after pregnancy and childbirth. This study suggests that a common mechanism might contribute to the two conditions.
Menstruating women experience cyclical hormone fluctuations through puberty, menstrual cycle, pregnancy ...
New imaging method illuminates oxygen's journey in the brain
2024-03-28
The human brain consumes vast amounts of energy, which is almost exclusively generated from a form of metabolism that requires oxygen. Consequently, the efficient and timely allocation and delivery of oxygen is critical to healthy brain function, however, the precise mechanics of this process have largely remained hidden from scientists.
A new bioluminescence imaging technique, described today in the journal Science, has created highly detailed, and visually striking, images of the movement ...
[1] ... [1272]
[1273]
[1274]
[1275]
[1276]
[1277]
[1278]
[1279]
1280
[1281]
[1282]
[1283]
[1284]
[1285]
[1286]
[1287]
[1288]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.