Sandia pumps $140B into the economy through technology development
2024-04-03
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — To say that the technology and products Sandia National Laboratories researchers have helped imagine, innovate and industrialize have had a massive impact on the country would be an understatement.
Two studies commissioned by Sandia and the National Nuclear Security Administration show Sandia’s work has had an overall economic impact of $140 billion since the year 2000. That’s a significant figure, especially considering it spans just 20 years, less than a third of Sandia’s 75-year existence.
“I am very proud of how Sandia excels in fulfilling its technology transfer mission to deliver economic impact to the U.S.,” ...
Even moderate alcohol usage during pregnancy linked to birth abnormalities, UNM researchers find
2024-04-03
University of New Mexico researchers have found that even low to moderate alcohol use by pregnant patients may contribute to subtle changes in their babies’ prenatal development, including lower birth length and a shorter duration of gestation.
In a new paper published in the journal Alcohol Clinical & Experimental Research, a team led by Ludmila Bakhireva, MD, PhD, MPH, professor and assistant dean for Clinical and Translational Research in the UNM College of Pharmacy, also reported some sex-related differences in the effects of drinking during pregnancy on the developing ...
Sylvester physician co-authors global plan to combat prostate cancer
2024-04-03
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL APRIL 4, 2024, at 6:30 pm EDT) – Annual prostate cancer cases worldwide are projected to double by the year 2040, and annual deaths are projected to increase by 85% to almost 700,000 over the same timeframe – mainly among men in low- and middle-income countries. A commissioned report published online in The Lancet on April 4 highlights the future landscape of prostate cancer and seeks to guide cancer experts worldwide on how to manage the massive influx of prostate cancer patients projected over the next two decades.
Brandon Mahal, M.D., radiation oncologist and ...
Last chance to record archaic Greek language ‘heading for extinction’
2024-04-03
A new data crowdsourcing platform aims to preserve the sound of Romeyka, an endangered millennia-old variety of Greek. Experts consider the language to be a linguistic goldmine and a living bridge to the ancient world.
The initiative, led by Professor Ioanna Sitaridou from the University of Cambridge, contributes to the UN’s International Decade of Indigenous Languages (2022-32), which aims ‘to draw global attention on the critical situation of many indigenous languages and to mobilise stakeholders and resources for their preservation, revitalization and promotion.’
Romeyka is thought to have only a couple of thousand ...
Chicks prove vision and touch linked at birth
2024-04-03
Newly hatched chicks raised in darkness and allowed to touch either a smooth or bumpy cube for 24 hours instantly recognised the object with their vision upon first exposure to light.
This suggests chicks can link touch and vision without any prior experience combining these senses, challenging the long-held belief that such integration requires learning.
The discovery implies a pre-wired ability in the brain for cross-modal perception, potentially redefining our understanding of animal cognition and sensory processing.
In a study published in Biology Letters, researchers at Queen Mary University of London have cracked ...
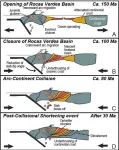
Researchers propose new step in tectonic squeeze that turns seafloor into mountains
2024-04-03
Scientists use tiny minerals called zircons as geologic timekeepers. Often no bigger than a grain of sand, these crystals record chemical signatures of the geological environment where they formed. In a new study led by scientists at The University of Texas at Austin, researchers used them to describe what could be an overlooked step in a fundamental tectonic process that raises seafloors into mountains.
In a study published in the journal Geology, the researchers describe zircons from the Andes mountains of Patagonia. Although the zircons formed when tectonic plates were colliding, they have a chemical signature associated ...
Gut bacteria that strongly influence obesity are different in men and women, study finds
2024-04-03
Novel approach finds gut microbiota that are highly predictive of BMI, waist circumference, and fat mass are different in men and women
And might change the chemical makeup (metabolome) of the gut in ways that affect the metabolism of different bioactive molecules that influence metabolic disease development
Interventions to help prevent obesity-favourable microbiome may need to be different in men and women
*This is an early press release from the European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2024) Venice 12-15 May. Please credit the Congress if using this material*
New research being presented at this year’s European ...
Double trouble: the risks of mixing alcohol and sports wagering
2024-04-02
It turns out that money isn’t the only thing sports gamblers are risking. According to a new study, bettors who wager on sporting events, esports, and daily fantasy sports are much more likely than other individuals to binge drink.
The findings, compiled by a research team from UNLV and the University of New Mexico, were published this week in the journal JAMA Network Open.
Over the course of three weeks in spring 2022, researchers surveyed more than 4,300 adults across the U.S. Nearly 3,300 self-reported past year alcohol use, while about 1,800 identified themselves as gamblers who had bet on sports in the past year.
Researchers ...
Far-UVC light can virtually eliminate airborne virus in an occupied room
2024-04-02
NEW YORK, NY--Far-UVC light is a promising new technology for reducing airborne virus levels in occupied indoor spaces, but its effectiveness has not been evaluated in real-life scenarios.
A new study by Columbia researchers now shows that far-UVC light inactivated nearly all (>99%) of an airborne virus in an occupied work environment, showing that the technology can work as well in a real-life scenario as in the laboratory.
“The results show that far-UVC is highly effective at reducing airborne pathogens in an ordinary occupied room, and so it’s practical to use far-UVC light in indoor areas where people are going about their business,” says David ...
A new estimate of U.S. soil organic carbon to improve Earth system models
2024-04-02
Soil contains about twice as much carbon as the atmosphere and plants combined. It is a major carbon sink, capable of absorbing more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere than it releases. Management of soil carbon is key in efforts to mitigate climate change, in addition to being vital to soil health and agricultural productivity.
Measuring soil carbon, however, is a painstaking, expensive process. Samples must be dug from the ground and sent to a lab for analysis, making upscaling measurements on a large spatial scale ...
Scientists’ urgent call: end destruction and forge a just, sustainable future
2024-04-02
An international team of scientists published a study today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences NEXUS emphasizing the urgent need to align political will, economic resources, and societal values to ensure a more sustainable and equitable world. Led by University of Hawai‘i at Mānoa researchers, the 18 authors combine their expertise in earth and ocean sciences, politics, law, public health, renewable energy, geography, communications, and ethnic studies to assess causes, impacts, and solutions to a multitude of worldwide crises.
“Climate change, ecological destruction, disease, pollution, and socio-economic inequality ...
First results from BREAD experiment demonstrate a new approach to searching for dark matter
2024-04-02
One of the great mysteries of modern science is dark matter. We know dark matter exists thanks to its effects on other objects in the cosmos, but we have never been able to directly see it. And it’s no minor thing—currently, scientists think it makes up about 85% of all the mass in the universe.
A new experiment by a collaboration led by the University of Chicago and Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, known as the Broadband Reflector Experiment for Axion Detection or BREAD, has released its first results in the search for dark matter in a ...
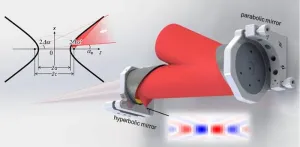
Focusing ultra-intense lasers to a single wavelength
2024-04-02
Ultra-intense ultrashort lasers are powerful tools used in various fields like physics, national security, industry, and healthcare. They help researchers delve into strong-field laser physics, laser-driven radiation sources, particle acceleration, and more.
“Peak power” measures the intensity of these lasers, like the Nova laser (Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, California, USA) with 1.5 petawatts of peak power, the Shanghai Super-intense Ultrafast Laser Facility (SULF, China) with 10 petawatts, or the Extreme Light Infrastructure – Nuclear Physics (ELI-NP, Romania) with a peak ...
Combining food taxes and subsidies can lead to healthier grocery purchases for low-income households
2024-04-02
Chapel Hill, NC, April 2, 2024 — A new study that models the combined effects of a sugar-based tax on beverages and targeted subsidies for minimally processed foods and drinks found that under these policies, low-income consumers would purchase less sugar-sweetened beverages and more fruits, vegetables, and healthier drinks, particularly in households without children.
Researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill developed a model to simulate what would happen if national-level taxes on less-healthy, ...
One in five people with cancer participate in medical research studies
2024-04-02
SEATTLE – April 2, 2024 – Researchers from Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network and peer institutions released new findings in the Journal of Clinical Oncology showing that when all types of cancer research studies are considered, at least one in five people with cancer, or 21.9%, participate in some form of clinical research.
The study evaluated all categories of cancer studies, such as treatment trials, biorepository studies and quality of life studies—the first time an estimate of participation in all types of cancer ...
Sunrise to sunset, new window coating blocks heat — not view
2024-04-02
Windows welcome light into interior spaces, but they also bring in unwanted heat. A new window coating blocks heat-generating ultraviolet and infrared light and lets through visible light, regardless of the sun’s angle. The coating can be incorporated onto existing windows or automobiles and can reduce air-conditioning cooling costs by more than one-third in hot climates.
“The angle between the sunshine and your window is always changing,” said Tengfei Luo, the Dorini Family Professor for Energy Studies at the University of Notre ...
Innovative molecular biology technique allows for discovery of novel targets for candidate vaccines against schistosomiasis
2024-04-02
Researchers in Brazil have used an innovative technique in molecular biology to identify targets for candidate vaccines against Schistosoma mansoni, the parasite that causes schistosomiasis.
Considered one of the world’s 17 neglected tropical diseases (NTDs), schistosomiasis affects some 200 million people in 74 countries, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Six million are estimated to be infected in Brazil, mainly in the Northeast region and Minas Gerais state.
The scientists used phage display, the study of protein interactions using bacteriophages, viruses that infect bacteria, to screen 99.6% of 119,747 DNA sequences encoding the proteins known ...
Study finds Netflix misses the mark by trivializing teenagers’ pain
2024-04-02
UCalgary led study finds Netflix misses the mark by trivializing teenagers’ pain. Findings are published in PainResearchers at the University of Calgary and the University of Bath, U.K., are calling on Netflix to do a better job of representing the kind of pain typically experienced by 12-to-18-year-olds. A new study finds the streaming channel should not emphasize stereotypes, like the heroic, stoic boy and the helpless, emotional girl who requires his rescue and prioritizes his pain and suffering.
“Media ...
TLI investigator Dr. Denise Al Alam receives $1.5 million grant from CIRM to explore genetic defects of lung disease in Down Syndrome
2024-04-02
The Lundquist Institute for Biomedical Innovation at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center (TLI) today announced that The California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM), one of the world’s largest institutions dedicated to regenerative medicine, has
awarded $1.5 million to TLI Investigator Denise Al Alam, PhD, to support research that aims to understand lung disease in individuals with Trisomy 21 (also known as Down Syndrome). Although Trisomy 21 impacts multiple organ systems, respiratory complications are a significant cause of death in children and adults with this genetic condition.
With the highest occurrence of Down Syndrome births in California within the Latinx ...
Increasing positive affect in adolescence could lead to improved health and well-being in adulthood
2024-04-02
Adolescents with high positive affect may have improved physical and mental health as adults, according to a study published April 2nd in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine by Eric Kim and Renae Wilkinson from Harvard University, US, and colleagues.
Positive affect is the experience of pleasurable emotions, such as happiness, joy, excitement, and calm. Research on adults has shown that positive affect is associated with healthier behaviors and decreased risk of chronic diseases, but data are limited in adolescents. Given that adolescence is a critical ...
Methods sections often lack critical details needed to reproduce an experiment, and the practice of citing previous papers instead of describing the methods in detail may contribute to this problem
2024-04-02
Methods sections often lack critical details needed to reproduce an experiment, and the practice of citing previous papers instead of describing the methods in detail may contribute to this problem
Analysis of >750 papers shows that >90% of papers use at least one shortcut citation, that these significantly impair reconstruction of the original method, and that <25% of journals have policies relating to previously described methods
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS ...
Study: AI writing, illustration emits hundreds of times less carbon than humans
2024-04-02
LAWRENCE — With the evolution of artificial intelligence comes discussion of the technology's environmental impact. A new study has found that for the tasks of writing and illustrating, AI emits hundreds of times less carbon than humans performing the same tasks. That does not mean, however, that AI can or should replace human writers and illustrators, the study’s authors argue.
Andrew Torrance, Paul E. Wilson Distinguished Professor of Law at KU, is co-author of a study that compared established systems such as ChatGPT, Bloom AI, DALL-E2 and others completing writing and illustrating to that of humans.
Like ...
Morris Animal Foundation-funded researchers develop early osteoarthritis detection tool
2024-04-02
Media Alert: DENVER/April 2, 2024 — Morris Animal Foundation-funded researchers introduced a straightforward questionnaire to help horse owners identify and monitor signs of osteoarthritis pain in their equine companions. This initiative aims to facilitate earlier and more effective treatment, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for horses.
Created by Dr. Janny de Grauw, Senior Lecturer at The Royal Veterinary College in the United Kingdom, Bryony Lancaster, Program Director, MSc Equine Science of the University of Edinburgh and Dr. Diane Howard, the questionnaire is modeled after the Brief Pain Inventory used to evaluate pain severity and its impact ...
Companies ignoring climate risks get punished by markets, new study reveals
2024-04-02
A pioneering study from the University of Florida has quantified corporations’ exposure to climate change risks like hurricanes, wildfires, and climate-related regulations and the extent to which climate risks are priced into their market valuations. The research also exposes a costly divide – companies that proactively manage climate risks fare much better than those that ignore the threats.
Using textual analysis of earnings call transcripts from almost 5,000 U.S. public companies, researchers developed novel measures of firms’ physical climate risk exposure ...
These plants evolved in Florida millions of years ago. They may be gone in decades.
2024-04-02
Scrub mints are among the most endangered plants you’ve probably never heard of. More than half of the 24 species currently known to exist are considered threatened or endangered at the state or federal level, and nearly all scrub mints grow in areas that are being rapidly developed or converted to agricultural pasture.
In a new study, researchers analyzed a distinct type of DNA marker, which shows there are likely more scrub mint species waiting to be scientifically described. And at least one species has been left without federal protection because of a technicality.
“The Titusville balm is currently considered ...
[1] ... [1266]
[1267]
[1268]
[1269]
[1270]
[1271]
[1272]
[1273]
1274
[1275]
[1276]
[1277]
[1278]
[1279]
[1280]
[1281]
[1282]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.