Three University of Houston projects included in $17M+ funding for decarbonization and emissions research
2024-01-18
HOUSTON, January 18, 2024 – The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) recently announced $17.4 million funding for 19 early-stage research projects focused on expanding clean energy technologies at colleges and universities across America. These projects will establish visiting scholars’ programs, create new academic curricula related to geosciences, and provide interdisciplinary training in humanities-driven science, technology, engineering, and mathematics fields.
The list includes three projects from the University of Houston, a Carnegie-designated Tier One Research University. Two of these explore the feasibility and benefit of repurposing ...
Knowing what dogs like to watch could help veterinarians assess their vision
2024-01-18
Ever wonder what kind of TV shows your dog might choose if they could work the remote control? New research from the University of Wisconsin–Madison’s School of Veterinary Medicine provides some answers, but the study was more interested in solving a longstanding problem in veterinary medicine than turning canine companions into couch potatoes.
According to Freya Mowat, veterinary ophthalmologist and professor in the School of Veterinary Medicine’s department of surgical sciences, researchers wanted to determine factors, including age and vision, that influence a dog’s ...
Household income and health insurance among factors in decision to withdraw life support after hemorrhagic stroke
2024-01-18
Living in a high-income neighborhood, having private health insurance, and being older are tied to an increased likelihood that life support will be withdrawn for people who have suffered severe bleeding in the brain, a new study shows.
Led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, the study focused on the social and economic factors linked to the withdrawal of life support and related death after being hospitalized for intracerebral hemorrhages. Such bleeds, sometimes referred to as hemorrhagic stroke, often lead to swelling in the brain, which can put a patient into a coma and frequently ...
Xue lab at the CDI publishes groundbreaking insights into memory T cells in Nature Immunology
2024-01-18
The Xue Lab at the Hackensack Meridian Center for Discovery and Innovation (CDI) has made another breakthrough in better understanding, and potentially modulating, the immune system to fight diseases.
The insights into a specific protein and how it regulates the training and efficacy of central memory T cells are published by Hai-Hui (Howard) Xue, a member of the CDI, in the journal Nature Immunology.
The immunological implications could produce better vaccines and cancer treatments in the future, according to the Xue lab, which is also part of the Institute for Immunologic ...
Don’t look back: The aftermath of a distressing event is more memorable than the lead-up, study suggests
2024-01-18
Halfway through a true crime podcast, a morning commuter jerks the wheel to narrowly avoid a collision. When discussing the podcast with a coworker later that day, the driver can easily recall the details of the episode’s second half but retains only a blurry recollection of how it began.
A new study from psychologists at the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology suggests that we remember the moments immediately following a distressing episode more sharply than the moments leading up to it. Clarifying the relationship ...
FIFA World Cup ends with win for Argentina and COVID-19, new research finds
2024-01-18
TORONTO, Jan. 18, 2024 – The 2022 FIFA World Cup ended with a tight win for Argentina over France on penalties, but it was also a triumph for SARS-CoV-2 with a significant jump in the number of cases, some of which York University researchers say could have been prevented.
New research published today and led by York used the 2022 FIFA World Cup as a case study to help determine the best ways to mitigate virus spread and hospitalizations at mass gatherings in the future. A technique was used ...
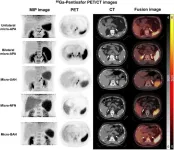
New PET/CT technique accurately diagnoses adrenal gland disorder, informs personalized treatment plans
2024-01-18
Reston, VA—A novel imaging approach, 68Ga-pentixafor PET/CT, has been shown to accurately identify sub-types of primary aldosteronism (an adrenal gland disorder), outperforming traditional methods for diagnosis. Reported in the January issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, this detailed imaging technique provides a clearer picture of the adrenal glands, helping doctors decide more confidently whether surgery is the right option for patients.
Primary aldosteronism is an endocrine disorder that occurs when the adrenal glands produce too much of the hormone aldosterone, frequently ...
A window into plant evolution: The unusual genetic journey of lycophytes
2024-01-18
An international team of researchers has uncovered a remarkable genetic phenomenon in lycophytes, which are similar to ferns and among the oldest land plants. Their study, recently published in the journal PNAS, reveals that these plants have maintained a consistent genetic structure for over 350 million years, a significant deviation from the norm in plant genetics.
"The exceptionally slow pace of genomic evolution sets these plants apart," said Dr. Fay-Wei Li, a professor at the Boyce Thompson Institute and a senior author of the study. ...
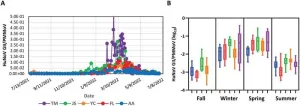
Climate change linked to spread of diarrheal illness
2024-01-18
Temperature, day length and humidity have been found to be linked to the increased spread of a diarrhoeal illness a new study from the University of Surrey reveals. The findings could help predict further outbreaks of the illness, potentially leading to better preparedness within health services.
During this unique study, researchers led by Dr Giovanni Lo Iacono, investigated the impact of weather on the transmission of campylobacteriosis, a bacterial infection which can cause diarrhoea and stomach pains. According to the World Health Organisation, Campylobacter infections are the most common causes of human bacterial gastroenteritis in the world. Infections are generally ...
Injectable agents could improve liquid biopsy for cancer detection and monitoring
2024-01-18
Scientists have developed two agents, made of therapeutic nanoparticles and antibodies, that could be given to patients shortly before a blood draw to allow physicians to better detect tumor DNA in blood using a technology called liquid biopsy.
Liquid biopsies promise to transform how cancers are diagnosed, monitored, and treated by detecting DNA that tumors shed into the blood. But the body presents a significant challenge. Immune cells in the liver and DNA-degrading enzymes in blood remove circulating tumor DNA from the bloodstream within minutes, making this DNA difficult to capture and detect in a blood test.
To overcome this, a team from the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard ...
A fungal pathogen, Rosellinia necatrix, that attacks plants, produces antimicrobials to combat the plant-hosted bacteria that would otherwise inhibit its infection success
2024-01-18
A fungal pathogen, Rosellinia necatrix, that attacks plants, produces antimicrobials to combat the plant-hosted bacteria that would otherwise inhibit its infection success.
####
Article Title: The soil-borne white root rot pathogen Rosellinia necatrix expresses antimicrobial proteins during host colonization
Article URL: http://journals.plos.org/plospathogens/article?id=10.1371/journal.ppat.1011866
Author Countries: Germany, Spain, the Netherlands
Funding: EACC and DET acknowledge receipt of PhD fellowships from CONACyT, Mexico. ALM is holder of a postdoctoral research fellow funded by the 'Fundación Ramón Areces'. BPHJT ...
Researchers improve blood tests’ ability to detect and monitor cancer
2024-01-18
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Tumors constantly shed DNA from dying cells, which briefly circulates in the patient’s bloodstream before it is quickly broken down. Many companies have created blood tests that can pick out this tumor DNA, potentially helping doctors diagnose or monitor cancer or choose a treatment.
The amount of tumor DNA circulating at any given time, however, is extremely small, so it has been challenging to develop tests sensitive enough to pick up that tiny signal. A team of researchers from MIT and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard has now come up with a way to significantly boost that signal, by temporarily slowing the clearance of tumor DNA circulating in the bloodstream.
The ...
Sea otters may be key drivers of changes in California's kelp forests, according to data spanning a century
2024-01-18
Sea otters may be key drivers of changes in California's kelp forests, according to data spanning a century
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Climate: https://journals.plos.org/climate/article?id=10.1371/journal.pclm.0000290
Article Title: Sea otter recovery buffers century-scale declines in California kelp forests
Citation: Nicholson TE, McClenachan L, Tanaka KR, Van Houtan KS (2024) Sea otter recovery buffers century-scale declines in California ...
Norovirus outbreaks are detectable by wastewater monitoring earlier than by other surveillance methods depending on reporting practices, making this a potentially important public health tool
2024-01-18
Norovirus outbreaks are detectable by wastewater monitoring earlier than by other surveillance methods depending on reporting practices, making this a potentially important public health tool.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/water/article?id=10.1371/journal.pwat.0000198
Article Title: Norovirus GII wastewater monitoring for epidemiological surveillance
Author Countries: USA
Funding: This study was supported by funding from the University of Michigan through the Public Health Infection ...
Climate change may reduce life expectancy by half a year, study suggests
2024-01-18
The cost of climate change may be six months off the average human lifespan, according to a study published January 18, 2024, in the open-access journal PLOS Climate by Amit Roy from Shahjalal University of Science and Technology and The New School for Social Research, U.S.
Temperature and rainfall — two telltale signals of climate change — cause myriad public health concerns, from the acute and direct (e.g., natural disasters like flooding and heat waves) to the indirect yet equally devastating (e.g., respiratory and mental illnesses). While impacts like these are observable and well documented, existing research has not established a direct link between climate change and life ...
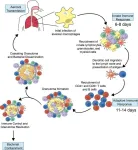
Remodeling the immune system to fight tuberculosis
2024-01-18
AMHERST, Mass. – Tuberculosis, caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) kills upwards of 1.6 million people a year, making it one of the leading causes of death by an infectious agent worldwide—and that number is only growing larger. How, exactly, Mtb evades the immune system isn’t yet known, but a collaborative team of researchers from the University of Massachusetts Amherst and Seattle Children’s Research Institute recently discovered something surprising: prior exposure to a genus of bacteria called Mycobacterium seems to remodel the first-line defenders in the body’s immune system. Furthermore, how ...
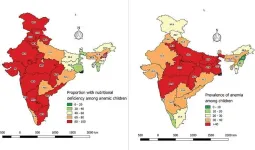
6 in 10 sampled under-5s in India have micronutrient deficiencies, and 4 in 10 have anaemia, per survey of 17,230 children
2024-01-18
6 in 10 sampled under-5s in India have micronutrient deficiencies, and 4 in 10 have anaemia, per survey of 17,230 children.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/globalpublichealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgph.0002095
Article Title: Prevalence and determinants of anemia due to micronutrient deficiencies among children aged 12–59 months in India–Evidence from Comprehensive National Nutrition Survey, 2016–18
Author Countries: India
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
DNA becomes our ‘hands’ to construct advanced nanoparticle materials
2024-01-18
Evanston, IL In a paper to be published in Science Jan. 18, scientists Chad Mirkin and Sharon Glotzer and their teams at Northwestern University and University of Michigan, respectively, present findings in nanotechnology that could impact the way advanced materials are made.
The paper describes a significant leap forward in assembling polyhedral nanoparticles. The researchers introduce and demonstrate the power of a novel synthetic strategy that expands possibilities in metamaterial design. These are the unusual materials that underpin “invisibility cloaks” and ultrahigh-speed optical computing systems.
"We manipulate ...
Repeated sexual failures cause social stress in fruit flies
2024-01-18
Repeated failures to reproduce make fruit flies stressed and frustrated, which in turn makes them less resilient to other types of stress, Julia Ryvkin at Bar-Ilan University and colleagues report in the open-access journal PLOS Genetics, publishing January 18.
Animals are motivated to take actions that improve their survival and reproduction through reward systems in the brain, but failure causes stress. The reward systems have been extensively studied, but less attention has been paid to how animals respond to failure. To investigate, researchers compared ...
Complement system causes cell damage in Long Covid
2024-01-18
Most people infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus recover after the acute illness. However, a significant proportion of infected individuals develop long-lasting symptoms with a wide range of manifestations. The causes and disease mechanisms of Long Covid are still unknown, and there are no diagnostic tests or targeted treatments.
Part of the immune system active for too long
A team of researchers led by Onur Boyman, professor of immunology at the University of Zurich (UZH) and Director of the Department of Immunology at the University Hospital Zurich (USZ), has shown in a study that the complement system plays an important role in Long Covid. It is part of the innate immune system ...
Analysis of brain tumor blood vessels yields a candidate therapy—and a platform to find more
2024-01-18
JANUARY 18, 2024, NEW YORK – A Ludwig Cancer Research study has generated a granular portrait of how the cellular and molecular components of the blood vessels that feed brain metastases of melanoma and lung and breast cancers differ from those of healthy brain tissue, illuminating how they help shape the internal environment of tumors to support cancer growth and immune evasion.
Led by Ludwig Lausanne’s Leire Bejarano and Johanna Joyce, researchers also developed a platform to identify potentially targetable vulnerabilities in the vasculature of brain metastases. They report in the current issue of Cancer ...
UChicago, Caltech study suggests that physical processes can have hidden neural network-like abilities
2024-01-18
We tend to separate the brain and the muscle—the brain does the thinking; the muscle does the doing. The brain takes in complex information about the world and makes decisions, and the muscle merely executes. This has also shaped how we think about a single cell; some molecules within cells are seen as ‘thinkers’ that take in information about the chemical environment and decide what the cell needs to do for survival; separately, other molecules are seen as the ‘muscle,’ building structures needed for survival.
But a new study shows how the molecules that build structures, i.e, the muscle, can themselves do both the thinking and the doing. The ...
Wireless drug patch shows promise as chronic disease treatment delivery system
2024-01-18
CHAPEL HILL, NC – University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill scientists created a new drug delivery system, called the Spatiotemporal On-Demand Patch (SOP), which can receive commands wirelessly from a smartphone or computer to schedule and trigger the release of drugs from individual microneedles. The patch’s thin, soft platform resembles a Band-Aid and was designed to enhance user comfort and convenience, since wearability is a crucial factor for chronically ill patients.
The research team, led by Juan Song, PhD, professor of pharmacology ...
AI can boost service for vulnerable customers
2024-01-18
AUSTIN, Texas –– Artificial intelligence has become the Swiss Army knife of the business world, a universal tool for increasing sales, optimizing efficiency, and interacting with customers. But new research from Texas McCombs explores another purpose for AI in business: to contribute to the social good.
It can do so by helping businesses better serve vulnerable consumers: anyone in the marketplace who experiences limited access to and control of resources.
“AI is widely recognized for its operational and ...
Structural study points the way to better malaria drugs
2024-01-18
Structural insights into a potent antimalarial drug candidate’s interaction with the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum have paved the way for drug-resistant malaria therapies, according to a new study by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and Van Andel Institute.
The antimalarial molecule, TDI-8304, is one of a new class of experimental therapeutics that targets the proteasome, an essential, multiprotein complex in P. falciparum cells. Two years ago, the researchers showed in a preclinical study that TDI-8304 potently kills malaria parasites at multiple stages of their life cycle and ...
[1] ... [1434]
[1435]
[1436]
[1437]
[1438]
[1439]
[1440]
[1441]
1442
[1443]
[1444]
[1445]
[1446]
[1447]
[1448]
[1449]
[1450]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.