Bladder cancer treatment can be better targeted and more effective, trials show
2024-04-05
Testing for tumour DNA in the blood can successfully identify advanced bladder cancer patients who will not relapse following surgery, new research shows.
This could allow doctors to target treatments more effectively to those who need it, and spare those patients for whom further treatment is unnecessary, researchers say.
The findings from the screening phase of the IMvigor011 Phase III trial are presented today [Friday 5 April] at the European Association of Urology Congress in Paris.
They show that just over 90% of muscle invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) patients with a ...
Ocean floor a 'reservoir' of plastic pollution, world-first study finds
2024-04-05
New research from CSIRO, Australia’s national science agency, and the University of Toronto in Canada, estimates up to 11 million tonnes of plastic pollution is sitting on the ocean floor.
Every minute, a garbage truck’s worth of plastic enters the ocean. With plastic use expected to double by 2040, understanding how and where it travels is crucial to protecting marine ecosystems and wildlife.
Dr Denise Hardesty, Senior Research Scientist with CSIRO, said this is the first estimate of how much plastic waste ends up on the ocean floor, where it accumulates before being ...
Scientists discover potential treatment approaches for polycystic kidney disease
2024-04-04
Researchers have shown that dangerous cysts, which form over time in polycystic kidney disease (PKD), can be prevented by a single normal copy of a defective gene. This means the potential exists that scientists could one day tailor a gene therapy to treat the disease. They also discovered that a type of drug, known as a glycoside, can sidestep the effects of the defective gene in PKD. The discoveries could set the stage for new therapeutic approaches to treating PKD, which affects millions worldwide. The study, partially funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), is published in Cell Stem Cell.
Scientists ...
UTEP study: prairie voles display signs of human-like depression
2024-04-04
EL PASO, Texas (April 4, 2024) – Psychology researchers at The University of Texas at El Paso are making progress towards understanding the biological underpinnings of depression, a leading cause of disability that affects approximately 280 million people around the world.
In a study published this April in the Journal of Affective Disorders, UTEP psychologist Sergio Iñiguez, Ph.D., and his co-authors make the case that prairie voles, small rodents that are found throughout the central United States and Canada, can be effectively used as animal models to further the study of ...
Researchers envision sci-fi worlds involving changes to atmospheric water cycle
2024-04-04
Human activity is changing the way water flows between the Earth and atmosphere in complex ways and with likely long-lasting consequences that are hard to picture.
Land use change is altering where clouds form and how precipitation is distributed. Meanwhile, weather modification activities like cloud seeding are shifting how nations plan for water use in the face of climate change. These and other changes to the planet’s atmospheric water cycle were once hard to imagine but are increasingly part of modern water management on the planet.
Colorado State University Assistant Professor Patrick Keys is an expert ...
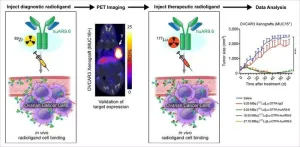
Novel theranostic tool allows for noninvasive identification and treatment of ovarian cancer
2024-04-04
Reston, VA—A new radiotheranostic system has the ability to detect and treat ovarian cancer noninvasively, according to new research published in the April issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. Combining the highly specific huAR9.6 antibody with PET and therapeutic radionuclides, this theranostic platform may provide more personalized treatment to improve health outcomes for ovarian cancer patients.
Ovarian cancer causes more deaths than any other gynecologic malignancy, with a five-year survival rate below 30 percent for patients diagnosed at advanced stages. The current standard of care for ovarian cancer consists of surgery followed by platinum-based chemotherapy; however, ...
An NSF bootcamp for future scientists
2024-04-04
Research today doesn't only occur in a lab; indeed, many university researchers extend their work into the community with the goal of inspiring the next generation of scientists and engineers. And some government agencies, like the National Science Foundation, provide the funding to do so. Most recently, Xiayun Zhao, assistant professor of mechanical engineering & materials science at the University of Pittsburgh, completed such outreach at the Carnegie Science Center (CSC).
Zhao ...
Small protein plays big role in chronic HIV infection
2024-04-04
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- NeuroHIV refers to the effects of HIV infection on the brain or central nervous system and, to some extent, the spinal cord and peripheral nervous system. A collection of diseases, including neuropathy and dementia, neuroHIV can cause problems with memory and thinking and compromise our ability to live a normal life.
Using a mouse model of neuroHIV, a research team led by biomedical scientists at the University of California, Riverside, studied the effects of interferon-β (IFNβ), a small protein involved in cell signaling and integral to the body’s natural defense mechanism against viral infections. The researchers found that higher or lower than ...
Perinatal women of Mexican descent propose solutions to pandemic-related stressors affecting Latinos
2024-04-04
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Public policies blocked many families of Mexican descent living in the U.S. from accessing vital services such as food and mental health care during the COVID-19 pandemic, even though these communities experienced some of the highest infection and mortality rates.
Thirty-eight perinatal women and mothers of young children were interviewed about the challenges they faced during the pandemic and proposed solutions to better meet the needs of their communities during future large-scale crises in a study led by University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign kinesiology and community health ...
Novel biological mechanism discovered that could lead to new treatments for neurological disorders, cancers
2024-04-04
The lab of Yongchao C. Ma, PhD, at Stanley Manne Children’s Research Institute at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago discovered a fundamental biological mechanism that could lead to new treatments for neurological diseases, such as spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) and autism, as well as different cancers. The study was published in the journal Human Molecular Genetics.
Dr. Ma’s team found that chemical modification of RNA (called RNA methylation) regulates mitochondrial ...
Stellar collisions produce strange, zombie-like survivors
2024-04-04
Despite their ancient ages, some stars orbiting the Milky Way’s central supermassive black hole appear deceptively youthful. But unlike humans, who might appear rejuvenated from a fresh round of collagen injections, these stars look young for a much darker reason.
They ate their neighbors.
This is just one of the more peculiar findings from new Northwestern University research. Using a new model, astrophysicists traced the violent journeys of 1,000 simulated stars orbiting our galaxy’s central supermassive black hole, Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*).
So densely packed with stars, the region commonly experiences brutal stellar collisions. ...
Rusty-patched bumblebee’s struggle for survival found in its genes
2024-04-04
A team of researchers has uncovered alarming trends in the first range-wide genetic study of an endangered bee species. The study, led by Colorado State University and published in the Journal of Insect Science, will inform conservation and recovery efforts for the rusty-patched bumblebee – a species that was once common in the United States but has declined from about 90% of its historic range.
The rusty-patched bumblebee was the first bee species to be federally listed as endangered in 2017 through the U.S. Endangered Species Act. Its numbers dropped rapidly starting in the late 1990s, likely due to a combination of pesticides, ...
Research collaboration aims to enhance cereal crop resilience to acidic soils and improve agriculture sustainability
2024-04-04
ST. LOUIS, MO., April 4, 2024 — Acidic soil caused by changing climate patterns threatens agriculture sustainability across the globe. But the problem goes far beyond rising temperatures. One major cause for concern is more acidic soil, a product of increasing rainfall. Acidic soils with low pH are widespread globally and common in tropical and sub-tropical regions, where food security is a serious challenge. Climate change has exacerbated the problem. Acidic soil can result in aluminum toxicity, putting further stress on global agriculture. A new collaborative research team from the US and Brazil received a $2 ...
Introducing New York Valves: The Structural Heart Summit
2024-04-04
NEW YORK – April 4, 2024 – The Cardiovascular Research Foundation® (CRF®) is excited to introduce New York Valves: The Structural Heart Summit, the expanded next iteration of our renowned annual Transcatheter Valve Therapy (TVT®) conference. Taking place June 5-7, 2024, at the Jacob K. Javits Convention Center, North in New York City, the new summit will be a world-class educational experience in the field of structural heart interventions.
“New York Valves 2024 signifies an important milestone for our organization,” said Juan F. Granada, MD, President and Chief Executive Officer of CRF® and New York ...
"Drop industrial agriculture": Major study reports that people and environment both benefit from diversified farming, while bottom lines also thrive
2024-04-04
Mixing livestock and crops, integrating flower strips and trees, water and soil conservation and much more: Massive new global study led by the University of Copenhagen and University of Hohenheim, has examined the effects of diversified agriculture. The conclusion is abundantly clear – positive effects increase with every measure, while negative effects are hard to find.
Laura Vang Rasmussen of the University of Copenhagen can finally wipe the sweat from her brow. For the last four years, she has served as the link between 58 researchers on five continents and as lead author of a major agricultural study which gathered ...
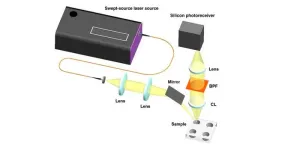
Portable swept-source Raman spectrometer for chemical and biomedical applications
2024-04-04
In 1928, Indian physicist Sir C. V. Raman and his colleague K. S. Krishnan discovered that when light interacts with matter, parts of the scattered light undergo changes in energy due to interaction with molecular vibrations, resulting in what is known as Raman scattering. The discovery laid the foundation for Raman spectroscopy, a technique that takes advantage of these energy changes to create a unique fingerprint of the molecular structure of the material.
Currently, dispersive Raman spectroscopy ...
An hereditary liver disease cured with the help of gene scissors
2024-04-04
Argininosuccinate lyase deficiency (ASLD), also known as argininosuccinic aciduria, is a disease that has been enriched in the Finnish genetic heritage. In this severe metabolic disease, the body does not process proteins normally, instead resulting in a very dangerous accumulation of argininosuccinic acid and ammonia. Excess ammonia causes disturbances of consciousness, coma and even death.
In Finland, infants are screened for ASLD to determine the disease risk before symptoms develop. The treatment is an extremely ...
Dr. C. Barrett Bowling to be honored with the 2024 Thomas and Catherine Yoshikawa Outstanding Scientific Achievement in Clinical Investigation Award at #AGS24
2024-04-04
New York (April 4, 2024) — Today, the American Geriatrics Society (AGS) and the AGS Health in Aging Foundation (HiAF) announced that the 2024 Thomas and Catherine Yoshikawa Award for Outstanding Scientific Achievement in Clinical Investigation will be awarded to C. Barrett Bowling, MD, MSPH, Associate Professor in the Division of Geriatrics at Duke University School of Medicine.
The award will be presented at the AGS 2024 Virtual Annual Scientific Meeting (#AGS24), May 9-11 (pre-conference days May 7 & 8). At the conference, Dr. Bowling will deliver a lecture on “Geriatricizing” Chronic Disease Research: A Geriatrician’s ...
Finds at Schöningen show wood was crucial raw material 300,000 years ago
2024-04-04
During archaeological excavations in the Schöningen open-cast coal mine in 1994, the discovery of the oldest, remarkably well-preserved hunting weapons known to humanity caused an international sensation. Spears and a double-pointed throwing stick were found lying between animal bones about ten meters below the surface in deposits at a former lakeshore. In the years that followed, extensive excavations have gradually yielded numerous wooden objects from a layer dating from the end of a warm interglacial period 300,000 years ago. The findings suggested a hunting ground on the lakeshore. An interdisciplinary ...
Cells engineered to produce immune-boosting amino acids in prizewinning research
2024-04-04
Bacterial proteins often play a successful hide and seek game with the body’s immune system, making it difficult to combat the bacteria that cause diseases like staph infections.
Now, biomolecular engineer Aditya Kunjapur and colleagues have come up with a strategy to create bacteria that build and incorporate a key amino acid into their own proteins, which makes the proteins more “visible” to the immune system.
For this work toward building a better platform for possible future bacterial vaccines, Kunjapur is the winner of the 2024 BioInnovation Institute & Science Prize for Innovation. ...
Flexible fiber, coupled to the human body, enables chipless textile electronics
2024-04-04
A flexible electronic fiber that utilizes the human body as part of the circuit enables textile-based electronics without the need for batteries or chips, researchers report. According to the authors, the approach is well-suited for scalable manufacture of comfortable fiber-based electronics for a wide range of applications, including “smart” clothing. Textile electronic systems are designed to equip textile or fiber assemblies with electronic functions for sensing, computation, display, or communication. They create vast opportunities ranging from physiological monitoring to powering ...
Governance frameworks should address the prospect of AI systems that cannot be safely tested
2024-04-04
In this Policy Forum, Michael Cohen and colleagues highlight the unique risks presented by a particular class of artificial intelligence (AI) systems: reinforcement learning (RL) agents that plan more effectively than humans over long horizons. “Giving [such] an advanced AI system the objective to maximize its reward and, at some point, withholding reward from it, strongly incentivizes the AI system to take humans out of the loop,” write Cohen and colleagues. This incentive also arises for long-term planning agents (LTPAs) more generally, say the authors, and in ways empirical testing is unlikely to cover. It is thus critical to address extinction risk from these ...
Revealed: Mechanical damage during an asthma attack
2024-04-04
In asthma, the tightening of muscles around the bronchi causes damage to the airway by squeezing and destroying epithelial cells, which promotes the airway inflammation and mucus production often associated with an asthma attack, researchers report. The findings suggest that preventing the mechanical damage caused by an asthma attack, rather than treating only its downstream symptoms, could pave the way for therapies that stop the whole asthma inflammatory cycle. Asthma is a common airway disorder affecting more than 300 million people worldwide. Although it is primarily considered an inflammatory disease, a diagnostic feature of asthma is mechanical bronchoconstriction – the ...
Agricultural diversification yields joint environmental and social benefits
2024-04-04
Promoting livestock biodiversity and soil conservation strategies provides both social and environmental benefits, according to a new study. The findings suggest that well-designed polices aimed at incentivizing the adoption of multiple diversification strategies could mitigate simplified agriculture’s negative environmental, health, and social impacts. “Our interdisciplinary analysis spanning a wide array of regions provides convincing evidence that agricultural diversification is a promising win-win strategy for providing social and environmental benefits,” write the authors. Agricultural lands tend to be simplified ecosystems designed ...
Nerve cells not entirely “young at heart”
2024-04-04
After two decades in the United States, Martin Hetzer returned home to Austria in 2023 to become the 2nd President of the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA). A year into his new role, the molecular biologist remains engaged in the realm of aging research.
Hetzer is fascinated by the biological puzzles surrounding the aging processes in organs like the brain, heart, and pancreas. Most cells comprising these organs are not renewed throughout a human’s entire life span. Nerve cells (neurons) in the human brain, for instance, can be as old as the organism, even ...
[1] ... [1261]
[1262]
[1263]
[1264]
[1265]
[1266]
[1267]
[1268]
1269
[1270]
[1271]
[1272]
[1273]
[1274]
[1275]
[1276]
[1277]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.