Cognitive decline may be detected using network analysis, according to Concordia researchers
2024-04-09
We all lose our car keys or our glasses from time to time. Most people would be correct to laugh it off as a normal part of aging. But for others, cognitive decline may start as a worrying but clinically unnoticeable step toward cognitive impairment, be it relatively mild or as severe as Alzheimer’s disease.
The vast complexity of the human brain makes early diagnosis of cognitive decline difficult to achieve, which has potentially important implications for treatment and prevention. This is especially true ...
Clinical trial finds nasal spray safely treats recurrent abnormal heart rhythms
2024-04-09
A clinical trial led by Weill Cornell Medicine investigators showed that a nasal spray that patients administer at home, without a physician, successfully and safely treated recurrent episodes of a condition that causes rapid abnormal heart rhythms. The study, published March 25 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, provides real-world evidence that a wide range of patients can safely and effectively use the experimental drug, called etripamil, to treat recurrent paroxysmal supraventricular ...
FAU lands $1.3 million grant to ‘clean up’ stinky seaweed in Florida
2024-04-09
In the last decade, the emergence of a massive expanse of Sargassum, the Great Atlantic Sargassum Belt, has wreaked havoc on ecosystems and economies throughout the Caribbean. Conversely, this stinky brown seaweed provides vital habitats for marine life including loggerhead sea turtles.
One of the worst invasions of Sargassum in recent history, especially for Florida, occurred in 2022 and potential impacts this year are yet to be determined. Decomposing Sargassum produces hydrogen sulfide and ammonia, which can result in potential human and environmental health impacts. Once Sargassum deluges beaches, removing, disposing and repurposing the seaweed presents many logistical ...
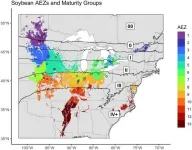
Breeding more resilient soybeans may come down to test site selection
2024-04-09
URBANA, Ill. — In the quest to optimize crop productivity across environments, soybean breeders test new cultivars in multiple locations each year. The best-performing cultivars across these locations are selected for further breeding and eventual commercialization. However, a new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign suggests current soybean testing locations may not be delivering breeders the biggest bang for their buck.
“We met with most of the soybean breeders in public research universities across the Midwest and asked where they set up their trials over the last 30 to 40 years,” said Nicolas Martin, ...
Morphine tolerance results from Tiam1-mediated maladaptive plasticity in spinal neurons
2024-04-09
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – Morphine and other opioids are vital to treat severe and chronic pain. However, they have two problems — prolonged use creates morphine tolerance, where ever-increasing doses are needed for the same pain relief, and paradoxically, prolonged use also can create an extreme sensitivity to pain, called hyperalgesia.
Researchers at the University of Alabama at Birmingham and Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, now have shown that blocking the activity of an enzyme called Tiam1 in certain ...
USC-led study leverages artificial intelligence to predict risk of bedsores in hospitalized patients
2024-04-09
Bedsores—also known as pressure injuries—are the fastest rising hospital-acquired condition, according to the U.S. Agency for Healthcare Research in Quality, and as a result have become the second most common reason for medical malpractice suits in the United States.
Although most hospital-acquired pressure injuries are reasonably preventable, approximately 2.5 million individuals in the United States develop a pressure injury in acute care facilities every year, and 60,000 die. The total annual cost for U.S. health systems to manage the acute needs of patients’ ...
IADR announces recipients of the 2024 IADR LION Dental Research Award
2024-04-09
Alexandria, VA, USA – The International Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (IADR) has announced three recipients of the 2024 IADR LION Dental Research Award. The recipients were recognized during the Opening Ceremonies of the 102nd General Session of the IADR, which was held in conjunction with the 53rd Annual Meeting of the American Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research and the 48th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research, on March 13-16, 2024, in New Orleans, LA.
The recipients are:
Andrea Escalante Herrera
University of ...
Cher Farrugia and Wei Qiao named winners of the 2024 IADR STAR Network Academy Fellowship
2024-04-09
Alexandria, VA, USA – The International Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (IADR) has announced Cher Farrugia and Wei Qiao as the winners of the 2024 IADR STAR Network Academy Fellowship. Farrugia, from the University of Bristol, England, UK, and Qiao, from The University of Hong Kong, SAR, China, were recognized during the Opening Ceremonies of the 102nd General Session of the IADR, which was held in conjunction with the 53rd Annual Meeting of the American Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research and the 48th Annual ...
Fiorella Ventura named winner of the 2024 IADR Norton Ross Fellowship
2024-04-09
Alexandria, VA, USA – The International Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (IADR) has announced Fiorella Ventura as the winner of the 2024 IADR Norton Ross Fellowship. Ventura, from the University of Buenos Aires, Argentina, was recognized during the Opening Ceremonies of the 102nd General Session of the IADR, which was held in conjunction with the 53rd Annual Meeting of the American Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research and the 48th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for ...
Diep Ha named winner of the 2024 IADR John Clarkson Fellowship
2024-04-09
Alexandria, VA, USA – The International Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (IADR) has announced Diep Ha as the winner of the 2024 IADR John Clarkson Fellowship. Ha, from The University of Queensland, Australia, was recognized during the Opening Ceremonies of the 102nd General Session of the IADR, which was held in conjunction with the 53rd Annual Meeting of the American Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research and the 48th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research, on March 13-16, 2024, in New Orleans, LA.
Ha is a dentist and a Senior Research Fellow at the University ...
Shivangi Singh named winner of the 2024 IADR David B. Scott Fellowship
2024-04-09
Alexandria, VA, USA – The International Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (IADR) has announced Shivangi Singh as the winner of the 2024 IADR David B. Scott Fellowship. Singh, from King George’s Medical University, Lucknow, India, was recognized during the Opening Ceremonies of the 102nd General Session of the IADR, which was held in conjunction with the 53rd Annual Meeting of the American Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research and the 48th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental ...
Enas Belal Abdellatif named winner of the 2024 IADR Newell Johnson Travel Award
2024-04-09
Alexandria, VA, USA – The International Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (IADR) has announced Enas Belal Abdellatif as the winner of the 2024 IADR Newell Johnson Travel Award. Abdellatif, from Alexandria University, Egypt, was recognized during the Opening Ceremonies of the 102nd General Session of the IADR, which was held in conjunction with the 53rd Annual Meeting of the American Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research and the 48th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research, on March 13-16, 2024, in New Orleans, LA.
Abdellatif is a Teaching Assistant ...
AADOCR announces recipients of the 2024 Hatton Competition and Award Winners
2024-04-09
Alexandria, VA – The American Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (AADOCR) has named the winners of the 2024 AADOCR Hatton Competition and Award. The recipients were recognized during the Opening Ceremonies of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the AADOCR, which was held in conjunction with the 102nd General Session of the International Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research and the 48th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research, on March 13-16, 2024 in New Orleans, LA.
The winners are:
JUNIOR ...
IADR announces recipients of the 2024 IADR Hatton Competition and Award Winners
2024-04-09
Alexandria, VA, USA – The International Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (IADR) has announced the winners of the 2024 IADR Hatton Competition and Award. The recipients were recognized during the Opening Ceremonies of the 102nd General Session of the IADR, which was held in conjunction with the 53rd Annual Meeting of the American Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research and the 48th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research, on March 13-16, 2024, in New Orleans, LA.
The recipients are:
JUNIOR CATEGORY
1st – Jeremie Oliver Piña, ...
IADR announces 2024 winners of the Joseph Lister Award for New Investigators
2024-04-09
Alexandria, VA, USA – The International Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (IADR) has announced the winners of the 2024 IADR Joseph Lister Award for New Investigators. The recipients were recognized during the Opening Ceremonies of the 102nd General Session of the IADR, which was held in conjunction with the 53rd Annual Meeting of the American Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research and the 48th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research, on March 13-16, 2024, in New Orleans, LA.
The winners are:
First Place
Kasia Gurzawska-Comis
University ...
Measuring improvement in the design of pulses for quantum systems
2024-04-09
Seeking a method for reducing error in noisy quantum systems, Kajsa Williams and Louis-S. Bouchard, researchers at the Center for Quantum Science and Engineering at the University of California, Los Angeles, implemented and evaluated single-qubit gates performance using specially designed composite and adiabatic pulses. While they found no particular advantages in terms of leakage and seepage of the gates compared to standard gates, robustness to control field error was greatly improved. Their research ...
New technique sheds light on memory and learning
2024-04-09
Less than twenty minutes after finishing this article, your brain will begin to store the information that you’ve just read in a coordinated burst of neuronal activity. Underpinning this process is a phenomenon known as dendritic translation, which involves an uptick in localized protein production within dendrites, the spiny branches that project off the neuron cell body and receive signals from other neurons at synapses. It’s a process key to memory—and its dysfunction is linked to intellectual disorders.
That makes the inner workings of dendritic translation a “holy grail for understanding memory formation,” says Rockefeller’s Robert ...
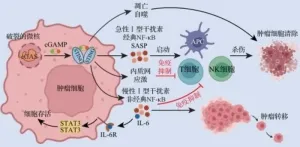
Unlocking the body's hidden weapon against cancer: the role of broken chromosomes
2024-04-09
Scientists have unraveled the mechanisms of the Cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate synthase-stimulator of interferon genes (cGAS-STING) signaling pathway activated by micronuclei, as well as its significant effects on tumor immunity. This study illuminates how chromosomal instability, marked by micronuclei formation, plays a critical role in controlling the capacity of the innate immune system to regulate tumor progression. These findings deepen our understanding of the intricate relationship between ...
No link between acetaminophen use during pregnancy and children’s risk of autism, ADHD, and intellectual disability says large sibling study from Drexel University and Sweden’s Karolinska Institutet
2024-04-09
Under Embargo Until:
April 9, 2024
11 AM ET
No Link Between Acetaminophen Use During Pregnancy and Children’s Risk of Autism, ADHD, and Intellectual Disability Says Large Sibling Study from Drexel University and Sweden’s Karolinska Institutet
PHILADELPHIA -- In the largest study to date on the subject, researchers found no evidence to support a causal link between acetaminophen use during pregnancy and increased risk of autism, ADHD and intellectual disability in children. The findings, using data from a nationwide cohort of over 2.4 million children born in Sweden, including siblings not exposed to the drug before birth, were published today in the Journal of the ...
A smarter city skyline for flood safety
2024-04-09
WASHINGTON, April 9, 2024 — A city’s skyline — the distinctive shapes and arrangements of its buildings — impacts the safety of its population during floods. When the streets flood, pedestrians can be swept under the current and injured or killed. With climate change and rising urbanization, the likelihood and severity of urban flooding are increasing.
Not all city blocks are created equal. In Physics of Fluids, an AIP Publishing journal, researchers from Beijing Normal University, Beijing Hydrological Center, and the China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research investigated how city design contributes to pedestrian ...
Is Interstate 95 the connection for moving guns up and down the east coast?
2024-04-09
Interstate gun transfers are a major contributor to gun crime, injury, and death in the United States. Guns used in crimes traced to interstate purchases move routinely between states along multiple major transportation routes, a phenomenon known as the “Iron Pipeline”, which refers most commonly to the Interstate 95 corridor. According to a new study at the Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, other such “Iron Pipelines” exist throughout the country, playing a significant role in the interstate transfer of firearms used in crimes. The findings are published in JAMA Network Open.
The researchers aimed to ...
Acetaminophen use during pregnancy and children’s risk of autism, ADHD, and intellectual disability
2024-04-09
About The Study: Acetaminophen use during pregnancy was not associated with children’s risk of autism, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), or intellectual disability in sibling control analysis. This suggests that associations observed in other models may have been attributable to familial confounding.
Authors: Brian K. Lee, Ph.D., of Drexel University in Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.3172)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
Bacteria in cancer unmasked
2024-04-09
Bacteria in cancer unmasked - a closer look at our microscopic co-inhabitants
Researchers at the Netherlands Cancer Institute have compiled a detailed catalogue of bacteria living in cancer metastases. Having analyzed over 4000 tumors, they shed light on the diversity of these co-inhabitants and how they might interact with cancer cells and their surroundings. For example, certain bacteria were linked to a worse response to immunotherapy. This study paves the way to a better understanding of how bacteria help or hinder cancer (therapy), and how we can use this for patients’ ...
Top factors in nurses ending health care employment between 2018 and 2021
2024-04-09
About The Study: The top contributing factors for leaving health care employment were planned retirement, burnout, insufficient staffing, and family obligations in this cross-sectional study of 7,887 nurses. The leading reasons signal opportunities for employers to reattract an existing nurse workforce and retain currently employed nurses.
Authors: K. Jane Muir, Ph.D., R.N., F.N.P.-B.C., of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Firearm ownership and support for political violence in the United States
2024-04-09
About The Study: In this survey study with 12,000 participants, firearm owners were only moderately more supportive of political violence than nonowners. Recent purchasers and owners who always or nearly always carried firearms in public were more supportive of and willing to engage in political violence than other subsets of firearm owners. These findings can guide risk-based prevention efforts.
Authors: Garen J. Wintemute, M.D., M.P.H., of the UC Davis School of Medicine in Sacramento, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
[1] ... [1253]
[1254]
[1255]
[1256]
[1257]
[1258]
[1259]
[1260]
1261
[1262]
[1263]
[1264]
[1265]
[1266]
[1267]
[1268]
[1269]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.