Respiratory allergies: newly discovered molecule plays a major role in triggering inflammation
2024-04-10
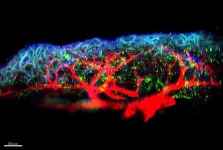
The inflammation process plays a crucial role in allergic respiratory diseases, such as asthma and allergic rhinitis. Although the pulmonary epithelium, the carpet of cells that forms the inner surface of the lungs, is recognised as a major player in the respiratory inflammation that causes these diseases, the underlying mechanisms are still poorly understood.
A research team has identified one of the molecules responsible for triggering these allergic reactions, in a study co-led by two CNRS and Inserm scientists working at l’Institut de pharmacologie et de biologie structural (CNRS/Université Toulouse ...
A BiCIKL ride to the Empowering Biodiversity Research conference for a report on a 3-year endeavor towards FAIR biodiversity data
2024-04-10
Leiden - also known as the ‘City of Keys’ and the 'City of Discoveries' - was aptly chosen to host the third Empowering Biodiversity Research (EBR III) conference. The two-day conference - this time focusing on the utilisation of biodiversity data as a vehicle for biodiversity research to reach to Policy - was held in a no less fitting locality: the Naturalis Biodiversity Center.
On 25th and 26th March 2024, the delegates got the chance to learn more about the latest discoveries, trends and innovations from scientists, as well as various stakeholders, including representatives of policy-making bodies, research institutions and infrastructures. ...
Visiting white parts of town make some Black kids feel less safe
2024-04-10
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Some Black youth feel less safe when they visit predominantly white areas of their city, a new study in Columbus has found.
And it was those Black kids who spent the most time in white-dominated areas who felt less safe, said Christopher Browning, lead author of the study and professor of sociology at The Ohio State University.
“Familiarity with white neighborhoods doesn’t make Black kids feel more comfortable and safer. In fact, familiarity seems to reveal ...
Deforestation harms biodiversity of the Amazon’s perfume-loving orchid bees
2024-04-10
LAWRENCE — A survey of orchid bees in the Brazilian Amazon state of Rondônia, carried out in the 1990s, is shedding new light the impact of deforestation on the scent-collecting pollinators, which some view as bellwethers of biodiversity in the neotropics.
The findings, from a researcher at the University of Kansas, are published today in the peer-reviewed journal Biological Conservation.
“This study on orchid bees was an add-on to previous research on stingless bees. Orchid bees are so easy to collect, so we added them to ...
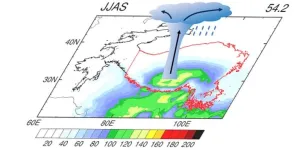
Long-term satellite observations show climatological characteristics of isolated deep convection over the Tibetan Plateau
2024-04-10
The Tibetan Plateau is a prevalent region for deep convection owing to its unique thermodynamic forcing. Deep convection can exist as isolated deep convection (IDC), which is small in size, or mesoscale convective systems (MCSs), which are convective storms organized into larger and longer-lived systems. Most previous research has focused on MCSs over the Tibetan Plateau, but less so on IDC systems (hereafter, IDCs).
Dr. Ying Na from Wuxi University, and Dr. Chaofan Li from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China, examined the climatological features of IDCs by using high-resolution satellite observations in June to September ...
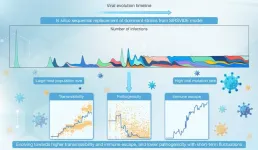
Modeling viral evolution: A novel SIRSVIDE framework with application to SARS-CoV-2 dynamics
2024-04-10
Understanding the mutation and evolution of viruses (such as SARS-CoV-2) is crucial for effective public health management and response. Traditional epidemiological models often assume that viral transmissibility and pathogenicity remain constant during disease transmission, ignoring the fact that viruses continuously evolve through natural selection and random mutations. This simplification limits the accuracy of these models in predicting epidemic trends, especially when facing rapidly mutating viruses.
To overcome these limitations, ...
New data: UTSA economic development institute added $2.6 billion to Texas’ economy
2024-04-10
SAN ANTONIO, TEXAS — The Valdez Institute for Economic Development (VIED) at UTSA generated an overall direct economic impact of $2.6 billion for the Texas economy in 2023, according to the organization’s 2023 annual report, which was released Tuesday.
The latest figure represents the work of the institute’s portfolio of time-tested economic development strategies and new innovations that enabled business owners and entrepreneurs to start and grow their small businesses.
During the 2023 fiscal year, the institute:
Served 41,231 business ...
Waterproof ‘e-glove’ could help scuba divers communicate
2024-04-10
When scuba divers need to say “I’m okay” or “Shark!” to their dive partners, they use hand signals to communicate visually. But sometimes these movements are difficult to see. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Nano have constructed a waterproof “e-glove” that wirelessly transmits hand gestures made underwater to a computer that translates them into messages. The new technology could someday help divers communicate better with each other and with boat crews on the surface.
E-gloves — gloves fitted ...
BioOne presents 2024 BioOne Ambassador Award to five early career scientists
2024-04-10
BioOne proudly announces the 2024 recipients of the BioOne Ambassador Award. Now in its seventh year, this prestigious award recognizes early-career researchers in the biological, ecological, and environmental sciences who demonstrate creative approaches to science communication thereby fostering greater science literacy and aiding in the understanding of the natural world. BioOne Ambassadors are nominated by BioOne publishing partners, and each winning author will receive a $1,000 award and have their work promoted through BioOne’s multiple channels.
This year’s honorees are:
Dr. Elis Fisk – Draw and Learn: A Bighorn Sheep Mystery; nominated by The Wildlife ...
Thinking outside the doctor’s office: Poll looks at older adults’ use of urgent care, retail clinics and more
2024-04-10
When today’s older adults were growing up, urgent care centers and clinics inside retail stores didn’t exist. But most of them have now embraced these non-traditional sites for getting medical care, a new national poll finds.
In the past two years, 60% of people age 50 to 80 have visited an urgent care clinic, or a clinic based in a retail store, workplace or vehicle, according to new findings from the University of Michigan National Poll on Healthy Aging.
Urgent care clinics were the most ...
New mechanism discovered for the life-threatening arrhythmias in Andersen-Tawil syndrome
2024-04-10
A team at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) has made a breakthrough discovery in the understanding of cardiac arrhythmias by unraveling the complexities of Andersen-Tawil syndrome (ATS), an extremely rare inherited cardiac disorder. Led by Dr. José Jalife, head of the CNIC Cardiac Arrhythmia Group, the study demonstrates that a specific genetic mutation (C122Y) in the Kir2.1 potassium channel alters the function not only of Kir2.1 but also of the main cardiac sodium channel NaV1.5, thus establishing a direct link with the life-threatening arrhythmias associated with ATS1.
The study, published in the journal Circulation Research, reveals that ...
Study suggests racial discrimination during midlife associated with Alzheimer’s disease pathology later in life
2024-04-10
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – April 10, 2024 – Racial discrimination experienced during midlife is associated with Alzheimer’s disease pathology, according to a new study from researchers at Wake Forest University School of Medicine and the University of Georgia.
The findings appear online today in Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association.
“We know that Black Americans are at an elevated risk of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias compared to non-Hispanic ...
The future of xenotransplantation is nearly here
2024-04-10
Embargoed until 10:30 a.m. Wednesday, 10 April, 2024 Central European Summer Time (GMT +2)
10 April, 2024, Prague, Czech Republic—Speaking today at the Annual Meeting and Scientific Sessions of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) in Prague, Muhammad Mohiuddin, MBBS, said xenotransplantation, hailed as the future of organ transplantation, is poised to become a clinical reality within the next several years.
In January 2022, the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) became the first institution in the world to implant a genetically modified pig heart ...
Treating gum disease after heart rhythm ablation reduced risk of AFib recurrence
2024-04-10
Research Highlights:
Treating gum disease within three months after a heart procedure to correct an irregular heart rhythm, known as atrial fibrillation (AFib), may lower the chances of it reoccurring.
Inflamed gums may predict AFib recurrence after heart ablation, a procedure to fix the irregular heartbeat.
AFib patients should be examined for gum disease and encouraged to seek dental treatment, researchers said.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, April 10, 2024
DALLAS, April 10, 2024 — Treating gum disease in the 3-months after a procedure to correct an irregular heartbeat known as atrial fibrillation ...
AI makes retinal imaging 100 times faster, compared to manual method
2024-04-10
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health applied artificial intelligence (AI) to a technique that produces high-resolution images of cells in the eye. They report that with AI, imaging is 100 times faster and improves image contrast 3.5-fold. The advance, they say, will provide researchers with a better tool to evaluate age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and other retinal diseases.
“Artificial intelligence helps overcome a key limitation of imaging cells in the retina, which is time,” said Johnny Tam, Ph.D., who leads the Clinical and Translational Imaging Section at NIH's National Eye Institute.
Tam ...
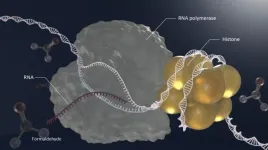
Impact of aldehydes on DNA damage and aging
2024-04-10
A team of researchers at Nagoya University in Japan has discovered that aldehydes are metabolic byproducts associated with premature aging. Published in Nature Cell Biology, their findings reveal insights into premature aging diseases and potential strategies to combat aging in healthy individuals such as controlling exposure to aldehyde-inducing substances including alcohol, pollution, and smoke.
A person's health can be harmed by aldehydes. However, the group’s findings suggest these detrimental effects also include aging. The team who made this discovery included Yasuyoshi Oka, Yuka Nakazawa, Mayuko Shimada, and Tomoo Ogi of Nagoya University.
“DNA ...
New method of measuring qubits promises ease of scalability in a microscopic package
2024-04-10
Chasing ever-higher qubit counts in near-term quantum computers constantly demands new feats of engineering.
Among the troublesome hurdles of this scaling-up race is refining how qubits are measured. Devices called parametric amplifiers are traditionally used to do these measurements. But as the name suggests, the device amplifies weak signals picked up from the qubits to conduct the readout, which causes unwanted noise and can lead to decoherence of the qubits if not protected by additional large components. More importantly, the bulky size of the amplification chain becomes technically challenging to work around as qubit counts increase ...
Study shedding new light on Earth’s global carbon cycle could help assess liveability of other planets
2024-04-10
Research has uncovered important new insights into the evolution of oxygen, carbon, and other vital elements over the entire history of Earth – and it could help assess which other planets can develop life, ranging from plants to animals and humans.
The study, published today in Nature Geoscience and led by a researcher at the University of Bristol, reveals for the first time how the build up of carbon-rich rocks has accelerated oxygen production and its release into the atmosphere. Until now the exact nature of how the atmosphere became oxygen-rich has long eluded scientists and generated conflicting explanations.
As carbon dioxide is steadily ...
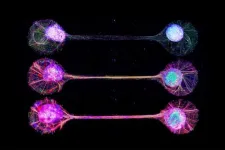
Connecting lab-grown brain cells provides insight into how our own brains work
2024-04-10
Tokyo, Japan – The idea of growing a functioning human brain-like tissues in a dish has always sounded pretty far-fetched, even to researchers in the field. Towards the future goal, a Japanese and French research team has developed a technique for connecting lab-grown brain-mimicking tissue in a way that resembles circuits in our brain.
It is challenging to study exact mechanisms of the brain development and functions. Animal studies are limited by differences between species in brain structure and function, and brain cells grown in the lab tend to lack the characteristic ...
Breakthrough for next-generation digital displays
2024-04-10
Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have developed a digital display screen where the LEDs themselves react to touch, light, fingerprints and the user’s pulse, among other things. Their results, published in Nature Electronics, could be the start of a whole new generation of displays for phones, computers and tablets.
“We’ve now shown that our design principle works. Our results show that there is great potential for a new generation of digital displays where new advanced ...
Wistar scientists identify pro-aging ‘sugar signature’ in the blood of people living with HIV
2024-04-10
PHILADELPHIA — (April 10, 2024) — The Wistar Institute’s associate professor Mohamed Abdel-Mohsen, Ph.D., along with his team and collaborators, has identified sugar abnormalities in the blood that may promote biological aging and inflammation in people living with HIV (PLWH). The findings, taken from a large data study comprising more than 1200 participants, are detailed in the new paper, “Immunoglobulin G N-glycan Markers of Accelerated Biological Aging During Chronic HIV Infection,” published in the journal Nature Communications.
Despite advances ...
CAMH develops first ever clinically validated natural supplement to prevent postpartum blues
2024-04-10
A new study published in the Lancet discovery science journal eClinicalMedicine has confirmed that a novel natural supplement—invented, researched, developed and commercialized at the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH)—prevents postpartum blues, and reduces symptoms of postpartum depression over the following six months after giving birth.
Up to 8 out of ten new mothers experience postpartum, or ‘baby,’ blues, characterized by mood swings, crying spells, anxiety and difficulty sleeping. The condition usually begins within the first few days after delivery and may last for up to two weeks. Postpartum ...
Breakthroughs in durable mechanical circulatory support (MCS) devices add years to lives and life to years for heart failure patients
2024-04-10
Embargoed until 10:00 a.m. Wednesday, 10 April, 2024 Central European Summer Time (GMT +2)
10 April, 2024, Prague, Czech Republic—The same technology that enables a bullet train to travel at speeds up to 200 mph without touching its rails now keeps a failing heart pumping—and in the near future, it will do so via a wireless power connection. Mandeep R. Mehra, MD, FRCP described the cutting-edge heart pump and other advances in mechanical circulatory support (MCS) today at the Annual Meeting and Scientific Sessions of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) in ...
AI will provide heart transplant surgeons with new decision-making data
2024-04-10
Embargoed until 10:00 a.m., Wednesday, 10 April, 2024 Central European Summer Time (GMT +2)
10 April 2024, Prague, Czech Republic—Artificial intelligence will significantly impact the heart transplantation process by helping physicians better assess the complex factors impacting patient outcomes, according to researchers at today’s Annual Meeting and Scientific Sessions of the International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) in Prague.
“Until now, we’ve assessed the likelihood of transplant success based on individual risk factors,” said Eileen Hsich, medical director of the Heart Transplant Program at the Cleveland ...
Novel UV broadband spectrometer revolutionizes air pollutant analysis
2024-04-10
Sunlight has a major influence on chemical processes. Its high-energy UV radiation in particular is strongly absorbed by all materials and triggers photochemical reactions of the substances present in the air. A well-known example is the formation of ground-level ozone when UV light hits nitrogen oxides. A research team led by Birgitta Schultze-Bernhardt from the Institute of Experimental Physics at Graz University of Technology (TU Graz) is now utilising this high reaction potential for a new method of environmental monitoring. ...
[1] ... [1263]
[1264]
[1265]
[1266]
[1267]
[1268]
[1269]
[1270]
1271
[1272]
[1273]
[1274]
[1275]
[1276]
[1277]
[1278]
[1279]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.